Add Service Config Files
On the Services page, as a part of managing the Services you created, you can add Service Config Files that can be used throughout your configuration settings.
For information about how configuration files are used in a Kubernetes deployment, see Kubernetes Deployments Overview.
Before You Begin
- Read the Create an Application topic to get an overview of how Harness organizes Services.
- Read the Add a Service topic to understand the process to add a Service to an Application.
- Read Configuration as Code to see how you can quickly configure your Harness Service using your existing YAML in Git.
Limitations
Files must be 1MB or less.
All file types are supported.
Review: Required Permissions
Make sure you have the update permission on the Service before you try to add the Service Config File. See Managing Users and Groups (RBAC) for more information about assigning permissions.
Review: String and Base64 Options
Harness can encode your file as a string or Base64.
When selecting an option, consider the content of the file and which encoding method will work best.
Base64 encoding schemes are commonly used when there is a need to encode binary data (credentials are a common example), but they are also preferable when the file content contains special characters which cannot be parsed as a string.
If you try string encoding and receive an error like the following, try Base64:
Invalid values file. Error tokenizing YAML. Line 6, column 15: Found a mapping value where it is not allowed
Review: Use Base64 to Avoid New Lines
If you are going to use a Config File in a spec or manifest, be aware that ${configFile.getAsString()} can cause problems by adding new lines to your spec or manifest (unless you have formatted the file very carefully).
Instead, use ${configFile.getAsBase64()}. This will ensure that the contents of the file are rendered as a single line.
Step 1: Add Config Files
Files added in the Config Files section are referenced using the configFile.getAsString("fileName") Harness functor:
${configFile.getAsString("fileName")}– standard text string.${configFile.getAsBase64("fileName")}– Base64 encoded.
For example, let's add a Config Files file named config-file-example.txt.
You would reference this file in a Workflow that uses this Service like this:
${configFile.getAsString("config-file-example.txt")}
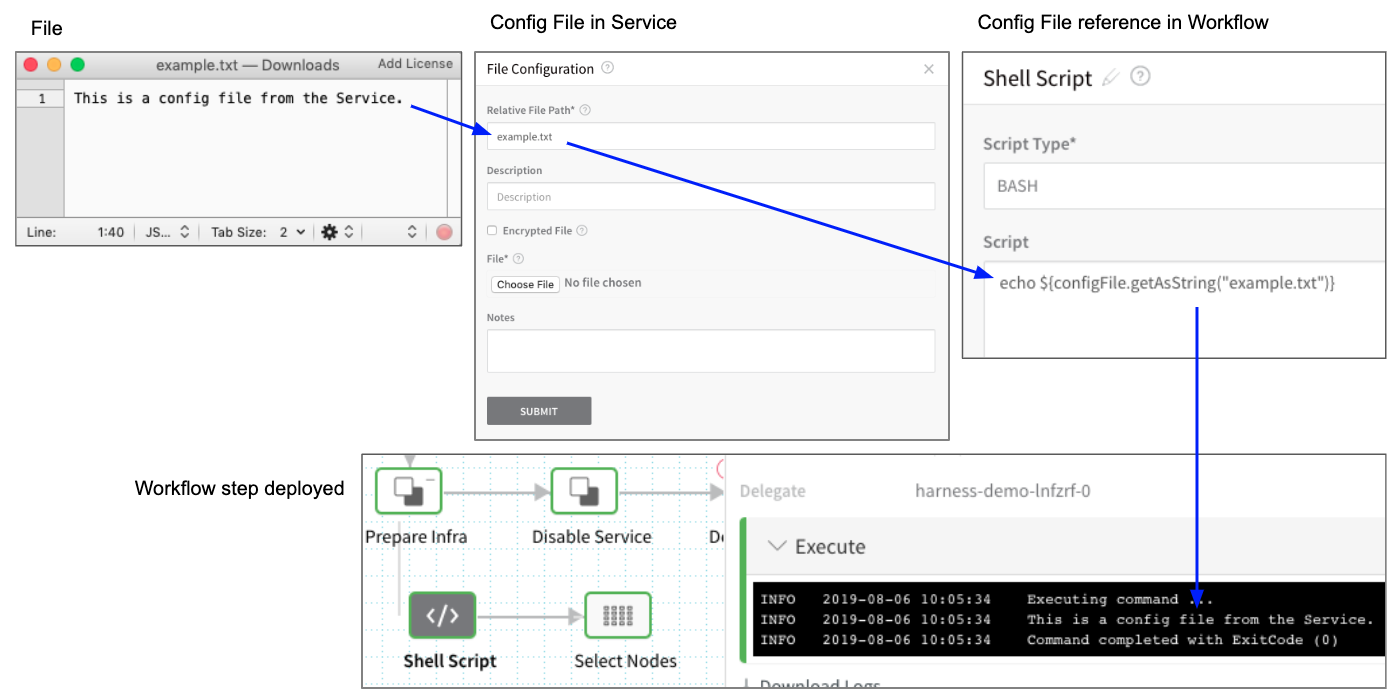
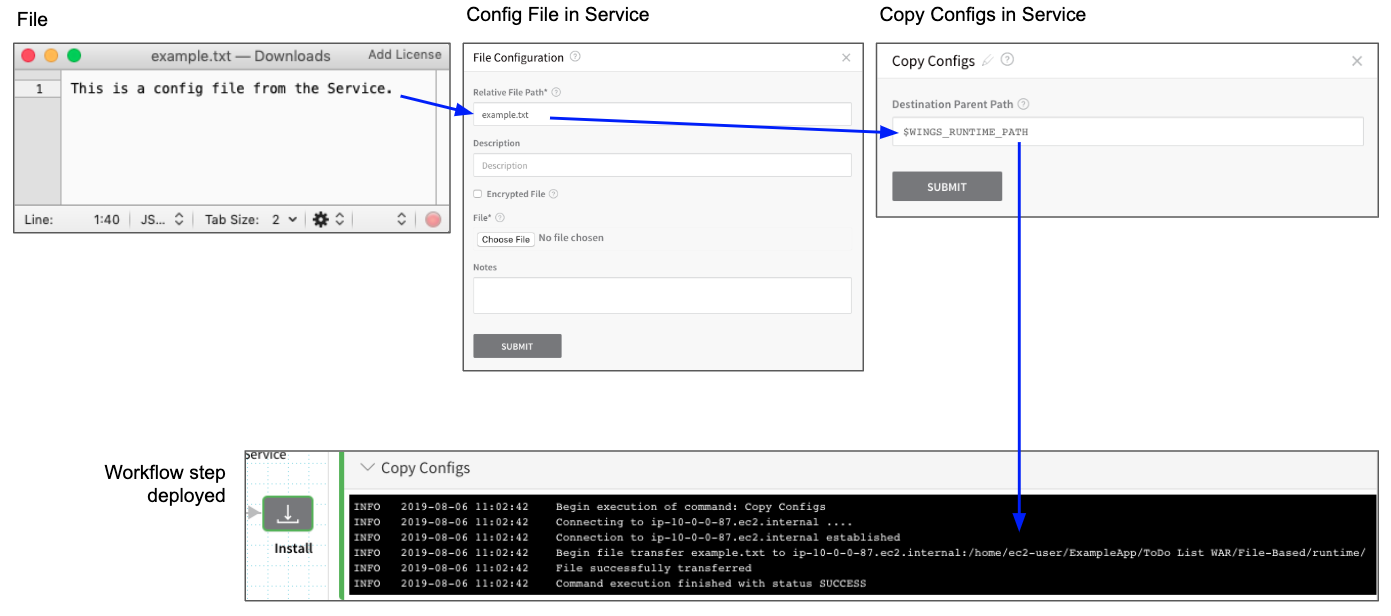
For example, here is an a config file named example.txt containing the string This is a config file from the Service added to a Service and then referenced in the Workflow that uses the Service. Finally, in the completed Workflow deployment, you can see the contents of the file output.
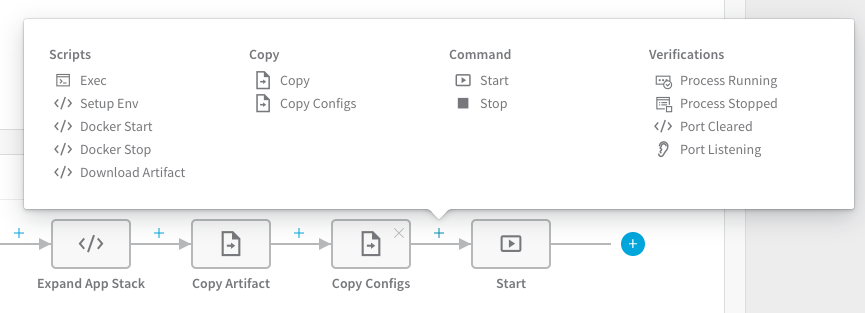
Step 2: Use Copy Configs Command
In most cases, use the Copy Configs command to copy the Config Files to your target hosts. You can add Copy Configs from the command menu in the Service:
In Copy Configs, you can change the location on the target host(s) where the files are added:
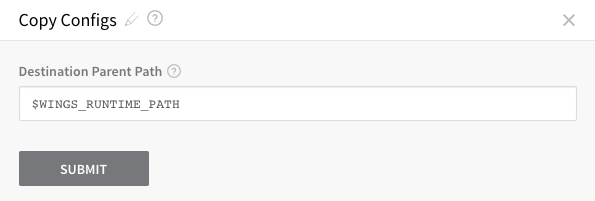
By default, it uses the Application Defaults path $WINGS_RUNTIME_PATH.
When the Workflow using this Service is deployed, the Copy Configs command copies the Service Config File to the target host:
Review: Use Config Files in Delegate Profiles
The ${configFile.getAsString("fileName")} and ${configFile.getAsBase64("fileName")} expressions are not supported in Delegate Profiles.
Instead, encode the file in base64 and then add the file to Harness as an Encrypted File Secret.
Next, in the Delegate Profile script, reference the secret, pipe it to base64 and output it to the path where you need it:
echo ${secrets.getValue("secret_name")} | base64 -d > /path/to/file
Notes
- If you sync your Harness Application as described in Harness Application-Level Git Sync, the Config Files are also synched to your remote repo.