Provision using CloudFormation Create Stack
This content is for Harness FirstGen. Switch to NextGen.This topic describes how to provision infrastructure using the Workflow CloudFormation Create Stack step.
Once you have created a CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner and added it to a Harness Infrastructure Definition, you add that Infrastructure Definition to a Workflow.
Next, you use the CloudFormation Create Stack step in that Workflow to run the same CloudFormation template added in the Infrastructure Provisioner.
During Workflow pre-deployment, the CloudFormation Create Stack step provisions the target infrastructure.
Next, during Workflow deployment, the Workflow deploys to the provisioned infrastructure as defined in its Infrastructure Provisioner.
Before You Begin
Ensure you have read the following topics before you add the CloudFormation Create Stack step to a Workflow:
- CloudFormation Provisioning with Harness
- Set Up Your Harness Account for CloudFormation
- Add CloudFormation Templates
- Map CloudFormation Infrastructure
Important Notes
- AWS Services Supported: Harness supports first class CloudFormation provisioning for AWS-based infrastructures:
- SSH
- AMI/Auto Scaling Group
- ECS
- Lambda
- Deployment Strategies Supported: For most deployments, Harness Infrastructure Provisioners are only supported in Canary and Multi-Service types. For AMI/ASG and ECS deployments, Infrastructure Provisioners are also supported in Blue/Green deployments.
- Control stack deployment wait time:
Currently, this feature is behind the Feature FlagCLOUDFORMATION_SKIP_WAIT_FOR_RESOURCES. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.- By default, Harness waits for 30 seconds after a successful stack deployment to ensure that resources have come up.
- You can can remove this wait time by enabling the Feature Flag
CLOUDFORMATION_SKIP_WAIT_FOR_RESOURCES. - If
CLOUDFORMATION_SKIP_WAIT_FOR_RESOURCESis enabled and you still want to have a waiting condition, use the AWS CreationPolicy attribute.
Where can I use CloudFormation Create Stack?
CloudFormation Create Stack can be used to provision infrastructure or for ad hoc provisioning.
When used in the Pre-deployment steps of a Workflow, the CloudFormation Create Stack provisions infrastructure that can be rolled back in the Workflow fails.
When used outside of the Pre-deployment steps of a Workflow, the CloudFormation Create Stack step does not participate in Workflow rollback. Only use the CloudFormation Create Stack step outside of the Pre-deployment steps of a Workflow for ad hoc provisioning.
To delete the ad hoc provisioned infrastructure in the case of a Workflow failure, add the CloudFormation Delete Stack to the Workflow Rollback Steps section. See Remove Provisioned Infra with CloudFormation Delete Stack.
Visual Summary
This topic describes steps 4 through 6 in the Harness CloudFormation Provisioning implementation process:
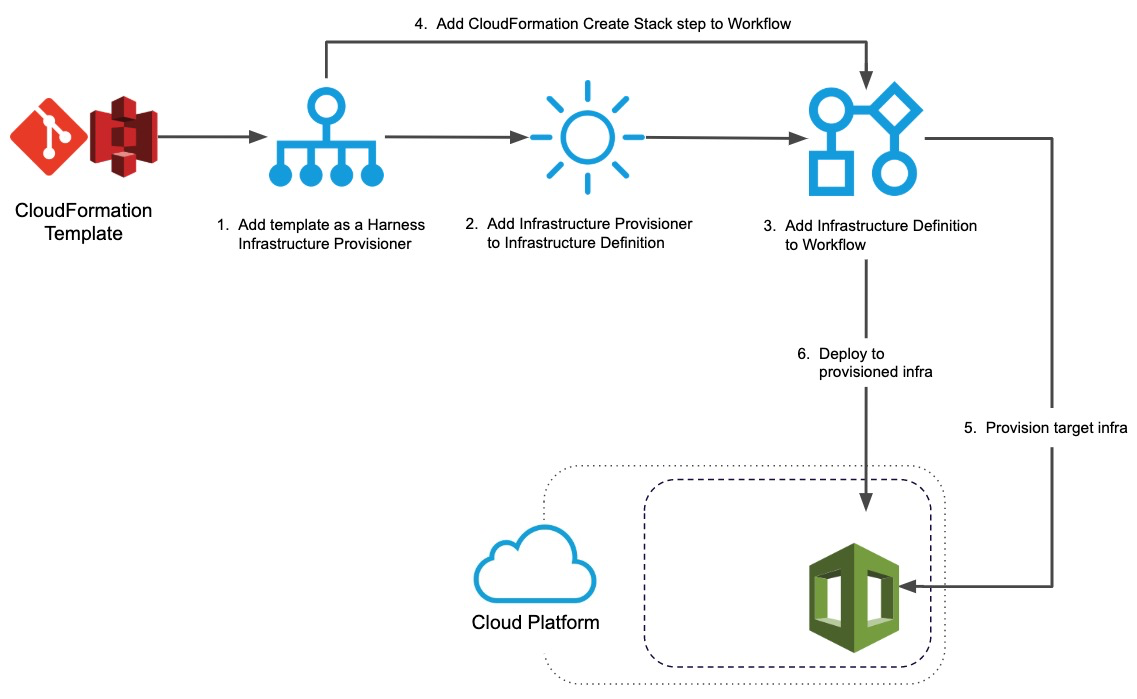
For step 1, see Add CloudFormation Templates. For step 2, see Map CloudFormation Infrastructure.
Here is an illustration using a deployment:
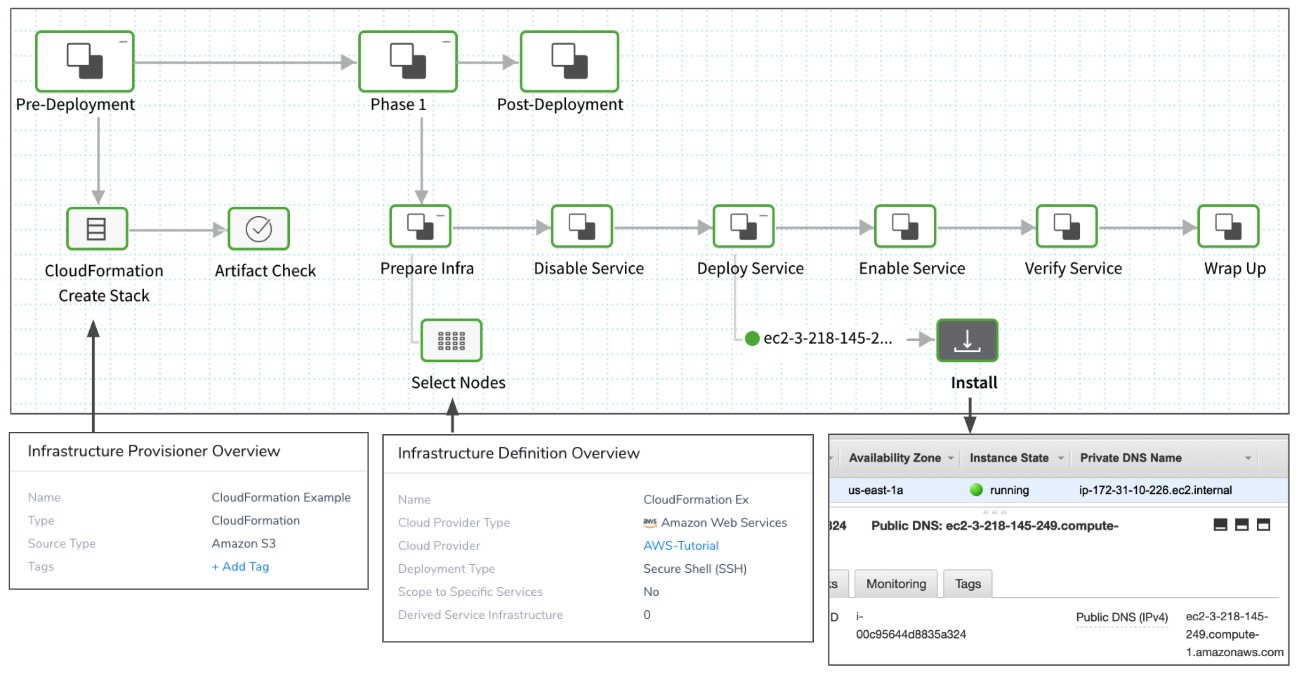
- The CloudFormation Create Stack step executes pre-deployment to build the infrastructure.
- The Infrastructure Definition is used to select the provisioned nodes.
- The app is installed on the provisioned node.
Step 1: Add Environment to Workflow
To use a CloudFormation Provisioner in your Workflow, do the following:
- In your Harness Application, click Workflows.
- Click Add Workflow. The Workflow dialog appears.
- Enter a name and description for the Workflow.
- In Workflow Type, select Canary.note
For most deployments, Harness Infrastructure Provisioners are only supported in Canary and Multi-Service types. For AMI deployments, Infrastructure Provisioners are also supported in Blue/Green deployments.
- In Environment, select the Environment that has the CloudFormation Provisioner set up in its Infrastructure Definitions.
- Click SUBMIT. The new Workflow is created.
By default, the Workflow includes a Pre-deployment Steps section. This is where you will add a step that uses your CloudFormation Provisioner.
Step 2: Add CloudFormation Create Stack Step to Pre-deployment Steps
In this step you will use the CloudFormation Create Stack step to select the same CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner you used in the Workflow Infrastructure Definition.
The CloudFormation Create Stack step will provision using the template in the CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner.
The CloudFormation Create Stack step is basically the same as the aws cloudformation create-stack command.
The CloudFormation Create Stack step provisions your target infrastructure, and so it is added to the Pre-deployment steps in the Canary Workflow.
To add the CloudFormation Create Stack step, do the following:
In your Workflow, in Pre-deployment Steps, click Add Step.
Select CloudFormation Create Stack, and click Next.
In Provisioner, select the same Harness CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner you used in the Infrastructure Definition of this Workflow.
In AWS Cloud Provider, typically, you will select the same Cloud Provider you used when setting up the Infrastructure Definition used by this Workflow.
noteYou need to select an AWS Cloud Provider even if the CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner you selected uses a manually-entered template body. Harness needs access to the AWS API for CloudFormation via the credentials in the AWS Cloud Provider. Ensure that the AWS Cloud Provider has the credentials described in Set Up Your Harness Account for CloudFormation.
In Region, select the region where you will be provisioning your resources.
You can use a Harness variable expression in the Region setting, such as a Workflow variable. This allows you to select the AWS region for the provisioning when you deploy your Workflow.noteCurrently, expressions in the Region setting is in Beta and behind a Feature Flag. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature. Feature Flags can only be removed for Harness Professional and Essentials editions. Once the feature is released to a general audience, it is available for Trial and Community Editions.
To name your stack, select Use Custom Stack Name and enter a name for your stack. If you do not select this option, Harness will automatically generate a unique name for your stack prefixed with
HarnessStackand the ID for your Harness Environment, such asHarnessStack-7HklGe0N6AvviJmZ.
If you plan on using the CloudFormation Delete Stack step later in this Workflow, it is a good idea to name your stack.In Role ARN, enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an AWS IAM role that CloudFormation assumes to create the stack. If you don't specify a value, Harness uses the credentials you provided via AWS Cloud Provider. This allows you to tune the step for provisioning a specific AWS resource. For example, if you will only provision AWS S3, then you can use a role that is limited to S3.
You can also use Harness variable expressions in Role ARN. For example, you can create a Service or Workflow variable and then enter its expression in Role ARN, such as${serviceVariables.roleARN}or${workflow.variables.roleArn}.To acknowledge the capabilities in the CloudFormation template, enable Specify Capabilities.
This acknowledges that the template contains certain capabilities (for example,CAPABILITY_AUTO_EXPAND), giving AWS CloudFormation the specified capabilities before it creates the stack. This is the same as using the--capabilitiesoption in theaws cloudformation create-stackCLI command. See create-stack.
In Capabilities, select one or more of the capabilities from the spec.To add CloudFormation Tags, enable Add CloudFormation Tags.
Enter the tags in JSON format only (lowercase is required):
```
[{
"key": "string",
"value": "string"
},{
"key": "string",
"value": "string"
}]
```
The tags you add here are applied to all of the resources in the stack. AWS has a limit of 50 unique tags for each stack.
You can use Harness variable expressions in the keys and values. See Built-in Variables List and Set Workflow Variables.
In Skip based on Stack Status, you can add the stack states that will not prevent provisioning.
noteHarness checks if the stack is in ROLLBACK_COMPLETE state before the deployment. If present, Harness deletes the stack and then triggers the deployment.
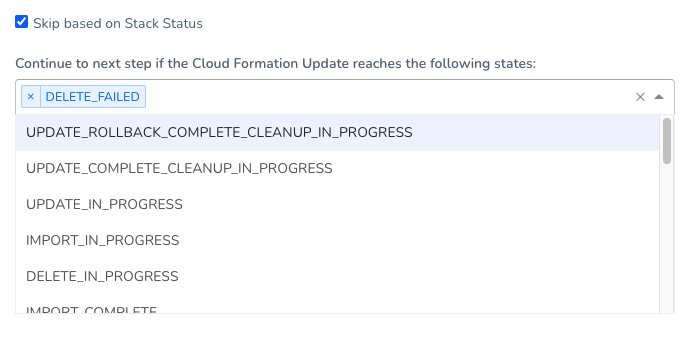
In Timeout, enter how long Harness should wait for the successful CloudFormation Provisioner set up before failing the Workflow.
Click Next. The Input Values settings appear.
Option 1: Enter Input Values from Parameter Files
You can use CloudFormation parameters files to specify input parameters for the stack.
This is the same as using the AWS CloudFormation CLI create-stack option --parameters and a JSON parameters file:
aws cloudformation create-stack --stackname startmyinstance
--template-body file:///some/local/path/templates/startmyinstance.json
--parameters https://your-bucket-name.s3.amazonaws.com/params/startmyinstance-parameters.json
Where the JSON file contains these parameters:
[
{
"ParameterKey": "KeyPairName",
"ParameterValue": "MyKey"
},
{
"ParameterKey": "InstanceType",
"ParameterValue": "m1.micro"
}
]
Use a CloudFormation Parameter File
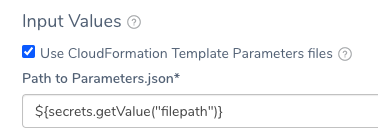
- In Input Values, select Use CloudFormation Template Parameters files.
- In Path to Parameters.json, enter the path to the parameter file.
Source Types
Parameter files can be used with git repo and AWS S3 source types. See Add CloudFormation Templates.
Git-based Parameter Files
Enter the full path to the file.
For Git-based parameter files, the path entered is relative to the URL setting of the Source Repo Provider used by the CloudFormation Provisioner.
For example, the CloudFormation Provisioner you select in Provisioner uses a Source Repo Provider with a URL setting of https://github.com/account-name/cf-files.
In the cf-files repo folder there is a file named parameters.json. So, in Path to Parameters.json, you would simply enter parameters.json.
Encrypted Text Secrets
Use can use Harness encrypted text secrets in Path to Parameters.json. See Use Encrypted Text Secrets.
Multiple Parameter Files
You can enter paths to single and multiple files. Separate multiple files using commas:
https://my-bucket.s3.amazonaws.com/parameters1.json,https://my-bucket.s3.amazonaws.com/parameters3.json
Workflow Variable Expressions in Paths
You can use Harness Workflow variables in Path to Parameters.json.
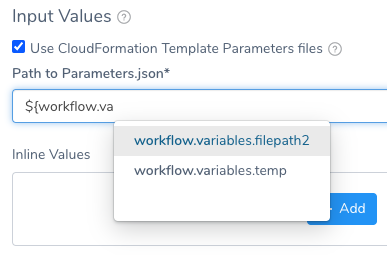
When the Workflow is deployed, by itself, in a Pipeline, or in a Trigger, you will provide values for the Workflow variables. This allows you to templatize the path.
See Set Workflow Variables and Templatize a Workflow.
Workflow Variable Expressions in Files
You can use Harness builtin and Workflow variables in the parameter values inside the parameter file. Harness will replace the variables when it executes the Pre-deployment Steps section.
For example:
[
{
"ParameterKey": "KeyPairName",
"ParameterValue": "${workflow.variables.KeyPairNameValue}"
},
{
"ParameterKey": "InstanceType",
"ParameterValue": "${workflow.variables.InstanceTypeValue}"
}
]
Use Parameters Files and Inline Values Together
You can use Use CloudFormation Template Parameters files and Inline Values together. Inline Values override parameter file values.
Option 2: Enter Inline Input Values
The Input Values are automatically populated with the same variables from the CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner Variables section, as described in Add CloudFormation Templates.
Enter or select a value for each variable in Input Values. For encrypted text values, select an Encrypted Text secret from Harness Secrets Management.
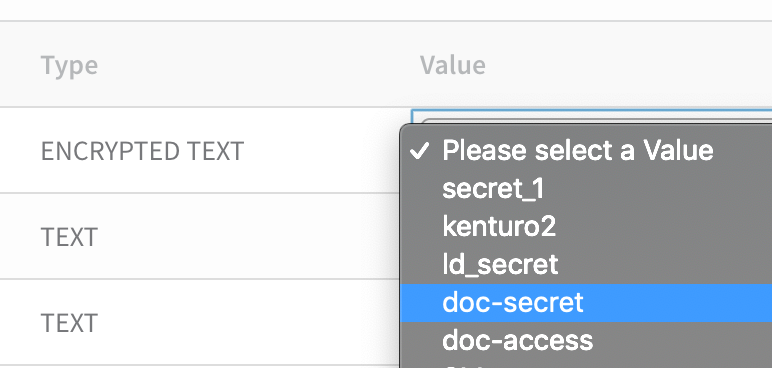
For more information, see Use Encrypted Text Secrets.
Click Submit. The CloudFormation Create Stack step is added to your Workflow.

Now your Workflow is set up to provision an infrastructure using your CloudFormation template in the CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner, and then deploy to the provisioned infrastructure.
Step 3: Add Infrastructure Definition to Phases
Now that the Workflow Pre-deployment section has your CloudFormation Create Stack step added, you need to add the target Infrastructure Definition where the Workflow will deploy.
This is the same Infrastructure Definition where you mapped your CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner outputs, as described in Map CloudFormation Infrastructure.
For Canary Workflows, Infrastructure Definitions are added in Phases, in the Deployment Phases section.
In the Deployment Phases section, click Add Phase. The Workflow Phase settings appear.
In Service, select the Harness Service to deploy.
In Infrastructure Definition, select the target Infrastructure Definition where the Workflow will deploy. This is the same Infrastructure Definition where you mapped your CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner outputs, as described in Map CloudFormation Infrastructure.
Here is an example: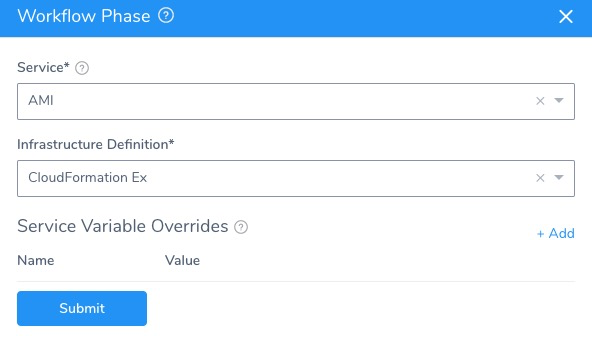
Click Submit. Use the same Infrastructure Definition for the remaining phases in your Canary Workflow.
Once you are done, your Workflow is ready to deploy.
Deployment Rollback
If you have successfully deployed CloudFormation resources and on the next deployment there is an error that initiates a rollback, Harness will roll back the provisioned infrastructure to the previous, successful version of the CloudFormation state.
Harness will not increment the serial in the state, but perform a hard rollback to the exact version of the state provided.
Harness determines what to rollback using a combination of the following Harness entities:
CloudFormation Infrastructure Provisioner + Environment
If you have templated these settings (using Workflow variables), Harness uses the values it obtains at runtime when it evaluates the template variables.
Next Steps
- The variables you use to map CloudFormation template outputs in an Infrastructure Definition can also be used in other Workflow commands. See Using CloudFormation Outputs in Workflow Steps.
- If you want to delete the stack as part of a Workflow, see Remove Provisioned Infra with CloudFormation Delete Stack.