Run chaos experiments as a GitLab pipeline
This tutorial explains how you can create chaos experiments using Harness Chaos Engineering (HCE) and run them in GitLab pipelines. Chaos experiments in Harness are created the same way in the chaos engineering module, irrespective of where they are invoked from.
Before you begin
Check out the first chaos experiment that will guide you through creating a new experiment in HCE. This will provide a solid foundation for your understanding of creating experiments in HCE.
Below are the steps to run chaos experiments in GitLab pipelines.
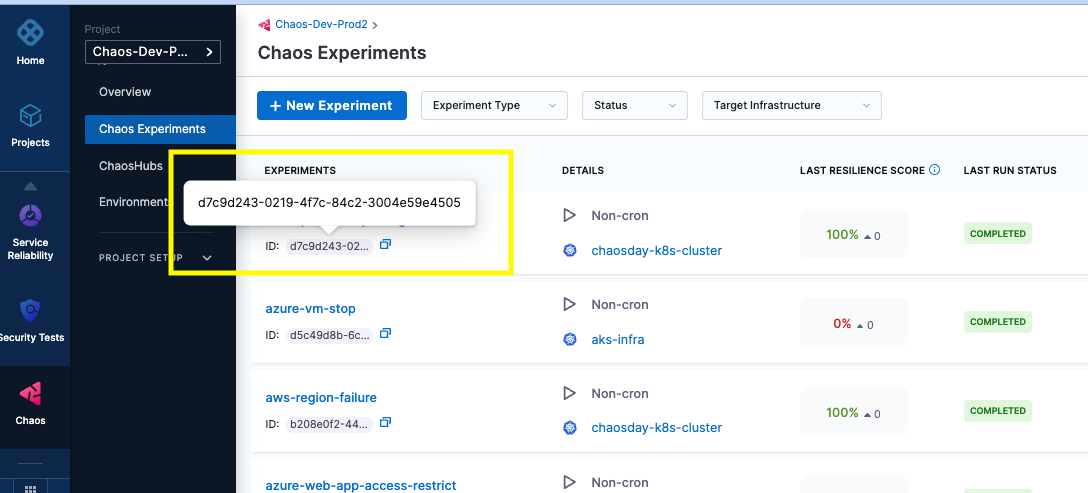
Create a chaos experiment
Create a chaos experiment in the Harness Chaos Module. Execute this experiment to verify the configuration and ensure that the resilience probes are working as expected. The experiment ID and resilience score determined from this experiment run will be used to integrate the experiment with GitLab.
Create a launch script
HCE APIs are used to invoke or launch a chaos experiment from the pipeline. To simplify creating an API call with the required secure parameters and data, a CLI tool is provided. Use this tool to create an appropriate API command to include in the pipeline script.
Below is a sample launch script.
#!/bin/bash
set -e
curl -sL https://storage.googleapis.com/hce-api/hce-api-linux-amd64 -o hce-api-saas
chmod +x hce-api-saas
output=$(./hce-api-saas generate --api launch-experiment --account-id=${ACCOUNT_ID} \
--project-id ${PROJECT_ID} --workflow-id ${WORKFLOW_ID} \
--api-key ${API_KEY} --file-name hce-api.sh | jq -r '.data.runChaosExperiment.notifyID')
echo ${output}
Insert chaos experiments into .gitlab-ci.yaml
You can include the above-mentioned launch script in the GitLab pipeline as a stage or a step. In the script: section, add the scripts for launching, monitoring and retrieving results. An example is shown below.
# Insert a chaos stage where each chaos experiment is inserted as a launch script.
chaos-job: # This job runs in the deploy stage.
stage: chaos # It only runs when *both* jobs in the test stage complete successfully.
environment: production
variables:
WORKFLOW_ID: "d7c9d243-0219-4f7c-84c2-3004e59e4505"
EXPECTED_RESILIENCE_SCORE: 100
before_script:
- apt-get update; apt-get -y install jq
script:
- echo "Launching Chaos Experiment.."; EXPERIMENT_NOTIFY_ID=$(sh scripts/launch-chaos.sh)
- echo "Monitoring Chaos Experiment.."; sh scripts/monitor-chaos.sh ${EXPERIMENT_NOTIFY_ID}
- echo "Deriving Resilience Score.."; ACTUAL_RESILIENCE_SCORE=$(sh scripts/verify-rr.sh ${EXPERIMENT_NOTIFY_ID} | tr -d '"')
- echo "Obtained Resilience Score is ${ACTUAL_RESILIENCE_SCORE}"
- if [ ${ACTUAL_RESILIENCE_SCORE} -lt ${EXPECTED_RESILIENCE_SCORE} ]; then exit 1; fi
rollback-job:
stage: rollback
environment: production
image:
name: bitnami/kubectl:latest
entrypoint: ['']
script:
- *prepare_kubecontext
- echo "Attempting Rollback.."; sh scripts/rollback-deploy.sh #write your own rollback logic here
needs: ["chaos-job"]
when: on_failure
The resilience score is the result of the experiment, and helps decide if a rollback job needs to be invoked.
Retrieve the resilience score
Retrieve the resilience score using the Harness Chaos API and take appropriate action in the pipeline. An example of how to use the Harness Chaos API is shown below.
#!/bin/bash
set -e
curl -sL https://storage.googleapis.com/hce-api/hce-api-linux-amd64 -o hce-api-saas
chmod +x hce-api-saas
resiliencyScore=$(./hce-api-saas generate --api validate-resilience-score --account-id=${ACCOUNT_ID} \
--project-id ${PROJECT_ID} --notifyID=$1 \
--api-key ${API_KEY} --file-name hce-api.sh)
echo "${resiliencyScore}"
Example end-to-end configuration
Go to GitLab demo for a sample configuration of the chaos launch script. You can include this script in the GitLab YAML file. This is a sample to include one single chaos experiment, but the same can be repeated so as to be included in multiple chaos experiments.