Use Drone plugins
Drone plugins are Docker containers that perform predefined tasks. You can use the Plugin step to run plugins from the Drone Plugins Marketplace in your Harness CI pipelines. You can also write your own custom plugins. For more information about plugins, go to Explore plugins.
This topic assumes you're familiar with pipeline creation. If you haven't created a pipeline before, try one of the CI tutorials.
About Drone
Drone was acquired by Harness in 2020 and is part of Harness CI.
For more information on the acquisition of Drone, go to the following blog posts:
Add a plugin to a Harness CI pipeline
To demonstrate how to add a Drone plugin to a Harness CI pipeline, these steps use the Download plugin as an example. This plugin downloads an archive to the stage workspace.
- Visual
- YAML
Add the Plugin step to the Build stage of your CI pipeline, and configure the settings as follows:
- Name: Enter a name for the step.
- Description: Optional description.
- Container Registry: Select a Docker connector.
- Image: Enter the plugin's Docker image, such as
plugins/download. You can find this on the plugin's page on the Drone Plugins Marketplace. - Settings: Enter key-value pairs representing plugin settings. You can find this on the plugin's page on the Drone Plugins Marketplace or in the plugin's README.
- For information about other settings, go to the Plugin step settings reference.
The following screenshot shows a Plugin step configured for the Download plugin.
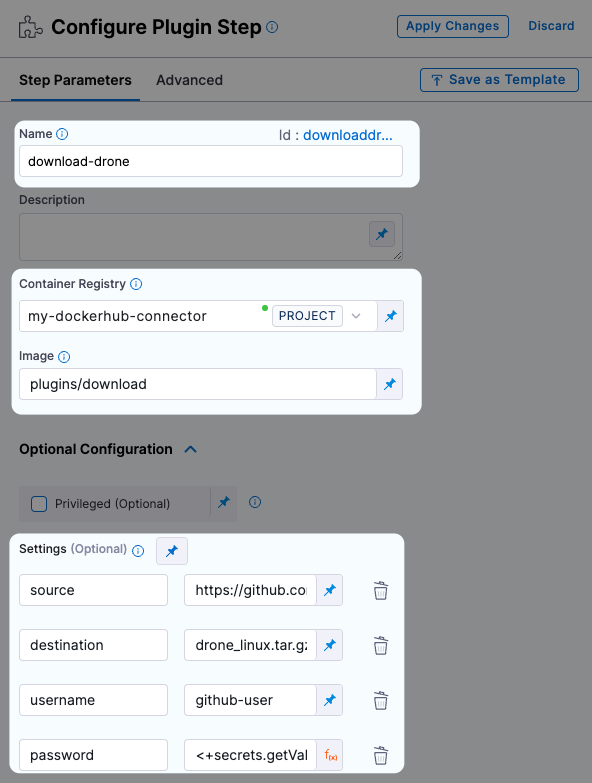
Add the Plugin step to your CI stage with the following settings:
type: Pluginname:A name for the stepconnectorRef:The ID of a Docker connector.image:The plugin's Docker image, such asplugins/download. You can find this on the plugin's page on the Drone Plugins Marketplace.settings:A mapping of key-value pairs representing plugin settings. You can find this on the plugin's page on the Drone Plugins Marketplace or in the plugin's README.- For information about other settings, go to the Plugin step settings reference.
The following examples show the YAML definition for a Plugin step configured for the Download plugin.
- Download Drone tarball
- Download AWS CLI
This example downloads the Drone Linux amd64 tarball. It provides a username and password for authentication to GitHub.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: drone plugin
identifier: drone_plugin
spec:
connectorRef: account.docker
image: plugins/download
settings:
source: https://github.com/drone/drone-cli/releases/download/v0.8.5/drone_linux_amd64.tar.gz ## Target to download
username: my-username ## Username for authentication to the source
password: `<+secrets.getValue("mygithubpersonalaccesstoken")>` ## Password for authentication to the source
This example downloads the AWS CLI for Linux and saves it to the default stage workspace directory under the name awscli.zip. Because the target is publicly accessible, authentication settings aren't required.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: drone plugin
identifier: drone_plugin
spec:
connectorRef: account.docker
image: plugins/download
settings:
source: https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip ## Target to download
destination: awscli.zip ## File name to assign the downloaded file.
Expanding on this example, you could use the following commands in a subsequent Run step to unzip and install this tool:
unzip awscli.zip
sudo ./aws/install
You could also write a custom plugin that downloads, unzips, and installs the AWS CLI in one step.
You can use variable expressions for Settings values, such as credentials: <+stage.variables.[TOKEN_SECRET]>, which uses a stage variable.
Create text secrets for sensitive information, such as passwords and tokens, required by the plugin.
When you run the pipeline, check the log output to verify that the plugin works as intended.
Plugin settings
For information about a plugin's settings, go to the plugin's page on the Drone Plugins Marketplace. In addition to the settings described on a plugin's Marketplace page, each plugin has a README where you can read about the plugin's settings in detail. The README can include additional or uncommon settings that aren't described on the Marketplace page or the Harness CI documentation. You can find README links at the top of each plugin's Marketplace page.
Output variables
For information about output variables produced by plugins, refer to Output variables in the Plugin step settings reference.
Plugin configuration examples
Here are some YAML examples and additional information about specific Drone plugins.
Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin
Use the artifact-metadata-publisher plugin to publish a URL of an artifact file to the Artifacts tab.
An example of the Plugin step configuration is provided below; however your pipeline must also include steps to upload the file that you want to link to on the Artifacts tab, as demonstrated in the Publish any URL to the Artifacts tab tutorial.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: metadata publisher plugin
identifier: metadata_publisher_plugin
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage ## A Docker connector ID
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/.../index.html ## URL for the storage location where the data file is located.
artifact_file: artifact.txt ## The name of the artifact file
GitHub Actions plugin
- With Harness Cloud build infrastructure, use the GitHub Action plugin step.
- With other build infrastructures, use the GitHub Actions Drone plugin in a Plugin step.
Jira plugin
Slack plugin
Harness has built-in notifications for email, Microsoft Teams, and Slack.
Convert Drone YAML to Harness YAML
The YAML examples in the Drone Plugins Marketplace can help you configure settings for a Plugin step in Harness CI. Many plugins offer both Harness and standalone Drone YAML samples, as indicated by the Drone/Harness toggle in the Example section.
Because Drone plugins can be used outside Harness CI, there are some differences, as explained below, in the YAML format when using Drone plugins in Harness CI versus outside Harness CI. This information focuses on the step YAML definition.
Step structure
The following examples compare the YAML structure for a step when a Drone plugin is used in a Drone pipeline and a Harness CI pipeline.
- Drone YAML
- Harness YAML
steps:
- name: download ## Step name
image: plugins/download ## Plugin's Docker image
settings: ## Plugin settings
source: https://github.com/drone/drone-cli/releases/download/v0.8.5/drone_linux_amd64.tar.gz
steps:
- step:
type: Plugin ## Indicates that this is a Plugin step.
name: drone plugin ## Step name
identifier: drone_plugin ## Step ID
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage ## Docker connector to pull the plugin's Docker image
image: plugins/download ## Plugin's Docker image
settings: ## Plugin settings
source: https://github.com/drone/drone-cli/releases/download/v0.8.5/drone_linux_amd64.tar.gz
Listed and nested settings
To convert list-formatted settings from Drone Plugin YAML to Harness CI YAML, merge them with comma separation.
- Drone YAML
- Harness YAML
Settings:
tags:
- latest
- '1.0.1'
- '1.0'
settings:
tags: latest,1.0.1,1.0
For nested settings, maintain key-value pair definitions, as shown in the following Harness CI YAML example:
settings:
mynestedsetting:
nextlevel:
varname: 100
mylistsetting:
- itemone
- itemtwo
It's often easier to define complex settings in the Harness Pipeline Studio's YAML editor, rather than the Visual editor.

Text secrets
The following snippets illustrate the different ways that Drone and Harness CI handle text secrets.
- Drone YAML
- Harness YAML
steps:
- name: download
image: plugins/download
settings:
username:
from_secret: username
password:
from_secret: password
source: https://github.com/drone/drone-cli/releases/download/v0.8.5/drone_linux_amd64.tar.gz
- step:
type: Plugin
name: download-drone
identifier: downloaddrone
spec:
connectorRef: mygithubconnector
image: plugins/download
privileged: false
settings:
username: <+secrets.getValue("myusernamesecret")>
password: <+secrets.getValue("mypasswordsecret")>
source: https://github.com/drone/drone-cli/releases/download/v0.8.5/drone_linux_amd64.tar.gz