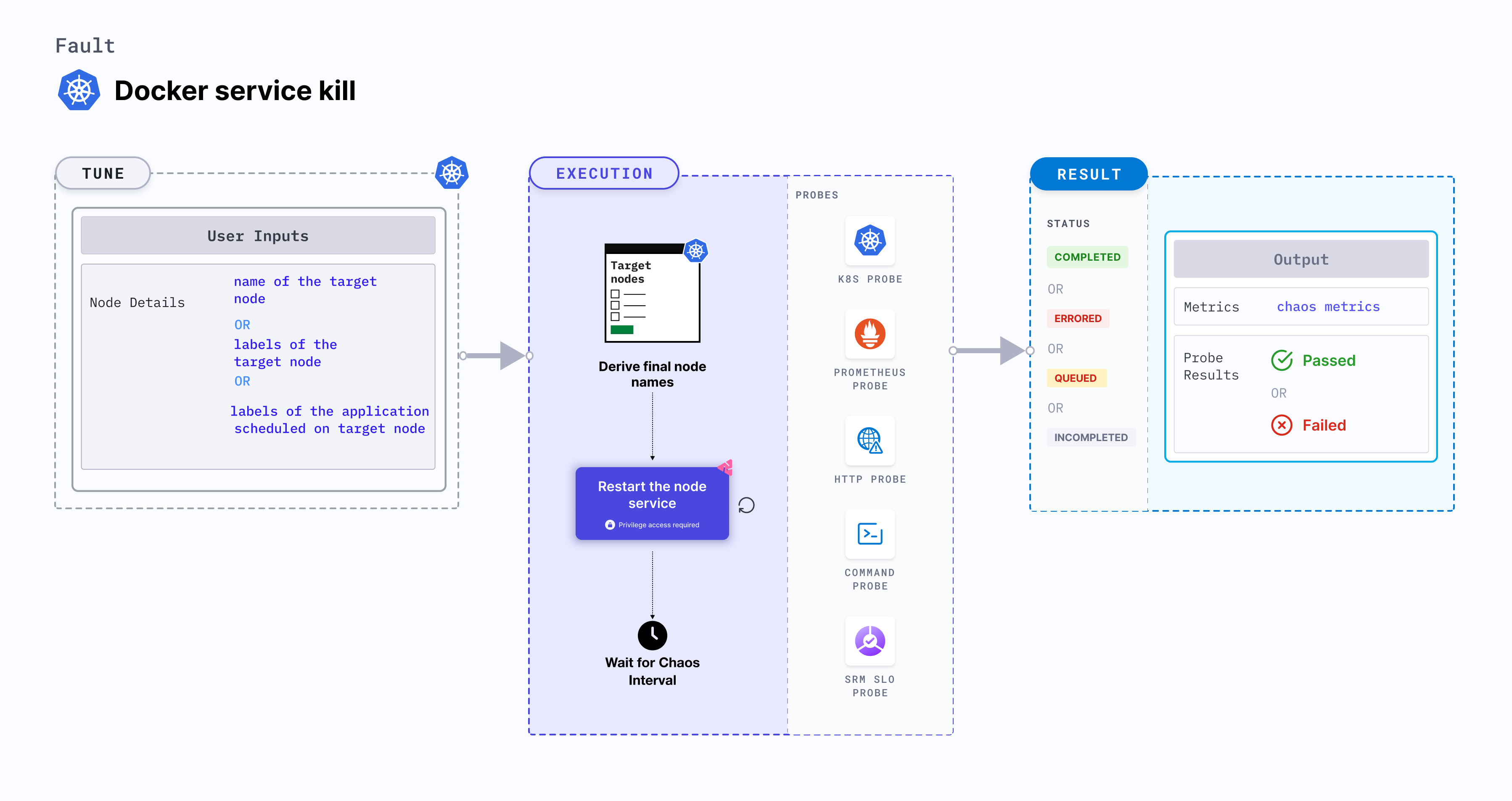
Docker service kill
Introduction
Docker service kill makes the application unreachable on the account of the node turning unschedulable (in NotReady status).
- Docker service is stopped (or killed) on a node to make it unschedulable for a specific duration.
- The application node goes back to normal state and services are resumed after a specific duration.
Use cases
Docker service kill fault determines the resilience of an application when a node becomes unschedulable, that is, NotReady state.
note
- Kubernetes > 1.16 is required to execute this fault.
- Node specified in the
TARGET_NODEenvironment variable (the node for which Docker service would be killed) should be cordoned before executing the chaos fault. This ensures that the fault resources are not scheduled on it or subject to eviction. This is achieved using the following steps:- Get node names against the applications pods using command
kubectl get pods -o wide. - Cordon the node using command
kubectl cordon <nodename>.
- Get node names against the applications pods using command
- The target nodes should be in the ready state before and after injecting chaos.
Fault tunables
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TARGET_NODE | Name of the target node. | For example, node-1. For For more information, go to target node. |
| NODE_LABEL | Node label used to filter the target node if TARGET_NODE environment variable is not set. | It is mutually exclusive with the TARGET_NODE environment variable. If both are provided, the fault uses TARGET_NODE. For more information, go to node label. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Default: 60 s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos. |
| SERVICE_NAME | Provide the name of service you want to stop. Supported docker and containerd | Default: containerd. For more information, go to service name |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
Target Node
Name of the target node. Tune it by using the TARGET_NODE environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# kill the docker service of the target node
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: docker-service-kill
spec:
components:
env:
# name of the target node
- name: TARGET_NODE
value: 'node01'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'
Kill target service
Name of the target service. Tune it by using the SERVICE_NAME environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# kill the target service of the target node
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: docker-service-kill
spec:
components:
env:
# name of the target node
# supported 'containerd' and 'docker'
- name: SERVICE_NAME
value: 'containerd'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'