AutoStopping idle VMs behind a reverse proxy
Harness Intelligent Cloud AutoStopping™ revolutionizes cloud resource optimization by introducing powerful automation capabilities. This groundbreaking feature empowers businesses to effortlessly optimize their cloud costs by automatically halting idle cloud resources.
AutoStopping goes beyond just stopping idle resources; it possesses the intelligence to reactivate them when necessary. This dynamic functionality allows previously stopped idle resources to be automatically brought back up during periods of activity or increased demand based on the AutoStopping rules defined in Harness CCM. AutoStopping supports a wide range of resources in multiple cloud providers, read more about them here.
AutoStopping an EC2 instance
Let’s assume that you have a setup in AWS, where a domain todolist.example.com is mapped to an AWS ALB, pointing it to an underlying TargetGroup with one EC2 after checking the host headers as shown in the diagram below.
Routing based on Hostname to an EC2 under AWS ALB
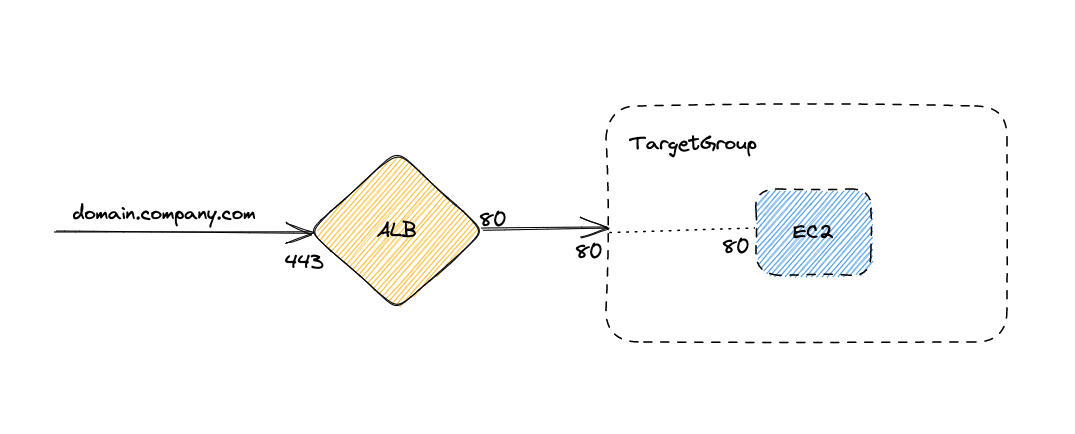
Incorporating this rule into AutoStopping is a simple process. By importing the ALB (Application Load Balancer) as a Harness load balancer and configuring an AutoStopping rule for the EC2 instance with the custom domain as todolist.example.com in the Harness platform, the AutoStopping feature seamlessly manages the EC2 instance based on the defined rule.
Adding a reverse proxy to the mix
The content assumes HAProxy as a reverse proxy between ALB and the EC2 instance. But this setup can be replicated for others (Nginx) as well.
Consider a scenario where an HAProxy serves as a reverse proxy, bridging the gap between the EC2 instance and the Application Load Balancer (ALB). This HAProxy plays a vital role in executing custom evaluations and rewrites, catering to various needs such as Blue/Green deployments, augmenting request headers, and fulfilling specific routing requirements.
HAProxy as a reverse proxy between ALB and EC2 instance
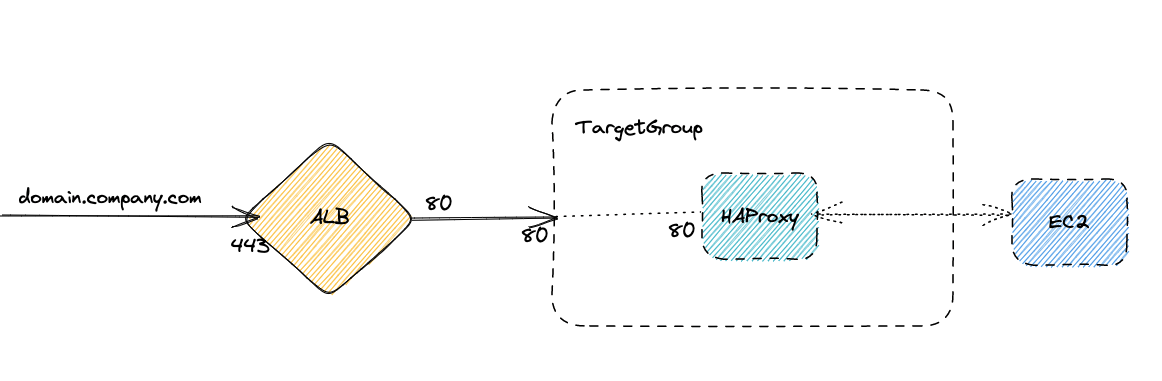
In this scenario, it is not feasible to directly onboard the EC2 instance to AutoStopping as previously done because the ALB does not directly send data to the resource. While it is possible to onboard the HAProxy machine, this is not the desired outcome since the goal is to AutoStop the EC2 machine itself. Additionally, since the HAProxy can be associated with multiple domains and applications, access to any of them would keep the proxy up, which would not result in the expected cost savings.
Introducing Harness AutoStopping Proxy
Harness AutoStopping Proxy is a valuable solution in this scenario. It is built on top of the envoy proxy, offering robust capabilities for handling routing and load balancing across different cloud providers. This proxy is not limited to HTTP traffic and can effectively handle any TCP-based traffic detection. Detailed documentation on creating an AutoStopping Proxy can be found here.
After setting up an AutoStopping proxy, select the newly created proxy as the load balancer, and then configure the custom domain as todolist.example.com for the proxy. To route the traffic to the underlying EC2 instance, hit the proxy IP with a host header Host: todolist.example.com.
Forwarding HAproxy to Harness AutoStopping Proxy
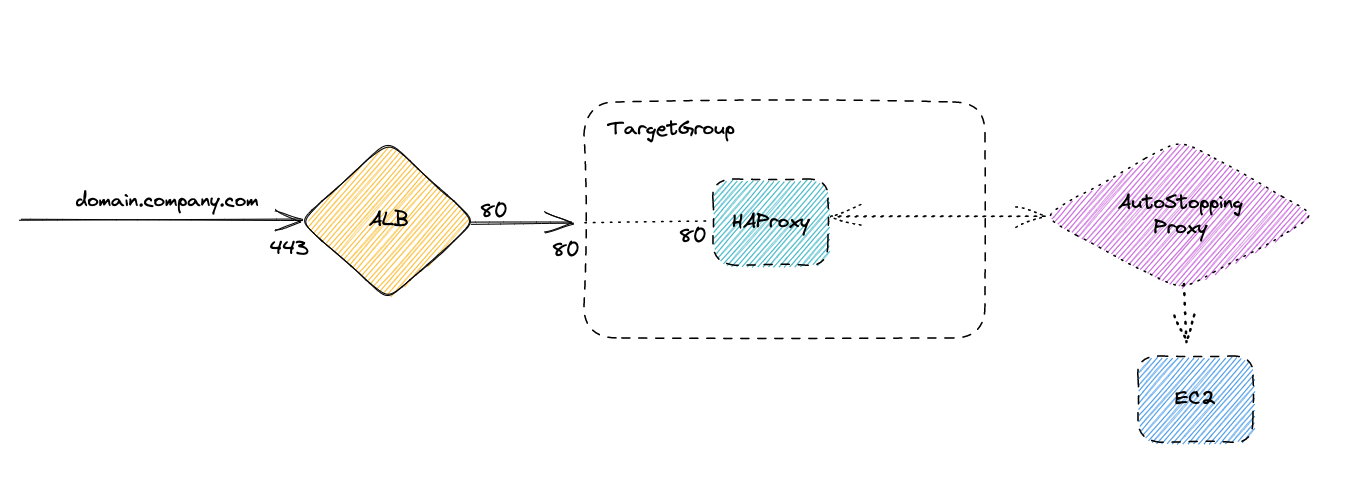
Now that the Harness AutoStopping proxy can route to the EC2 instance with the domain todolist.example.com, configure the HAProxy to route the traffic to the AutoStopping proxy instead of the Ec2 instance. The configuration looks like this:
frontend www-http
bind *:80
mode http
use_backend uiserver
backend uiserver
mode http
server dashbaord (replace ec2 IP with the Harness AutoStopping proxy IP)
After you reload the HAProxy configuration after this, the setup looks like the diagram below.
Setup with HAProxy forwarding requests to Harness AutoStopping Proxy
Warmup the instance
Once you have this setup in place, the flow for incoming HTTP traffic to the domain todolist.example.com is as follows:
- When an HTTP request is initiated, it first reaches the Application Load Balancer (ALB).
- The ALB performs certificate validation for the request.
- After successful validation, the request is forwarded to the HAProxy.
- The HAProxy performs various necessary actions such as rewriting the path, adding headers, etc., based on your configured settings.
- Next, the HAProxy forwards the request to the Harness AutoStopping proxy.
- Upon receiving the traffic, the AutoStopping proxy checks if the associated AutoStopping rule is active.
- If the AutoStopping rule is not active, the traffic triggers a warmup process for the rule.
- As part of the warmup process, the EC2 machine associated with the rule is started.
- Once the EC2 instance is found to be healthy, the request is forwarded to it.
Cooldown the instance
The AutoStopping Proxy actively monitors incoming activity. When the pre-configured idle threshold (idle time) for the rule is reached without any activity, the following actions take place:
- The AutoStopping rule recognizes the idle state based on the specified threshold.
- The AutoStopping rule transitions itself to the "down" state, indicating that it is no longer actively accepting traffic.
- Simultaneously, the associated EC2 instance is also transitioned to the "down" state, indicating that it is no longer serving requests.
An end note
In summary, by integrating Harness CCM's AutoStopping feature with setups utilizing HAProxy as a reverse proxy, you can leverage a robust solution for automating cloud resource optimization. It provides a powerful capability to automatically halt idle cloud resources and reactivate them as required. This approach allows you to efficiently manage your non-production cloud costs without compromising application availability. By dynamically controlling resource utilization, you can strike a balance between cost optimization and ensuring application availability in a flexible and automated manner.