Linux chaos infrastructure advanced management
This section describes the advanced setup, infrastructure service, and logs associated with the Linux chaos infrastructure.
Advanced setup
A set of mandatory input flags is required for the installation of the chaos infrastructure, including the infra-id, access-key and the server-url. However, certain aspects of the infrastructure can be tuned via the following flags:
log-directory: Specifies a custom log directory to store the log files. By default, the logs are stored at
/var/log/linux-chaos-infrastructure.task-poll-interval-seconds: Specifies the interval between subsequent poll queries to the server for a new experiment. The default value is 5 seconds.
task-update-interval-seconds: Specifies the duration between subsequent status updates of an active fault to the server. The default value is 5 seconds.
update-retries: Specifies the maximum number of retries in case of a failure while sending a fault status or result.
If the retry count is breached while sending the status, then the active fault is aborted after logging the error during each attempts and the result is then attempted to be sent.
If the retry count is breached while sending the result, then no result is sent by the infrastructure but the error during the attempts are logged.
The default value is 5.
update-retry-interval-seconds: Specifies the interval between the subsequent attempts to send a fault status or result, in case of a failure. The default value for it is 5 seconds.
chaos-infra-liveness-update-interval-seconds: Specifies the interval between the chaos infrastructure liveness heartbeats. The default value is 5 seconds.
chaos-infra-log-file-max-size-mb: Specifies the maximum size limit for the chaos infrastructure log file rotation. Upon breaching the size limit, a new log file is created to store the logs and the old log file is retired as a backup archive. The default value is 5 MB.
chaos-infra-log-file-max-backups: Specifies the maximum number of backup archives to be retained at any given time. The oldest archive is deleted when a new log file is created. The default value is 2.
experiment-log-file-max-age-days: Specifies the number of days after which the experiment log files will be deleted. The default value is 30.
Infrastructure service
Linux chaos infrastructure is installed as an executable binary on your Linux machine. This infrastructure is managed as a Systemd service.
- The service starts automatically when the system starts.
- If the service stops unexpectedly, the service automatically attempts to restart after a cooldown period of 5 seconds.
- By default, the service ensures that the chaos infrastructure process is owned by the root user.
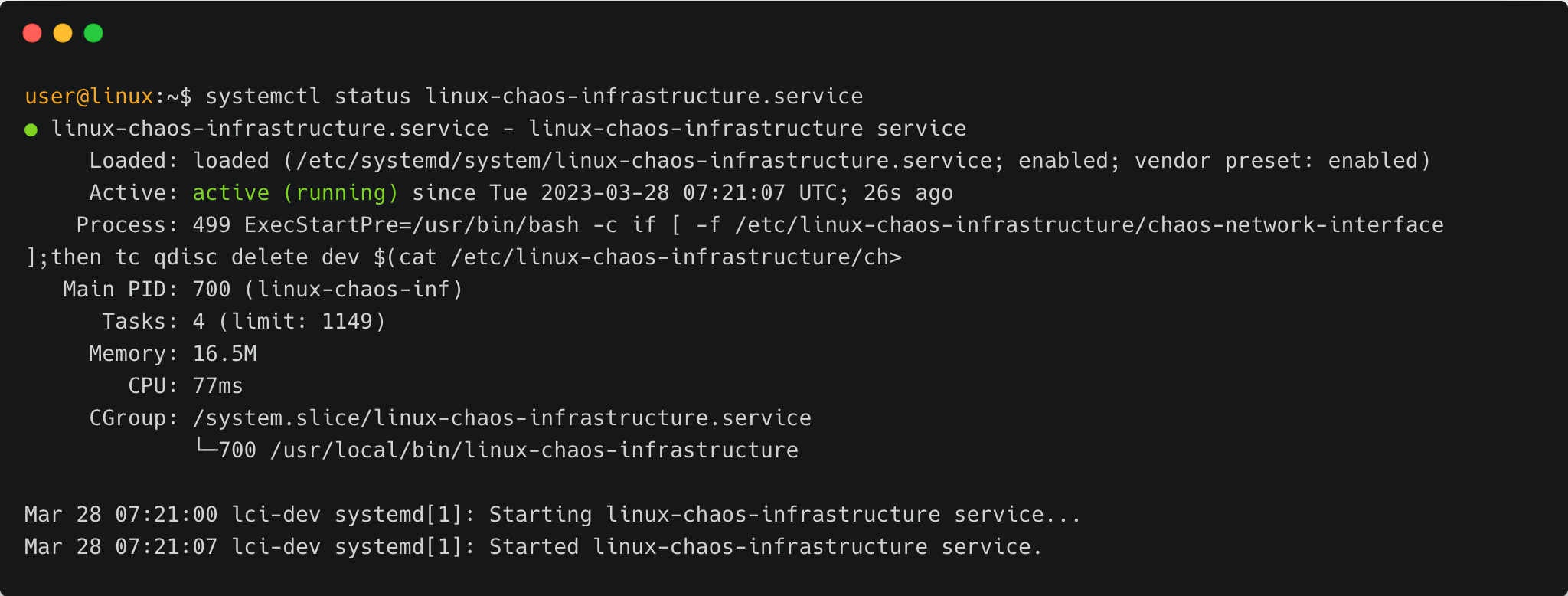
To check whether the infrastructure service is active and running, you can check the status using the following command. Any other status than the active status would indicate some issue with the infrastructure.
systemctl status linux-chaos-infrastructure.service
Logs
Logs that are generated are stored in the /var/log/linux-chaos-infrastructure directory by default. There are two types of logs:
Infrastructure logs: Infrastructure logs are generated as a result of any infrastructure operation which is not directly related to the execution of an experiment. Examples of such operations include:
- Start of execution of an experiment
- End of execution of an experiment
- Error during creation of an experiment log file
- Error while querying for an experiment
- Error while sending experiment status or result, etc.
By default this log file is located at
/var/log/linux-chaos-infrastructure/linux-chaos-infrastructure.logand can be used for troubleshooting the infrastructure.
- The file is rotated based on its size; when the file size is a specified size, it is archived in a separate file with the timestamp of rotation suffixed to the file name. By default, this value is 5 MB.
- Eventually the old archives are deleted. The maximum number of most recent archives that are retained at any given time can be specified. By default this value is 2.
- Experiment logs: Experiment logs are stored in separate files, which are scoped to the faults of the experiment. It contain information about the various steps of execution of that fault, including any error caused during the execution of the fault. The files use the unique fault name as mentioned in the experiment as their filename.
- These files are rotated based on their age, where files older than a specific number of days are removed. By default, this value is 30 days.