Tanzu Application Service (TAS) Quickstart
This quickstart shows you how to deploy a publicly available app to your Tanzu Application Service (TAS, formerly PCF) space using Harness.
Objectives
You'll learn how to:
- Install and run the Harness Shell Script Delegate on an EC2 host.
- Connect Harness with your TAS account.
- Connect Harness with Artifactory.
- Specify the TAS manifest to use for the app.
- Specify the target TAS org and space.
- Set the number of instances to deploy.
- Create and deploy a TAS Basic Workflow.
Before You Begin
- Review Harness Key Concepts to establish a general understanding of Harness.
- TAS space — You will need a TAS space for Harness to deploy the app.
- EC2 Instance for Harness Shell Script Delegate — The EC2 instance for the Harness Delegate must meet the following requirements:
- Linux/UNIX server.
- Minimum 1 CPU.
- Minimum 8GB RAM. For example, an AWS EC2 instance type such as m5a.xlarge has 16GB of RAM, 8 for the Delegate and 8 for the remaining operations.
- Minimum 6GB Disk space.
- Outbound Access: HTTP, HTTPS, SSH. This enables the Delegate to communicate with Harness, Artifactory, and your TAS account.
- IAM role: The EC2 instance only needs to make connections to Harness and TAS so its permissions are minimal.
Once you have the above prerequisites, the remaining steps in this tutorial will take about 10 minutes.
Visual Summary
The following diagram shows the very simple topology for this tutorial:
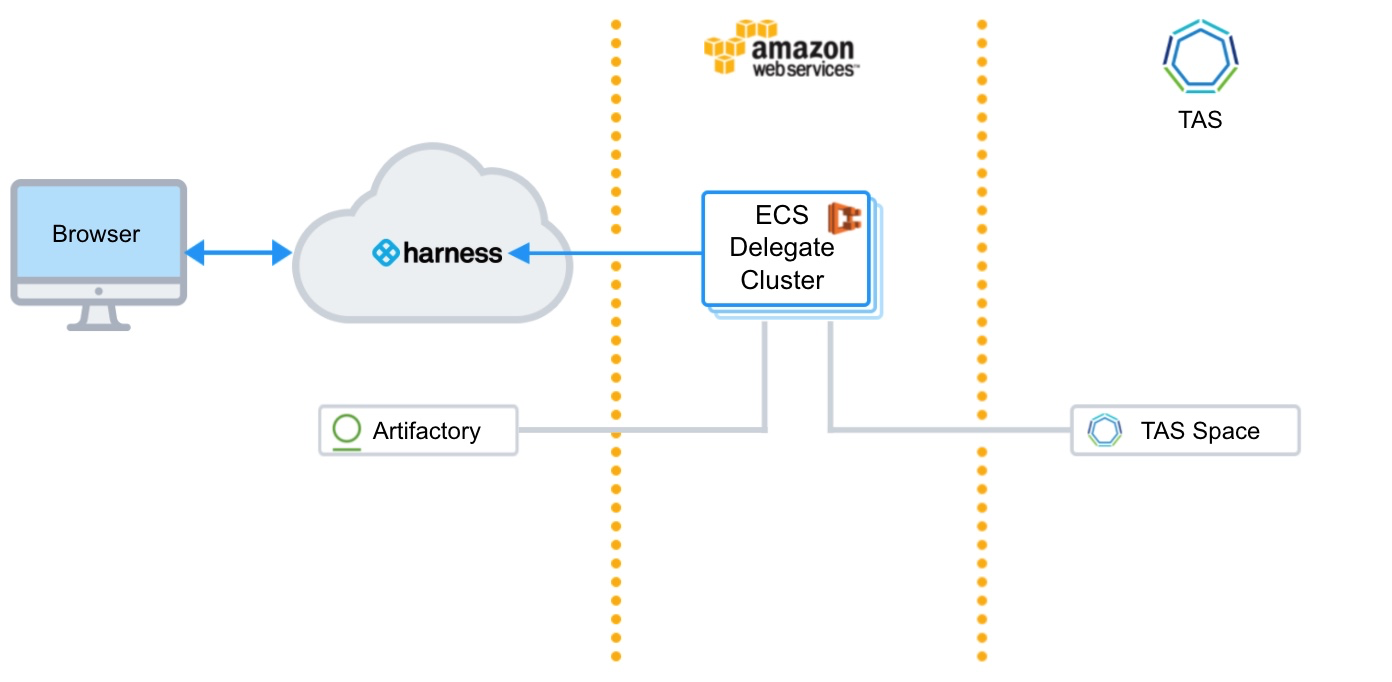
You will install the Harness Shell Script Delegate on an EC2 instance in your AWS account and connect Harness to TAS and Artifactory. Next, you'll set up your artifact, TAS manifests, and target space in Harness. Lastly, you'll create a Basic Workflow and deploy the number of new instances you need.
Step 1: Install and Launch the Shell Script Delegate
First we'll install the Harness Shell Script Delegate on the EC2 instance you set up. Ensure that the EC2 instance meets the requirements in Before You Begin.
To install the Delegate on your EC2 instance:
Sign into the Harness Manager.
Click Setup, and then click Harness Delegates.
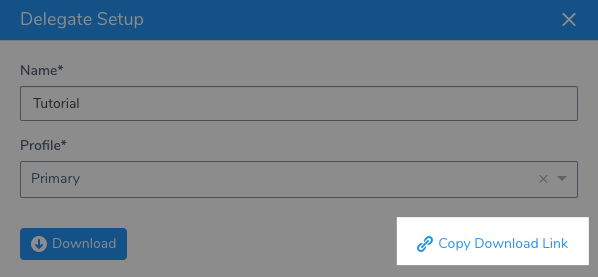
Click Download Delegate, and then click Shell Script.
Enter a name for the Delegate, and select the Primary Profile.
Click Copy Download Link.
Log into your EC2 instance, paste the Shell Script Delegate command, and hit Enter.
Once the Delegate is downloaded, unzip it (
tar -zxvf harness-delegate.tar.gz), change directories into the harness-delegate folder and run the start command:./start.sh. Ignore any warning about the ulimit.The Delegate will start and in a few moments you will see it listed in the Harness Delegates page.
Delegate Selectors
As a best practice, add a Delegate Selector to the Delegate so you can quickly identify it.
- In the Delegate listing on the Harness Delegates page, click Edit next to Selectors.
- Type in TAS-Tutorial, press Enter, and then click Submit.
The Selector is added to the Delegate.
Next we need to install the CF CLI on the Delegate so it can perform operations on your TAS space.
Step 2: Add the CF CLI to Delegate
The host running the Harness Delegate must run the CF CLI in order to execute the required commands.
You can follow the steps in Installing the cf CLI from Pivotal to install the CLI, or you can use a Harness Delegate Profile to install the CLI, described below.
In Harness, navigate to the Harness Delegates page if you are not already there.
Click Manage Delegate Profiles, and then click Add Delegate Profile.
In Display Name, enter Cloud Foundry CLI.
In Startup Script, enter the following script:
```
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/cloudfoundry-cli.repo https://packages.cloudfoundry.org/fedora/cloudfoundry-cli.repo
sudo yum -y install cf-cli
```
When you're done the Delegate Profile will look like this:
Click Submit.
Locate your Delegate, click its Profile (None by default), and select Cloud Foundry CLI.
It will take a few minutes for the CLI to install. When it is installed, a green checkmark appears next to the Profile on your Delegate.
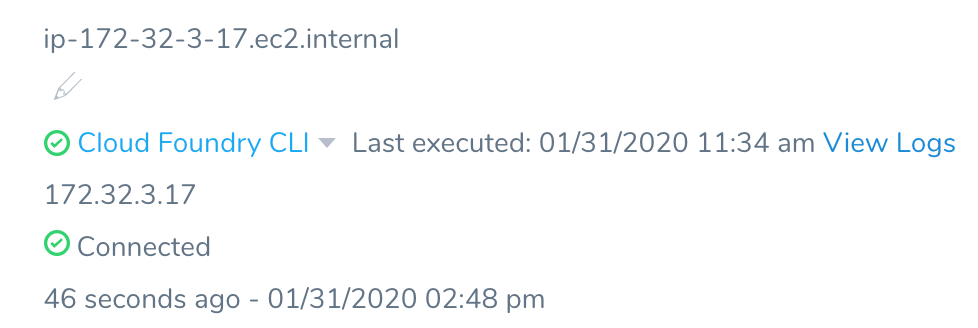
If you click View Logs, you can see the installation log:
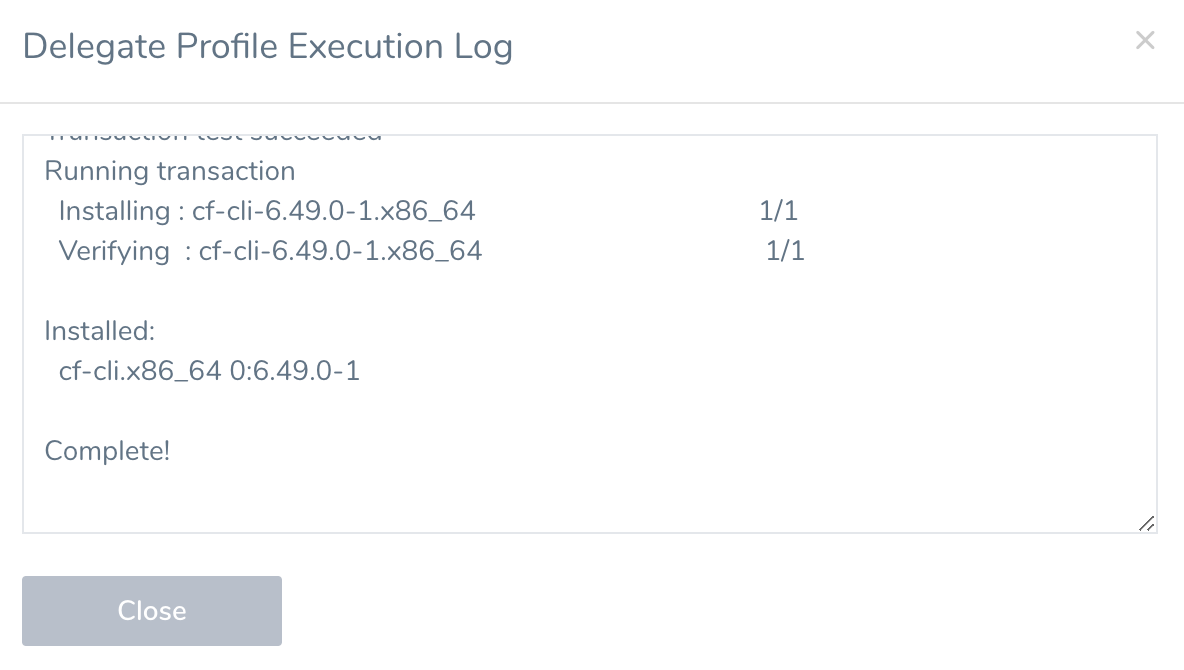
The version of the CF CLI you install on the Delegate should always match the TAS features you are using in your Harness TAS deployment. For example, if you are using buildpacks in your manifest.yml in your Harness Service, the CLI you install on the Delegate should be version 3.6 or later.
Next, we can use the Delegate to set up Harness' connections to TAS and Artifactory.
Step 3: Add the Harness TAS Cloud Provider
Harness integrates with many different types of repositories and providers. For this tutorial, you will connect to your TAS account.
The TAS user account you use must have Admin, Org Manager, or Space Manager role. The user account must be able to update spaces, orgs, and applications. For more information, see Orgs, Spaces, Roles, and Permissions from Pivotal.
In Setup, click Cloud Providers.
Click Add Cloud Provider. Enter the following settings:
- Type: Select Pivotal Cloud Foundry.
- Display Name: Enter TAS Tutorial.
- Endpoint URL: Enter api.run.pivotal.io.
- Username/Password: Enter the username and password for your TAS account.
Click Test, and then click the SUBMIT button.
The TAS Cloud Provider is added. Now we can connect to Artifactory where our publicly available app is located.
Step 4: Add the Artifactory Artifact Server
For this tutorial, we'll use a Todo List app artifact, todolist.war, available in a public Harness Artifactory repo.
In Harness, click Setup, and then click Connectors.
Click Artifact Servers, and then click Add Artifact Server. Enter the following settings:
- Type: Select Artifactory.
- Display Name: Enter Artifactory Public.
- Artifactory URL: Enter https://harness.jfrog.io/harness.
- Username/password: Leave these settings empty.
Click Test and the Submit. If the test fails, that means the Delegate can't connect to https://harness.jfrog.io/harness. Make sure that the EC2 instance hosting the Delegate can make outbound connections to https://harness.jfrog.io/harness.
Now all your connections are set up and you can define your TAS spec.
Step 5: Add Your Artifact and TAS Specs
A Harness Application represents your TAS apps, their deployment pipelines, and all the building blocks for those pipelines.
First, we'll create a Harness Application and Service, and look at the default TAS specs.
In Harness, click Setup, and then click Add Application. The Application settings appear.
Enter the name TAS Tutorial, and click Submit. Your new Application appears.
We won't cover all of the Application entities in this tutorial. We assume you've read Harness Key Concepts.
To add your specs, you create a Harness Service. Services represent your TAS apps. You define the sources of app artifacts and your TAS specs.
In your Harness Application, click Services. On the Services page, click Add Service. The Service dialog appears. Enter the following settings:
- Name: Enter TAS Tutorial.
- Deployment Type: Select Tanzu Application Services.
Click SUBMIT. The new Service is added.
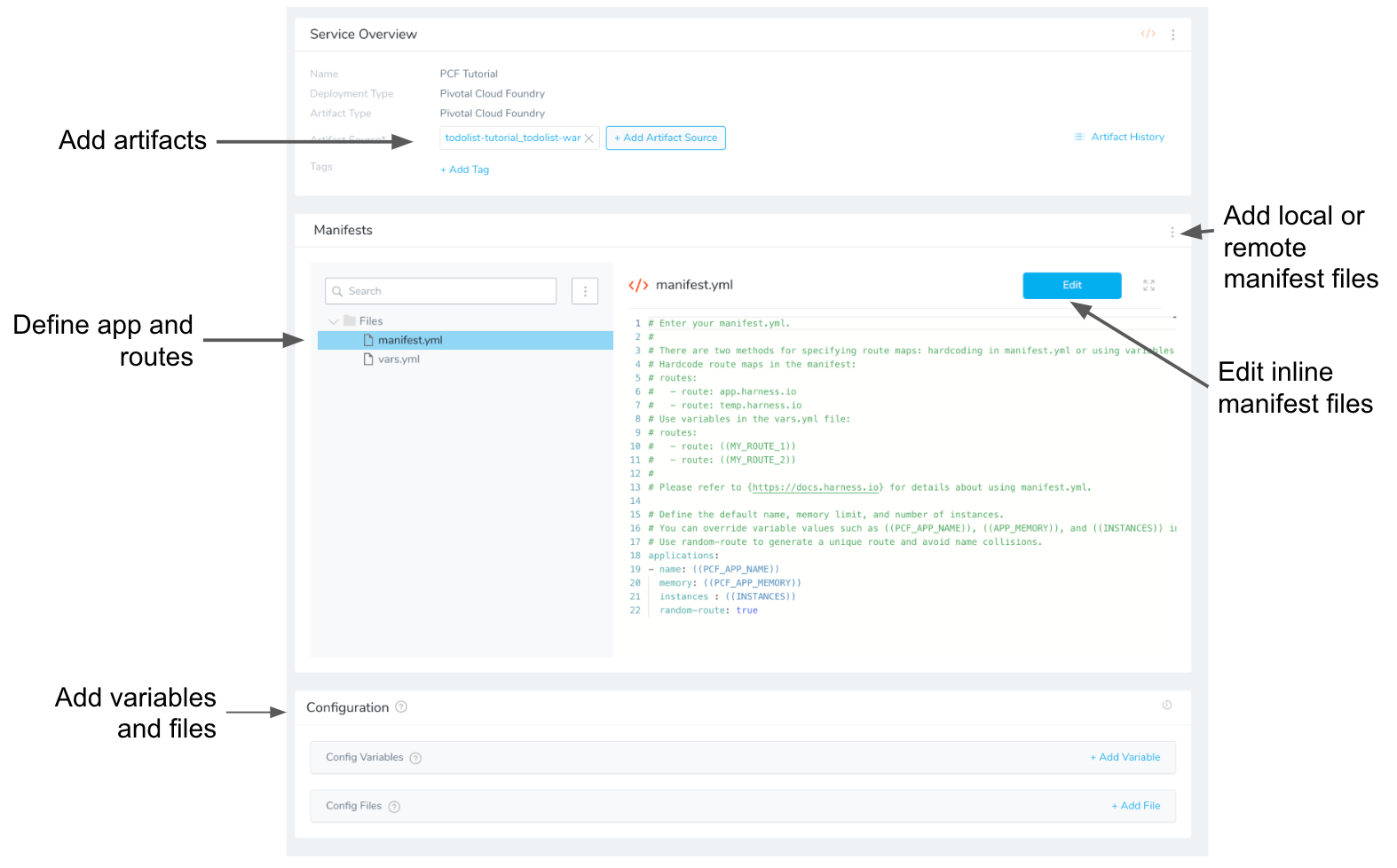
Next, we will add the WAR file artifact to the Service.
In your Service, click Add Artifact Source, and select the Artifactory artifact source. Enter the following settings:
- Display Name: Enter Todo List.
- Source Server: Select the Artifact Server you created earlier, Artifactory Public.
- Repository: Select todolist-tutorial.
- Artifact Path/File Filter: Enter todolist.war.
- Metadata Only: Do not select this option.
Click Submit. The artifact is added to the Service. Next we'll check the Artifact History to get a history of the WAR file. This primes the deployment with the history of artifacts.
Click Artifact History, and then click Manually pull artifact.
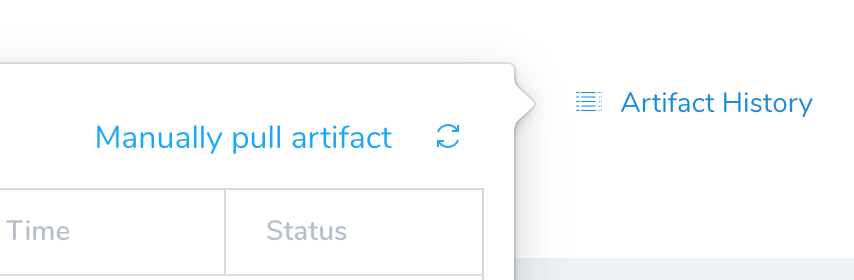
Enter the following settings:
- Artifact Stream: Select Todo List.
- Artifact: Select build# todolist.war.
Click Submit.
Now Harness has a history of all the artifacts. When you deploy the app, you can select a build number from this history.
Next, let's look at the Service Manifests section.
When you create the TAS Service, the Manifests section is created and the default manifest.yml and vars.yml files are added.
Harness uses a manifest file (manifest.yml) and variables file (vars.yml) for defining the TAS application, instances, and routes. Both files must be in YAML format and can use the .yaml or .yml extension.
Let's look at these files:
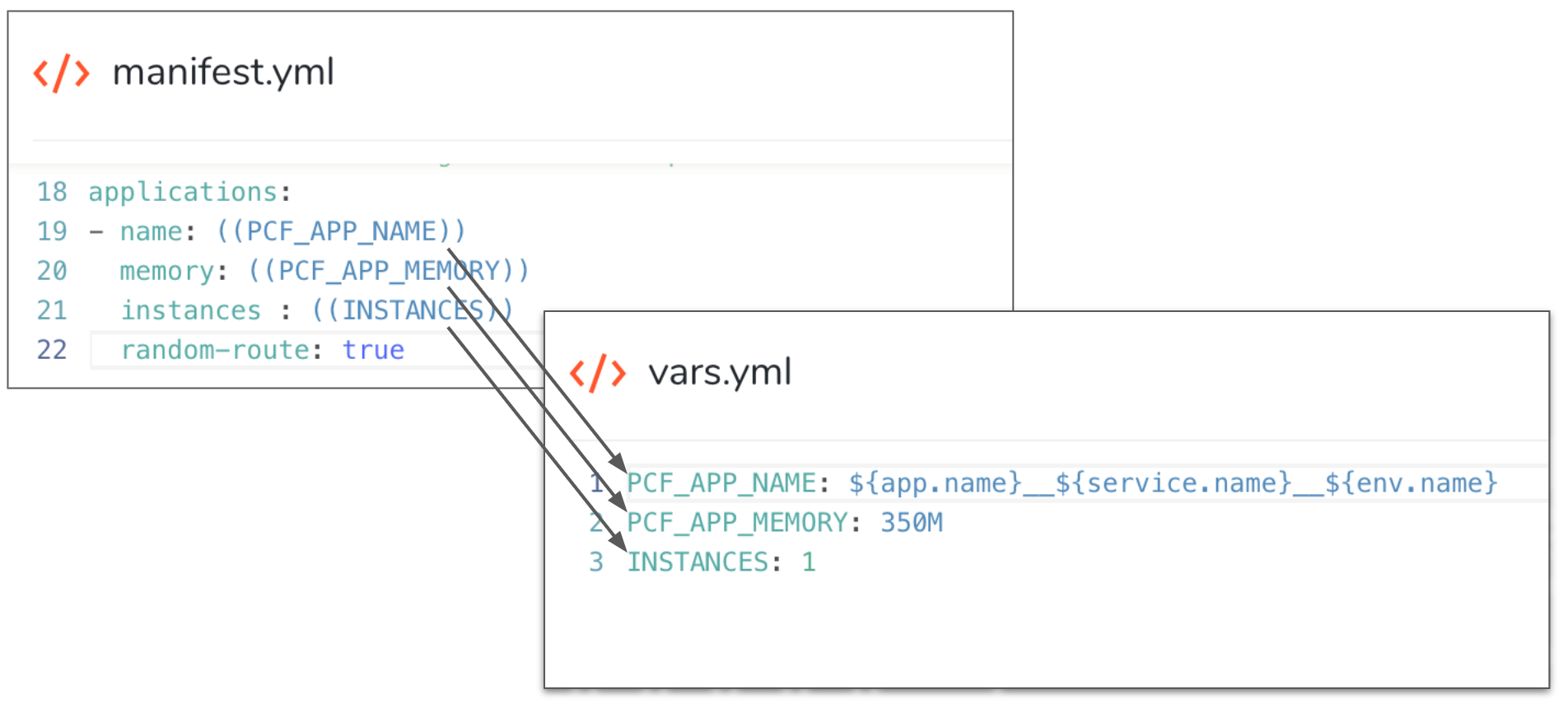
- manifest.yml - This file describes your application, host requirements, and routes. For example, the default name, memory limit, and number of instances. You can hardcode values or use variables defined in vars.yml.
This file follows the TAS app manifest requirements described in Deploying with App Manifests and Example Manifest from Pivotal. - vars.yml - This file is used to maintain variables used in the manifest.yml file.
Here is an example showing how the variables in manifest.yml are given values in vars.yml:
 For this tutorial, we'll use the default manifest files. You do not need to make any changes.
For this tutorial, we'll use the default manifest files. You do not need to make any changes.
Note that the name for the TAS app in vars.yml is a concatenation of your Harness Application, Service, and Environment names: PCF_APP_NAME: ${app.name}__${service.name}__${env.name}. This will help you find the deployed app in your TAS space later.Now that we have our artifact and specs, we can define our target space.
Step 6: Define Your Target TAS Space
Harness uses Environments to represent one or more of your deployment infrastructures, such as Dev, QA, Stage, Production, etc.
In each Environment, you define Infrastructure Definitions to describe your target TAS space. A single Infrastructure Definition can be used by multiple Harness TAS Services.
Use the breadcrumb navigation to jump to Environments.
Click Add Environment. The Environment dialog appears. Enter the following settings:
- Name: Enter TAS Tutorial.
- Environment Type: Select Non-Production.
Click Submit. The new Environment appears. Next we will add an Infrastructure Definition to identify the TAS space.
On your Environment page, click Add Infrastructure Definition. Enter the following settings:
- Name: Enter TAS Tutorial.
- Cloud Provider Type: Select Tanzu Application Services.
- Deployment Type: Select Tanzu Application Services.
- Cloud Provider: Select the TAS Cloud Provider you added earlier.
- Organization: Select your target TAS org.
- Space: Select your target space.
- Click Submit. The new Infrastructure Definition is added to your Environment.
You will select this Environment and Infrastructure Definition when you create your Harness Workflow next.
Step 7: Set up a TAS Basic Workflow
A TAS Workflow performing a Basic deployment simply takes your Harness TAS Service and deploys it to your TAS Infrastructure Definition.
Once the TAS app is set up in the Workflow using the App Setup command, you can resize the number of instances specified in the Service manifest.yml or App Setup command using the App Resize command.
Use the breadcrumb navigation to jump to Workflows, and then click Add Workflow. The Workflow settings appear.
Enter the following settings:
- Name: Enter TAS Tutorial.
- Workflow Type: Select Basic Deployment.
- Environment: Select TAS Tutorial.
- Service: Select TAS Tutorial.
- Infrastructure Definition: Select TAS Tutorial.
Click Submit. The TAS Basic Workflow is created.
There's nothing to change in the default Workflow settings. We simply need to open and confirm the defaults.
We'll walk through the default steps in the Workflow, App Step and App Resize.
Click App Setup. The App Setup command uses the manifest.yml in your Harness TAS Service to set up your app. We'll confirm the defaults.
- Name: This is the name of the step.
- Instance Count: The number of instances for your app. By default, we use the
INSTANCESsettings from the vars.yml in your Service Manifests section. The Match running instances setting can be used after your first deployment to override theinstancessetting in the manifest.yml. - Existing Versions To Keep: The number of previous app versions to downsize and keep.
- Additional Routes: Any additional routes to add to the mapping configured in the Service manifest.
- Use App Autoscaler Plugin: This setting can be used if the App Autoscaler plugin service running in your target Pivotal space and bound to the app you are deploying.
Click Submit.
Click App Resize. The App Resize command is displayed as incomplete. Harness simply needs you to confirm the default number of desired instances, 100 Percent.
- Name: This is the name of the step.
- Desired Instances: A percentage of the number specified in your manifest.yml, or if you used the App Setup Match desired count with current running instances setting, the current number of running instances. You can also use Count to explicitly set the number of desired instances.
Click Submit.
The Workflow is complete. You can run the Workflow to deploy the app to your TAS space.
Step 8: Deploy and Review
Now that your TAS Basic Workflow is complete you can deploy it to your space.
If you're not already on the main Workflow page, use the breadcrumb navigation to navigate to the TAS Tutorial Workflow.
Click the Deploy button. The Deploy settings appear. Enter the following settings:
- Artifacts > TAS Tutorial: Select an artifact from the Artifact Source you added to the Harness Service. In this tutorial, we are using a public Artifactory file. Select Buid# todolist.war.
- Send notification to me only: Enable this setting if you are doing this tutorial using your corporate Harness account. Enabling this setting will ensure that other users won't be notified of this deployment.
Click Submit. The deployment executes.
You now have a Todo List app deployed to your TAS space. Remember the app name is a concatenation of your Harness Application, Service, and Environment names: ${app.name}__${service.name}__${env.name}:
Click VIEW APP to see the running app.
Next Steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Install and run the Harness Shell Script Delegate on an EC2 host.
- Connect Harness with your TAS account.
- Connect Harness with Artifactory.
- Specify the TAS manifest to use for the app.
- Specify the target TAS org and space.
- Set the number of instances to deploy.
- Create and deploy a TAS Basic Workflow.
Read the following related How-tos:
- Tanzu Application Service How-tos which include Canary and Blue/Green TAS deployments.
- Triggers show you how to automate deployments in response to different events.
- Infrastructure Provisioners Overview will show you how to add provisioning as part of your Workflow.