Create AutoStopping Rules for GCP
AutoStopping Rules make sure that your non-production resources run only when used, and never when idle.
This topic describes how to create AutoStopping Rules for GCP.
Before you begin
- Create a GCP Connector for AutoStopping Rules
- Create a Kubernetes Connector for AutoStopping Rules
- AutoStopping Rules Overview
Prerequisites
To create an AutoStopping rule using an AutoStopping proxy load balancer:
- You must provide the required permissions to Harness to create an instance in your GCP account.
- You must provide the required permissions to read the secrets and fetch the certificates stored in the secret for TLS-based flows.
- Ensure that you reserve some IPs if you intend to allocate elastic IP while creating an AutoStopping proxy.
Add a cloud provider
Perform the following steps to link your GCP cloud account to Harness.
In Cloud Costs, click New AutoStopping Rule.
In AutoStopping Rules, select GCP. It is the cloud account in which your workloads are running that you want to manage using AutoStopping Rules.
If you have already linked your GCP account and want to use that account, then select the GCP account from the Connect to your GCP account drop-down list.
If you have not added your cloud account, click Connect to your GCP account drop-down list and then click New Connector. For the detailed steps, see Create a GCP Connector for AutoStopping Rules.
Add a new AutoStopping rule
Perform the following steps to add a new GCP AutoStopping rule:
Define an AutoStopping rule
Perform the following steps to get started with AutoStopping Rule.
- In Cloud Costs, in AutoStopping Rules, click New AutoStopping Rule.
- In the cloud account type, select GCP. It is the cloud account in which your workloads are running that you want to manage using AutoStopping rules.
- Select your GCP account from the Connect to your GCP account drop-down list and click Next. If you have not added a GCP cloud account, see Create a GCP Connector for AutoStopping Rules.
- In Define your AutoStopping rule, in Name your Rule, enter a name for your rule. This is the name of your AutoStopping rule.
- In Idle time, enter the idle time in minutes. This is the time that the AutoStopping rule waits before stopping the idle instances.
Select the resources to be managed by the AutoStopping rules
Select the Kubernetes workloads that you want to manage using this rule. AutoStopping Rule monitors the selected resources and stop them when they are idle beyond the configured idle time.
Option 1: Select Google Compute Engine (GCE) VM(s)
Add instance/s to be managed by your AutoStopping rule.
You can add multiple instances to a single Rule. However, all the VMs should be part of the same region.
- Select Instances and click Add an Instance.
- Select a Region and Zone from the drop-down list. This is the location where your instances are hosted.
- Select the instances that you want to manage using the AutoStopping rules. You can use the search option to search the instances.
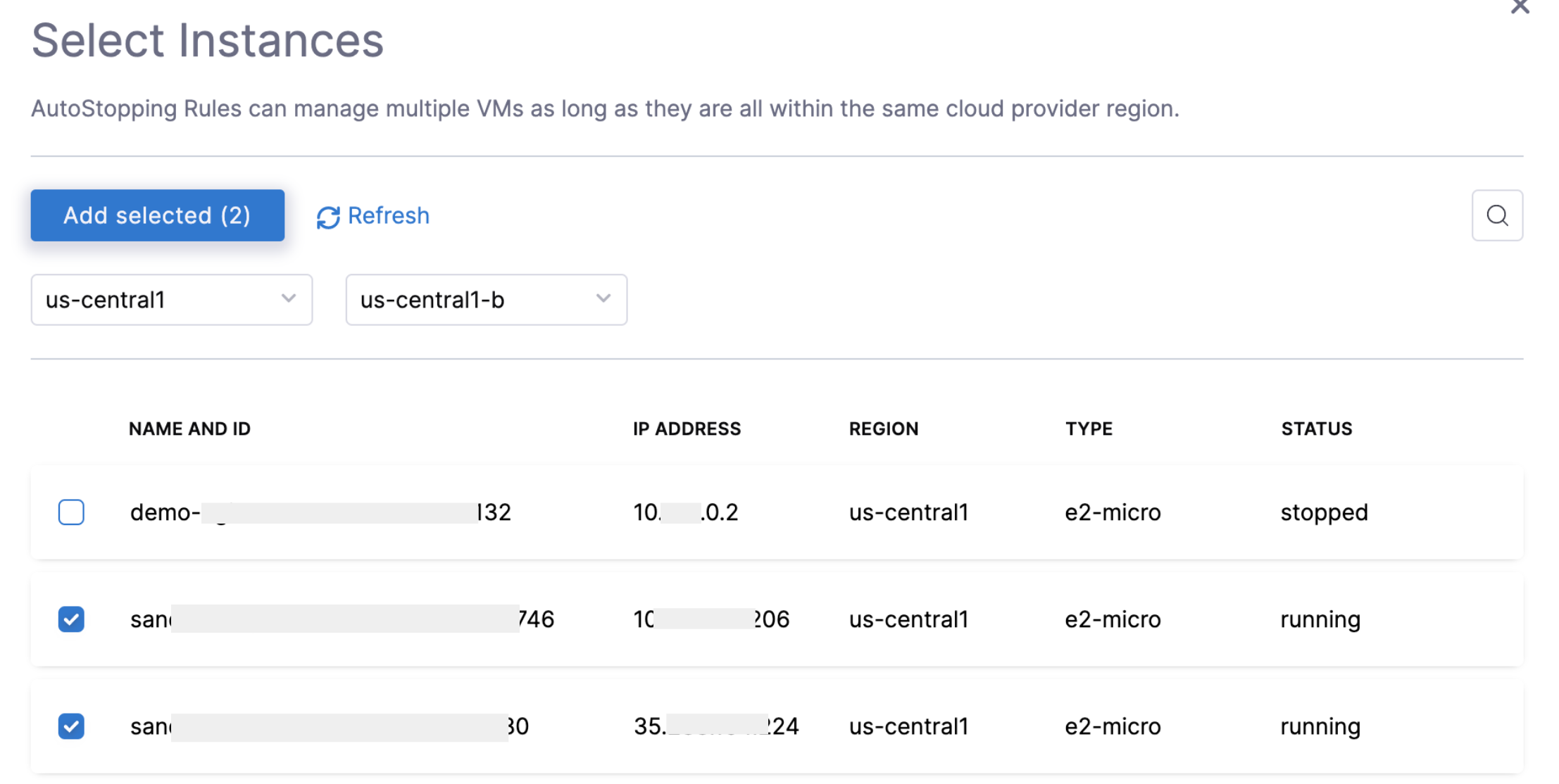
- Click Add Selected to select the instances.
Option 2: Select Kubernetes Cluster
- Select Kubernetes Cluster and then click Add a cluster.
- Select the Kubernetes cluster that you want to manage using the AutoStopping rules. If you wish to create a new connector for the Kubernetes cluster, see Create a Kubernetes Connector for AutoStopping Rules.
- Once you have finished selecting the Kubernetes cluster, click Add selected.
(Optional) Set up advanced configuration
In this step, you can configure the following settings:
Hide progress page
Toggle the button to disable the display of progress page during instances' warming up process. This option is especially useful when the service is invoked by an automation system, as it prevents misinterpretation of the progress page as the intended response from a service that is onboarded to AutoStopping. By hiding the progress page, the first response of warming up a rule after a downtime will be delayed until the intended service is up and running.

Dry Run
Toggle the button if you wish to evaluate this feature without terminating your cloud resources. For more information, go to Evaluate AutoStopping rules in dry-run mode.
Add Dependency
Set dependencies between two or more AutoStopping Rules when you want one Rule to make one or more Rules to be active based on the traffic that it receives. For example for an application server dependent on a database server, create two AutoStopping Rules managing both the servers. Add a dependency on the Rule managing the application server to be dependent on the Rule managing the database server.
- Click add dependency to add a dependency on any existing rule.
- Select the rule from the RULES drop-down list.
- In DELAY IN SECS, enter the number of seconds that rule should wait after warming up the dependent rule. For example, you have Rule 1 dependent on Rule 2 and you have set 5 seconds delay. In that case, when the request is received to warm up Rule 1, then first Rule 2 (dependent rule) is warmed up, and then there is a delay of 5 seconds before warming up Rule 1.
- Once you're done with all the configurations, click Next.
Fixed Schedule
Create fixed uptime or downtime schedules for the resources managed by this AutoStopping Rule. When a resource is configured to go up or down on a fixed schedule, it is unaffected by activity or idleness during that time period.
In certain scenarios, you would not want your resources to go down or up. For example, every Friday at 5 p.m. you want your ABC resource to go down. You can schedule downtime for your ABC resource. During this window, the resource is forced to go down regardless of the defined rule. You can choose to specify uptime for your resources in the same way.
The fixed schedule takes precedence over the defined AutoStopping Rule.
Harness executes scheduled rules using Dkron, an open-source workload automation service.
To create a fixed schedule for your rule, do the following:
In Fixed Schedules, click Add Fixed Schedule.
In New Fixed Schedule, enter a Name for your schedule.
In Type, select the type for your schedule. You can schedule an Uptime or Downtime for your rule. As per your schedule, the resources go up or down.
Select the Time Zone from the drop-down list.
In Set schedule period, use the date picker to set the start and end time for your schedule.
In Begins on, select the start date and time for your schedule. You can select a date and specify the time.
In Ends on, select the end date and time for your schedule. You can select a date and specify the time. Ensure that Never ends checkbox is unselected to set the end time.
If you don't specify an end time, the schedule continues to run until you manually update the settings or remove the schedule.
Select the checbox Never ends if you do not want to set end time for your schedule.
You can also set a recurring schedule for the rule. If you want to set a recurring schedule, in Uptime/Downtime in the selected period, in Repeats, select the repeat frequency.
- Select which days of the week you'd like your schedule to repeat. You can choose any day between Sunday and Saturday.
- Select Everyday, to set the schedule for all seven days of the week.
- Set your repeat schedule's beginning and ending time. In the Time field, specify the start and end time for the fixed schedule.
- Select All Day, if you wish to set your schedule for the entire day. If you choose All Day for your schedule, you won't be able to choose a start and end time.
Example 1:
In the following example, resources are up every Mon, Tue, Wed starting from 12:00 a.m. on February 14, 2022 till April 30, at 10:00 p.m.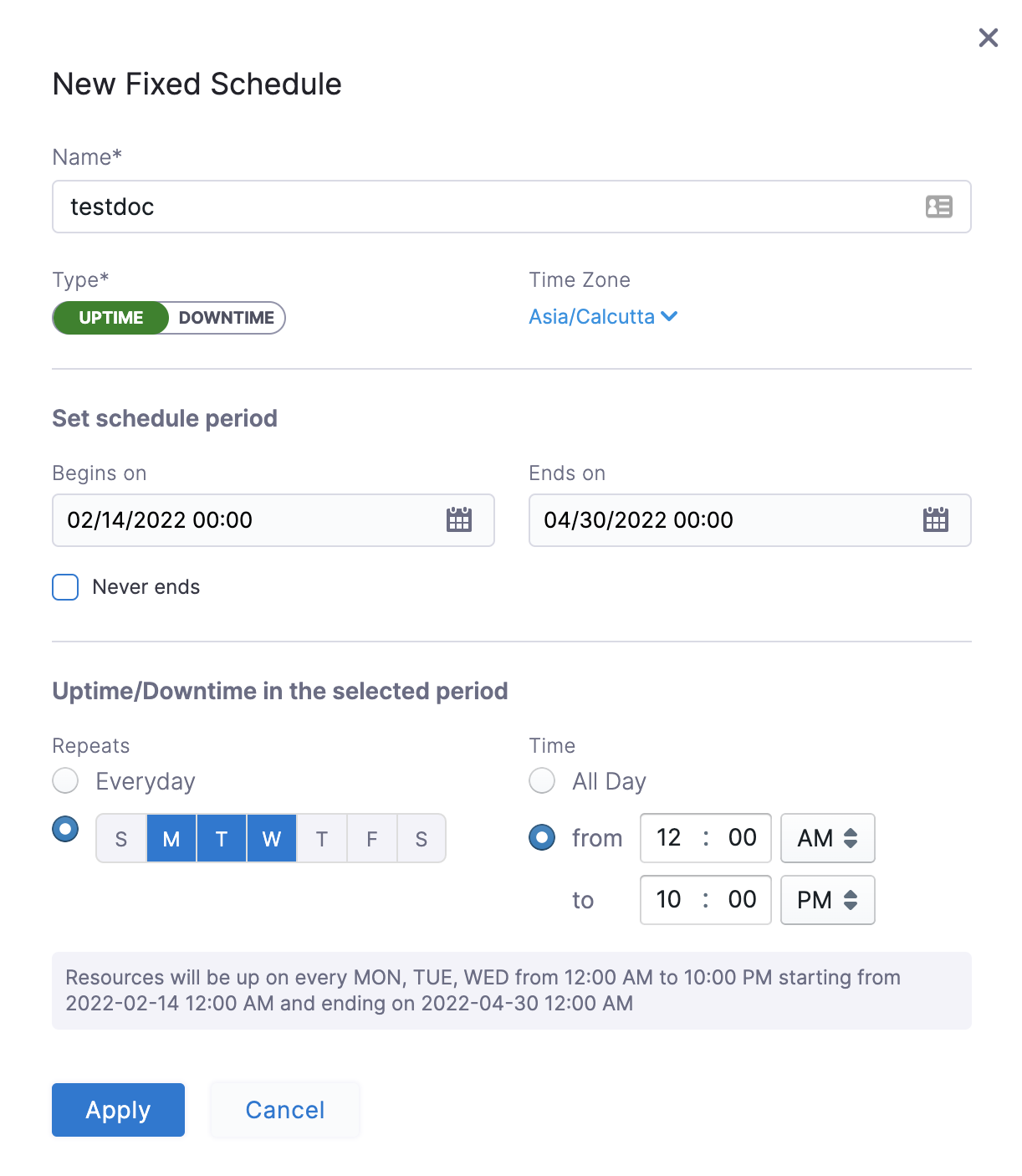
Example 2:
In the following example, resources are down every day (all day) starting from 12:00 a.m. on February 14, 2022 till April 30, at 12:00 a.m.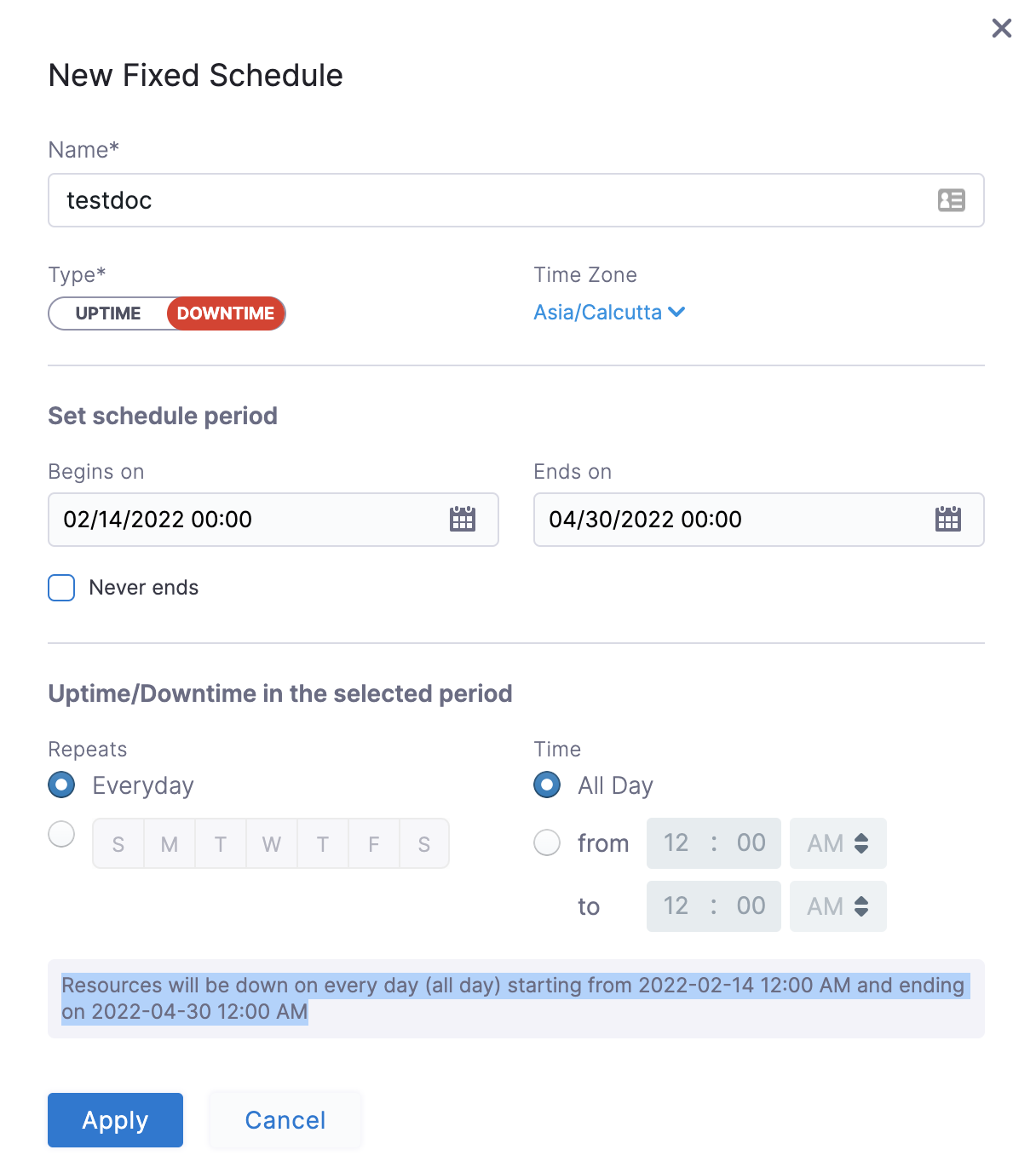
Click Apply.
Set up access for GCE VM(s)
Now that you have the AutoStopping rule configured, define how you would want to access the underlying application running on the resources managed by this Rule. You can use any of the following methods:
- Set up Access for HTTP/HTTPS workload: If the underlying applications running on the resources managed by the AutoStopping Rule are accessed by an HTTP or HTTPS URL.
- Setup Access for TCP workload or SSH/RDP: If the underlying applications running on the resources managed by AutoStopping Rule are accessed via TCP, SSH or RDP.
Set up access for TCP workload or SSH/RDP
Setting up access for TCP workload or SSH/RDP allows AutoStopping to detect activity and idleness, and ensure that the database is up and running only when you need it. Use the AutoStopping Proxy URL (IP/Hostname of the Proxy and a unique autogenerated port number) for this AutoStopping Rule when you connect to the RDS database using any database client. The Proxy URL is generated when you save the AutoStopping Rule. If you need to access the resources managed by this AutoStopping rule using TCP or SSH/RDP HTTPS URL, you need to perform the following steps:
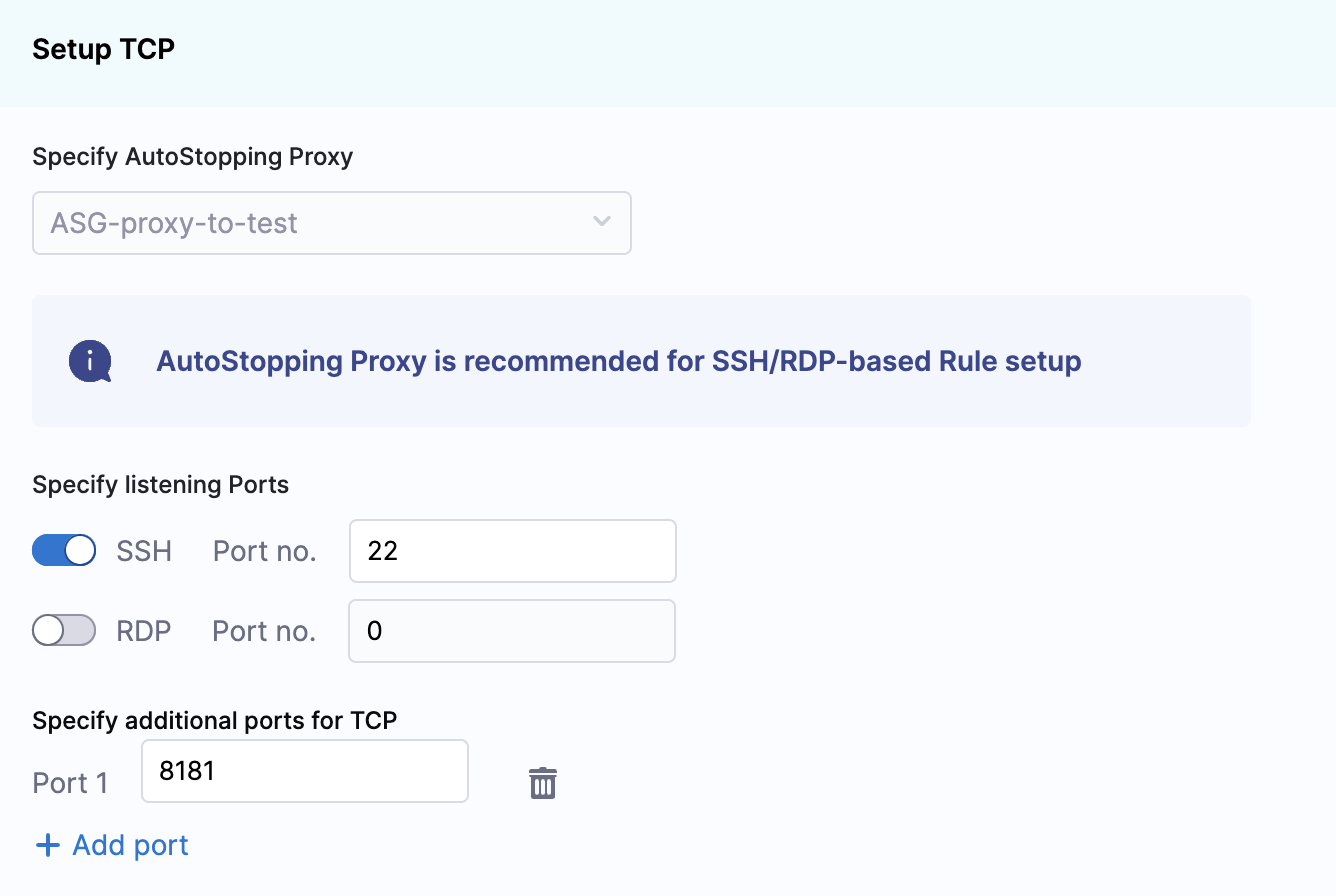
- Choose an AutoStopping Proxy load balancer from the Specify AutoStopping Proxy dropdown list to set up access.
- Toggle SSH or RDP to specify the listening ports. The port number is autopopulated.
- Specify the source port numbers and the target TCP ports your application is listening to. If the source port is not specified, a random port will be generated at the backend. This auto-generated port will continue to be used as long as the target port remains unchanged or unless the user explicitly modifies the source port.
- Click Next.
Set up access for HTTP/HTTPS workload
If you need to access the resources managed by this AutoStopping rule using an HTTP or HTTPS URL, you need to perform the following steps:
If you have not created an AutoStopping proxy load balancer already, go to Create an AutoStopping Proxy load balancer.
You can use the same proxy load balancer for more than one rule managing resources (VMs, ASG) within the same VPC.
Enter Routing Configuration and Health Check Details
- If the security groups are configured for the selected instances, then the routing information is autopopulated for those instances.
You can edit or delete the routing information. However, it is mandatory to have at least one port listed. For more information, see Listeners.
This is the load balancer routing configuration for the underlying application that is running on the cloud resources managed by this AutoStopping rule.
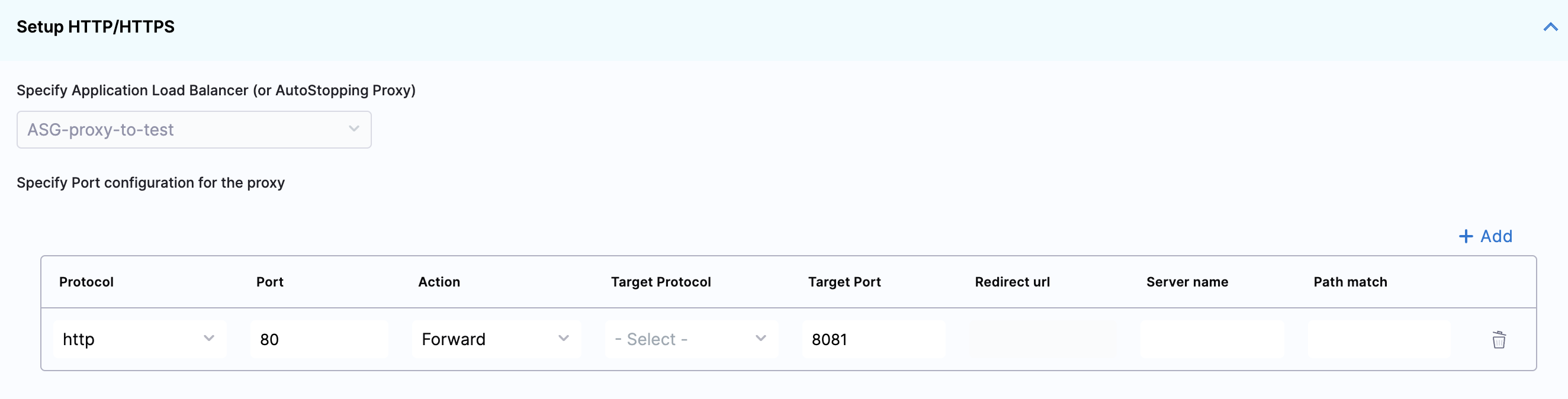
- Click Add if you need to add more ports. The following are some points to consider:
- If you are forwarding the same action to different ports, then specify the server name and/or path match.
- If you specify the server name, then the host uses the custom URL to access the resources. You cannot use an auto-generated URL to access the resources.
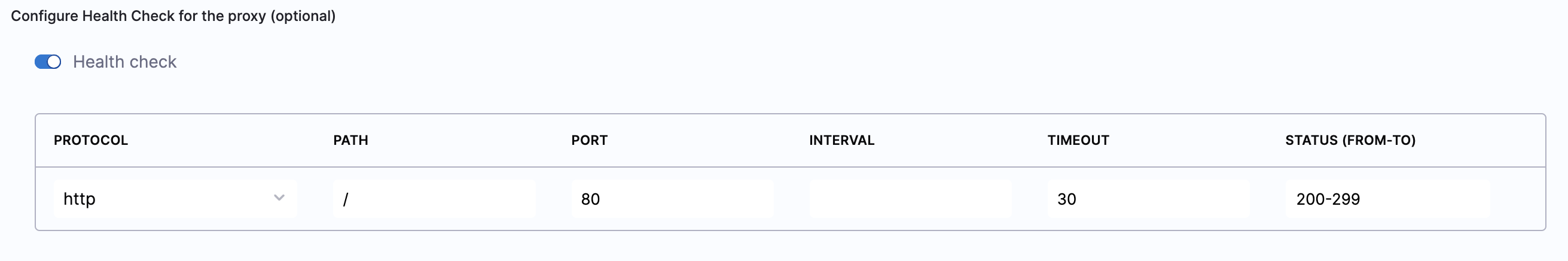
Toggle the Health check button to configure the health check. Health check status should be successful for the AutoStopping rules to come into effect. Set a health check for the underlying application that is running on the cloud resources managed by this AutoStopping rule. The load balancer periodically sends requests as per the settings below to the application. If your application does not support health check, or you do not have any application running, you can disable the health check.
By default, the health check is turned on.
In Protocol, select http or https.
Enter Path, port, and timeout details. For example, if you have configured port 80 and the timeout as 30 seconds for your instance, then the AutoStopping rule checks these specified parameters before bringing AutoStopping Rule into effect.
Specify the URL to access the resources
You can use either of the following methods:
- Auto-generated URL
- Custom URL
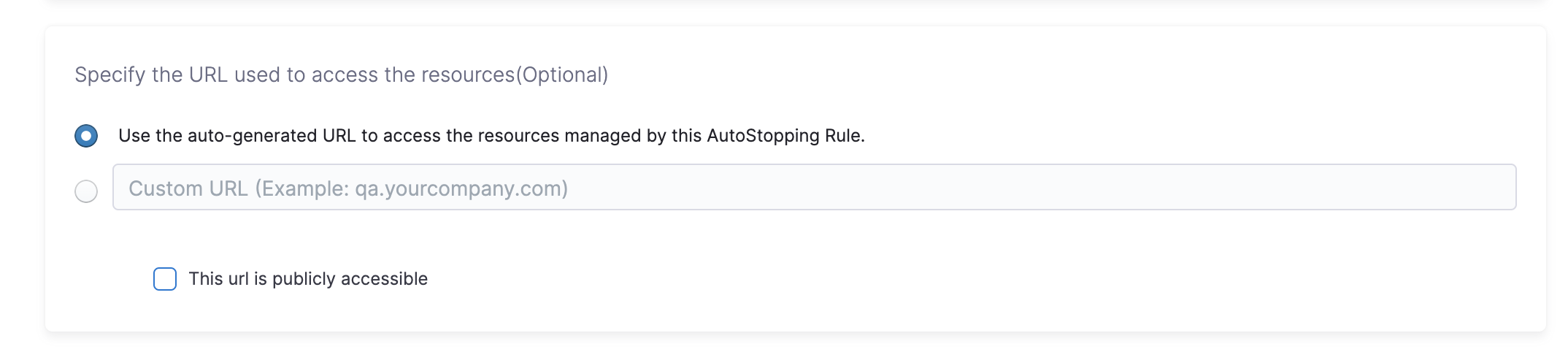
Auto-generated URL
Every AutoStopping rule has an auto-generated URL. This URL is a subdomain to the domain name specified for the load balancer. Since the load balancer configures a wildcard domain such as *.autostopping.yourcompany.com, the auto-generated URL works automatically and points to the correct load balancer.
Select Use the auto-generated URL to access the resources managed by this AutoStopping Rule.
Custom URL
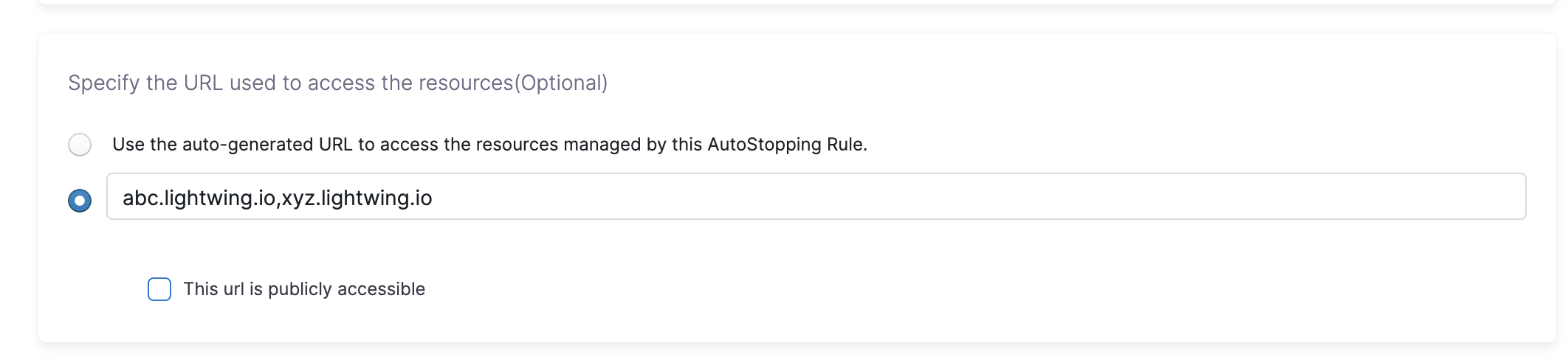
AutoStopping rule can use multiple custom domains. In such a case, it should be configured in the DNS provider. AutoStopping Rules also allows you to use custom domains or change the root of your site's URL from the default, like,autostop.harness.io, to any domain you own. To point your site's default domain to a custom domain, you can set it up in your DNS provider.
Enter the custom URL currently used to access the instances. The domain name should be entered without prefixing the scheme. A rule can have multiple URLs. You can enter comma-separated values into a custom URL to support multiple URLs.
Use the Harness CLI to access resources through SSH/RDP
SSH/RDP allows you to access the resources managed by the AutoStopping rule via SSH or RDP HTTPS URL. Select this option if the underlying applications running on the resources managed by AutoStopping Rule are accessed via SSH or RDP.
In Setup Access, select SSH/RDP.
Select your operating system to download the Harness CLI for your system.
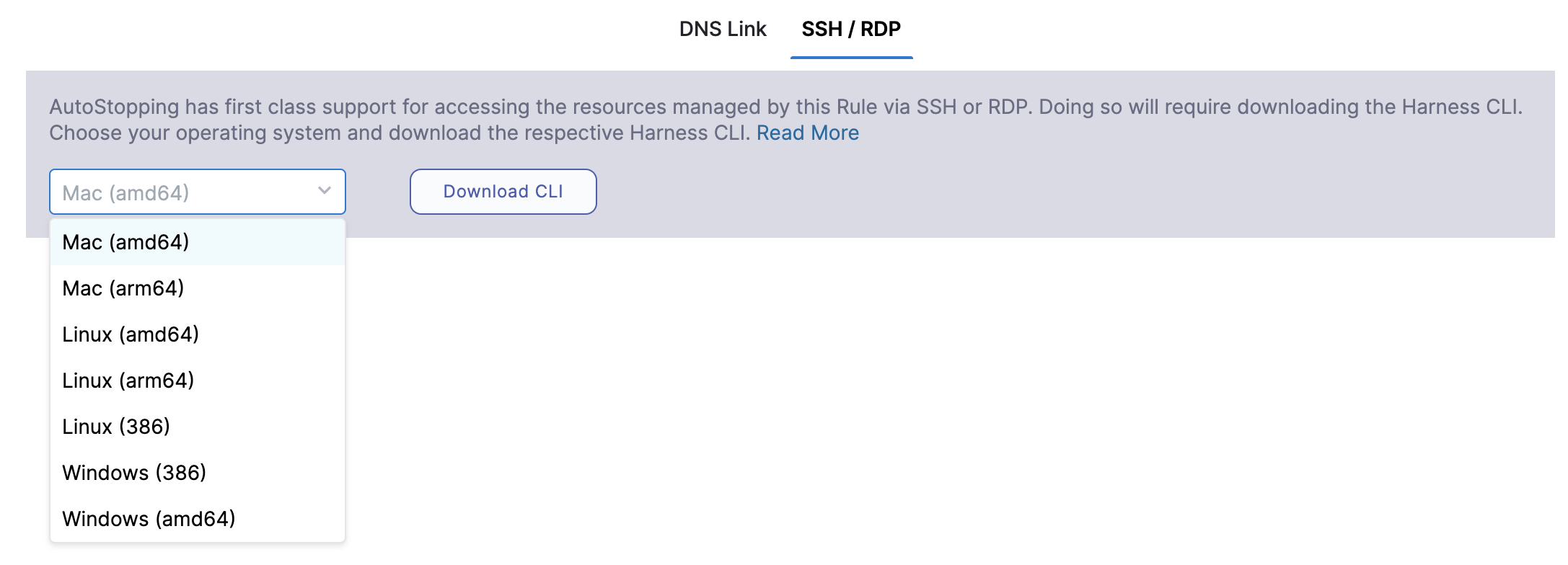
Click Download CLI.
You can connect using SSH or RDP.
SSH commands
To connect to remote servers via SSH/RDP, such as PuTTY, use the Harness CLI connect command. The connect command opens a proxy connection in your machine which can be used from other applications.
harness connect --host hostname --port <ssh/rdp port>
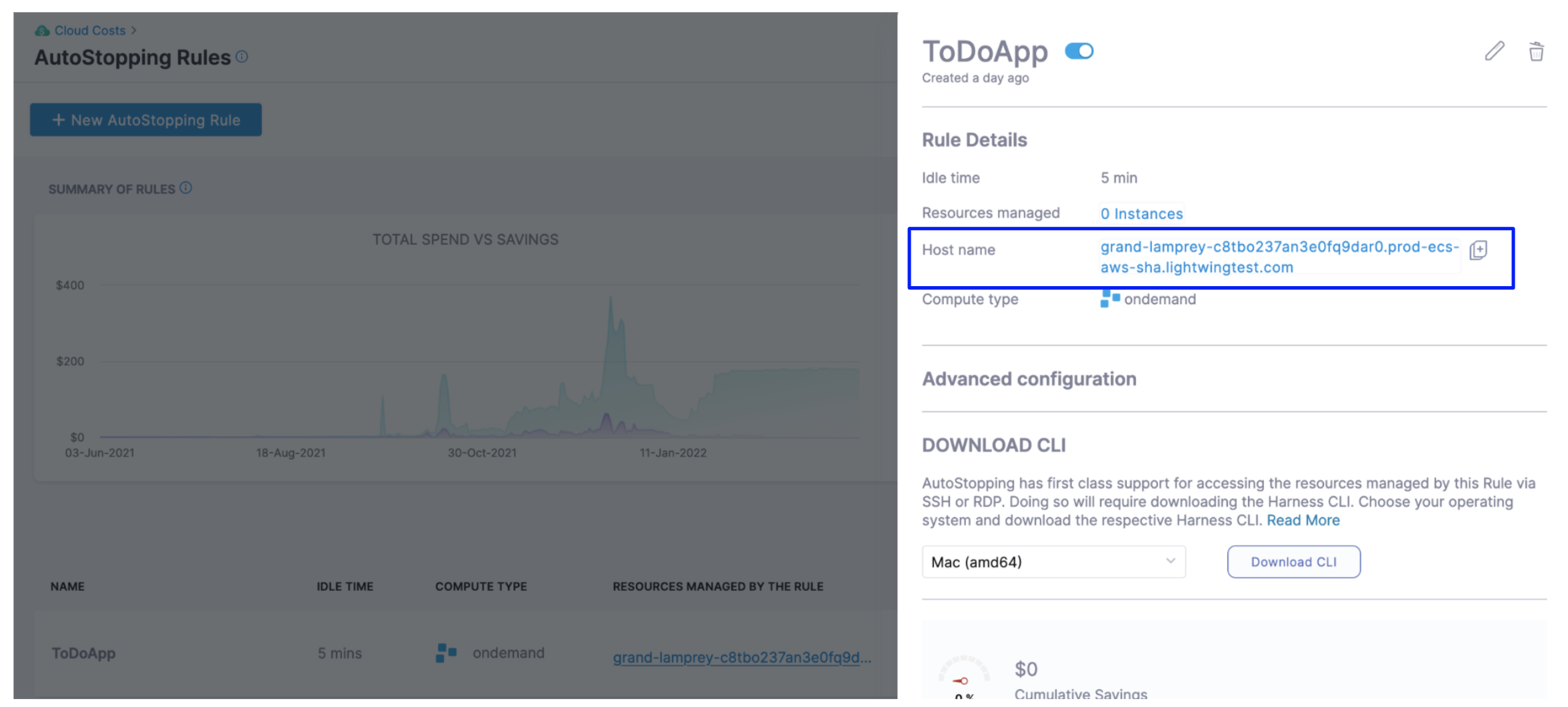
You can simply copy the hostname from the AutoStopping Rule dashboard view. Click on the AutoStopping Rule that you want to connect and copy the hostname.
For example:
harness connect --host default-test-ssh-1.abc1000test.lightwingtest.com --port 22 -- -i ~/.ssh/ry-jupyter.pem
Here is the output:
Proxy listening details:
Rule name: Test SSH 1
Listen address: 127.0.0.1
Port forwarding: 14527 => 22
Protocol: tcp
Started at: 2021-05-19 21:53:38.320943 +0530 IST m=+48.950643931
Harness connect created a secure tunnel from your computer to the given port after bringing up the VM. Now open the RDP/SSH client and use the hostname and port information provided above to connect.
harness ssh --host default-test-ssh-1.abc1000test.lightwingtest.com --user ubuntu --config lwc.toml -- -i ~/.ssh/ry-jupyter.pem
RDP commands
For RDP run the following command:
harness rdp --host default-test-rdp-1.abc1000test.lightwingtest.com
Run the following command to connect via private IP:
harness rdp --host default-test-rdp-1.abc1000test.lightwingtest.com --internal-ip
- Click Next.
Review
In Review, verify all the configuration details and click Save Rule. To edit any of the configuration settings, click EDIT and modify the settings.
Your AutoStopping rule is listed under the AutoStopping Rules summary page.
Set up access for Kubernetes clusters
For more information on setting up access for Kubernetes clusters, see Create AutoStopping Rules for a Kubernetes Cluster.