Adding custom approval stages and steps
Currently, this feature is behind the feature flag NG_CUSTOM_APPROVAL. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
Custom approval stages and steps add control gates to your pipelines by allowing you to approve or reject a pipeline or stage at any point during build execution. When you add a Custom Approval step, you add a script to the step, and then use the script results as approval or rejection criteria.
You might use a Custom Approval stage and step, for example, if you have a custom shell script ticketing system or if you prefer to script your approvals.
Harness has first class support for Jira and ServiceNow approval stages and steps, and Harness has a built-in Manual approval stages and steps.
This topic describes how to add Custom Approval stages and steps.
Before You Begin
Requirements and limitations
- A Custom Approval stage can be added to any pipeline created in any module, such as in Continuous Delivery (CD), Continuous Integration (CI), or Feature Flags.
- A Custom Approval step can be added to a Custom Approval stage, CD Build stage, or Feature Flags stage.
- A Custom Approval step is not available in the CI stage currently.
- A Custom Approval step must have at least one Approval criteria. Rejection criteria is optional.
Review: Custom Approval stages and steps
When you add a Custom Approval stage, a Custom Approval step is added to the stage automatically. You can also add a Custom Approval step to a Continuous Delivery (CD) Deploy or Feature Flags stage.
In the Custom Approval step, you enter a script that is executed at Pipeline runtime.
If the script fails, the step fails and the step or stage Failure Strategy is initiated.
You must set approval criteria. Approval criteria can use the results of the script or other Harness features such as Harness built-in or custom variables.
Rejection criteria is optional.
Criteria can be the following:
- Evaluating a script output.
- For example, you set a value for a variable in your script, output that variable from the script, and then use that variable in the approval/rejection criteria of the Custom Approval step.
- When an evaluation results in a Boolean true, the approval criteria is met.
- Evaluating a JEXL Expression.
- Harness supports JEXL expressions and you can use these with script outputs or Harness variables to create expressions.
- If the resolved JEXL expression is a Boolean true, the approval criteria is met.
- For example, you could evaluate the output from a previous Shell Script step named test by referencing its output in a JEXL expression and comparing it to the value
Approved:<+execution.steps.test.output.outputVariables.status>=="Approved". - See Built-in and Custom Harness Variables Reference and Extracting Characters from Harness Variable Expressions.
Add a Custom Approval stage
Custom Approval stages automatically contain Custom Approval steps, and you can add Custom Approval steps to other Approval stages, CD Build stages, and Feature Flags stages.
In a Pipeline, click Add Stage.
In Select Stage Type, click Approval.
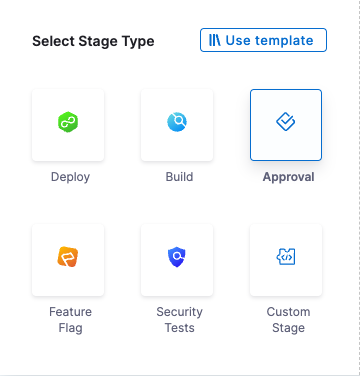
In About your Stage, enter a name for this stage, select Custom, and click Set Up Stage. The Approval Stage is set up.
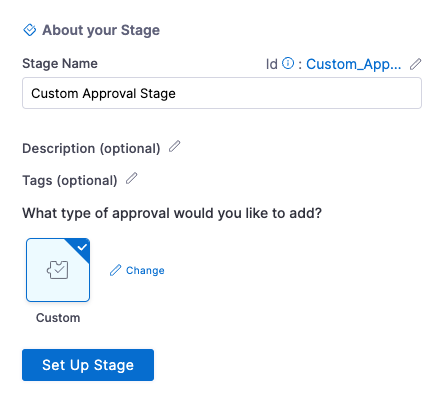
Click the Custom Approval step to set up your Step Parameters.
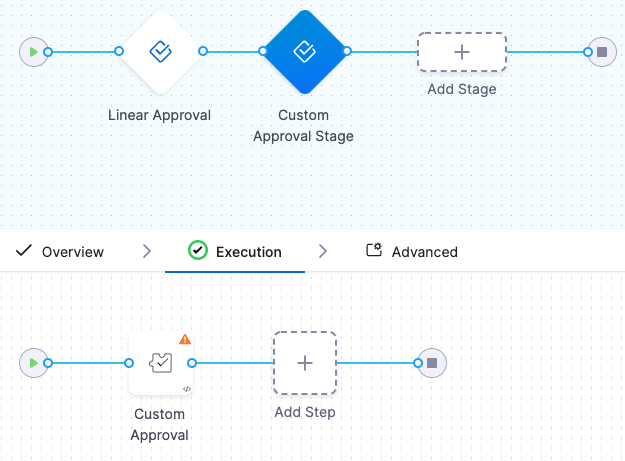
If you were adding a Custom Approval step to a different type of stage, you would simply click Add Step in that stage's Execution and select Custom Approval.### Step 2: Set up a Custom Approval Step
The Custom Approval step has the following settings.
Script
In Name, enter a name for the step.
In Script, enter your script.
The script is executed on the host of the Harness Delegate that runs the step. The script is not executed on the deployment target host(s).
You can select one or more specific Delegates using the Delegate Selector setting in the step's Advanced settings.
Timeout, Retry Interval, and Script Timeout
It's important to understand how the Timeout, Retry Interval, and Script Timeout settings relate to each other.
In Timeout, enter how long you want Harness to try to complete the step before failing (and initiating the stage or step Failure Strategy).
You can use **w** for week, **d** for day, **h** for hour, **m** for minutes, **s** for seconds and **ms** for milliseconds. For example, 1d for one day.
In Script Timeout, set how long the step should wait for the script to complete before timing out.
In Retry Interval, set how long the step should wait to run the script again if the Approval or Rejection criteria evaluate to false.
For example, if the Step Timeout is set as 10m, Script Timeout is set to 2m, and Retry Interval is set to 30s, then the script will be executed at least 4 times.
How many times a script executes within the Script Timeout depends on how fast the script executes.### Option: Script Output Variables
You can output variables from the script to be used in subsequent Pipeline steps or in the acceptance and rejection criteria.
Exporting Variables
To export variables from the script to the acceptance and rejection criteria or other steps in the stage, you use the Script Output Variables option.
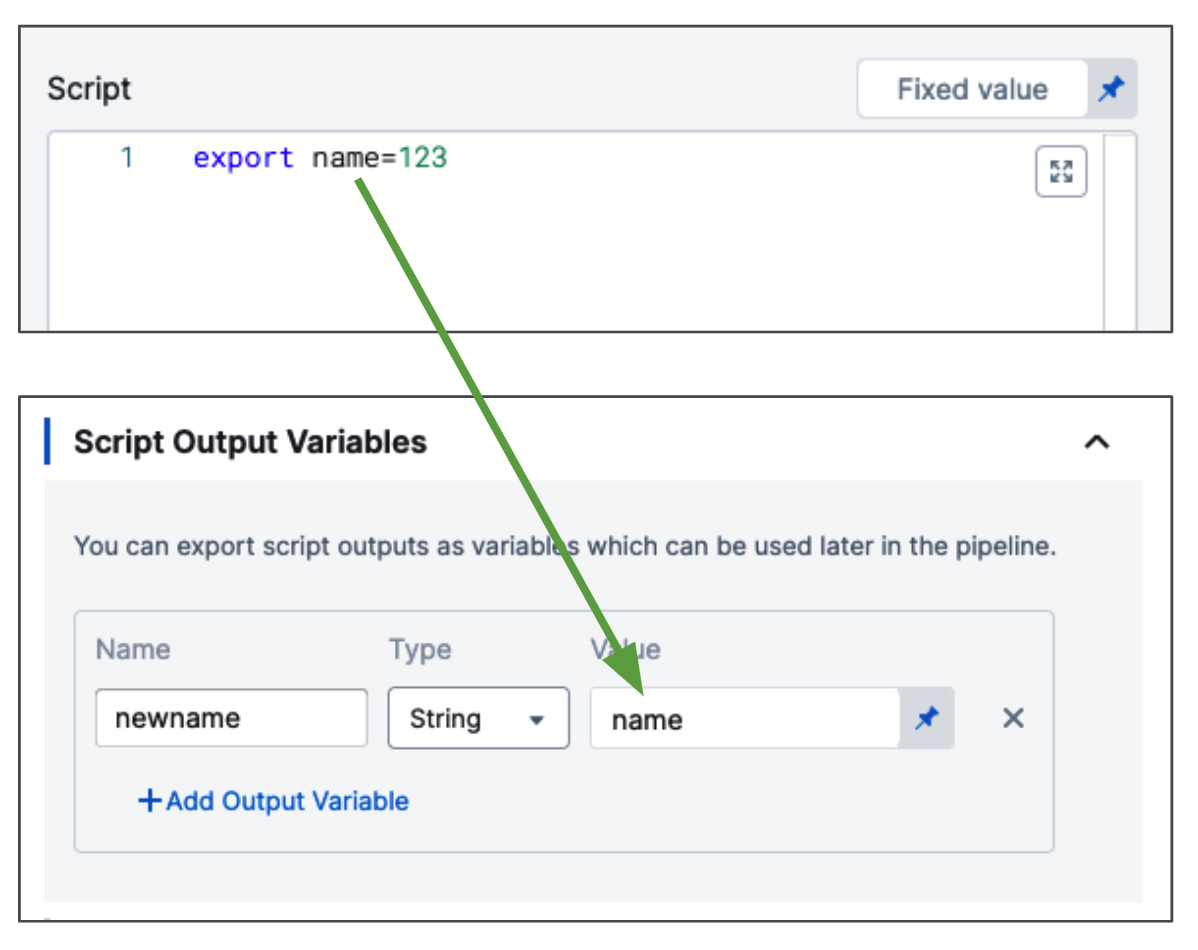
Let's look at a simple example of a script that exports the variable name:
export name=123
The name variable cannot be used outside the script unless you use Script Output Variables.
You do not need to export the variables with export to use them with Script Output Variables. You can simply declare them, like name="123". The export command is for using the variables in child processes within the script.In Script Output Variables, in Value, you enter the name of the script variable you want to output (for example, name).
In Name, enter a name to use in other steps that will reference this variable. This is the output variable name that will be used in a Harness expression for referencing the output variable.
The format to reference the output variable is <+steps.[step_id].output.outputVariables.[output_variable_name]>.
Here's an example showing how the Script Output Variables references the exported variable test, and how you reference the output variable Name var1 in a subsequent Shell Script step to get that value:
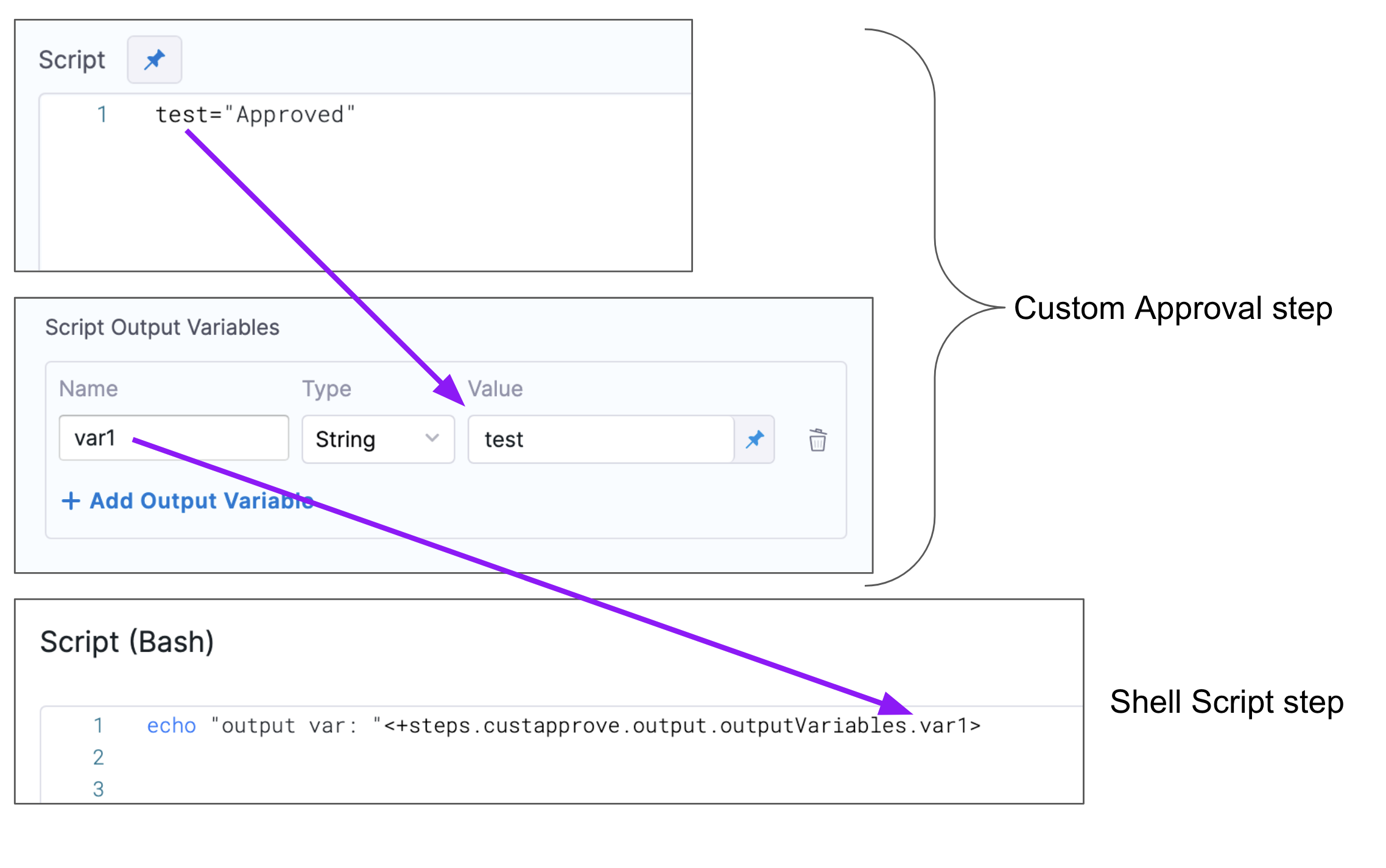
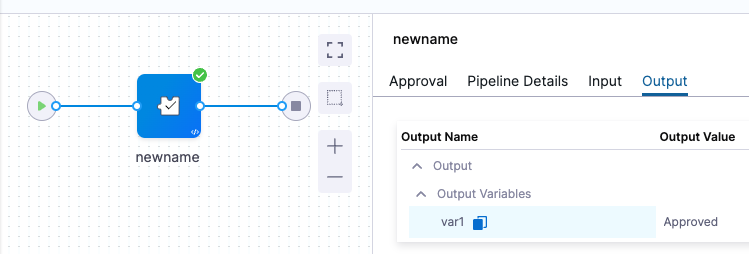
To find the expression to reference your output variables, execute the Pipeline, locate the step, and click its Output tab. You can copy the Output variable there.
Using Variables in Approval or Rejection Criteria
You can use script variables in your approval or rejection criteria by use them in Script Output Variables.
First, you create the variable in Script, then create a variable in Script Output Variables that references that variable, and then use the Script Output Variables variable and the Script variable's value in the Approval Criteria:
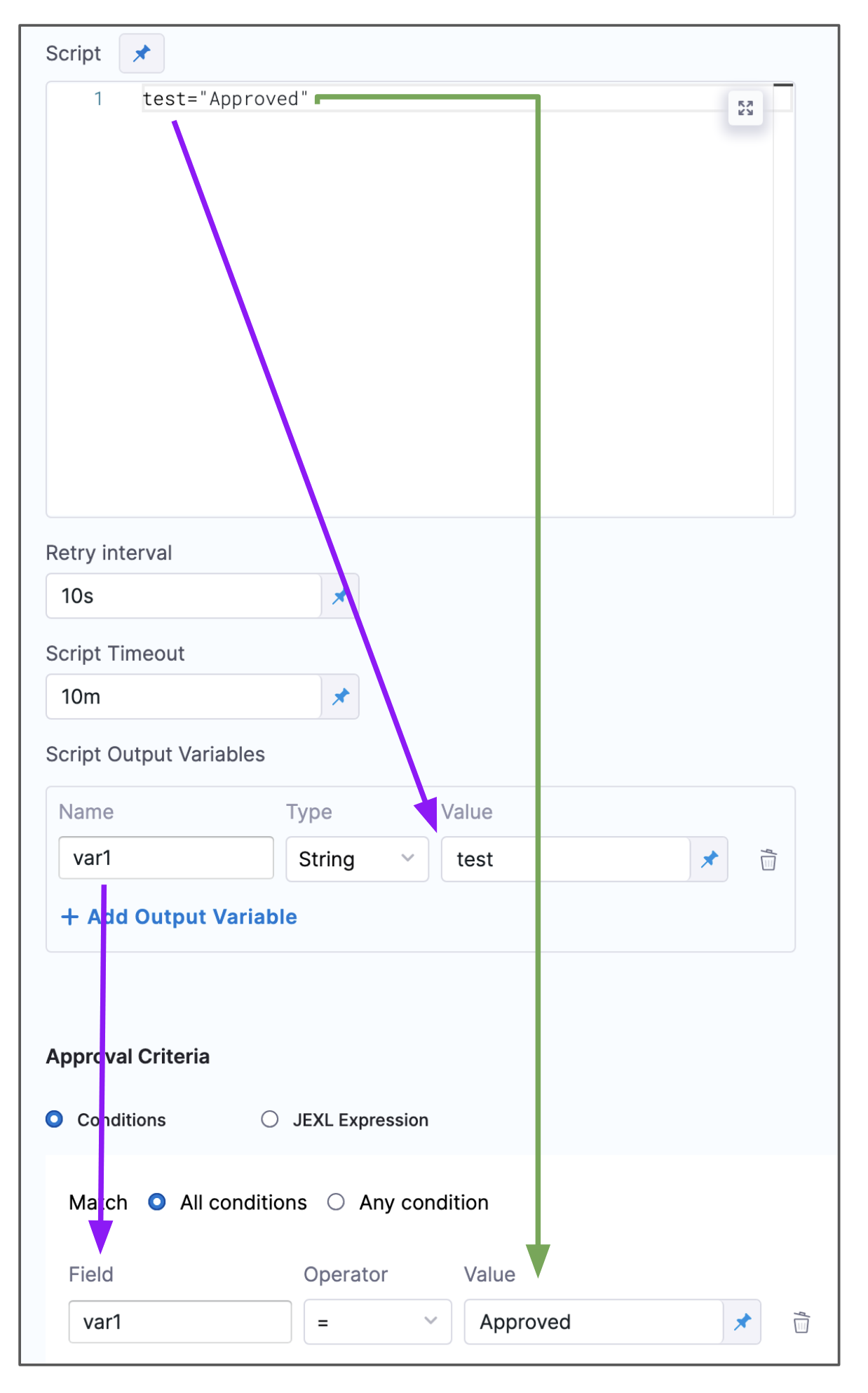
Set Approval Criteria
The Approval Criteria in the step determines if the Pipeline or stage is approved.
Custom Approval steps must have at least one Approval Criteria. You can also specify Rejection Criteria.
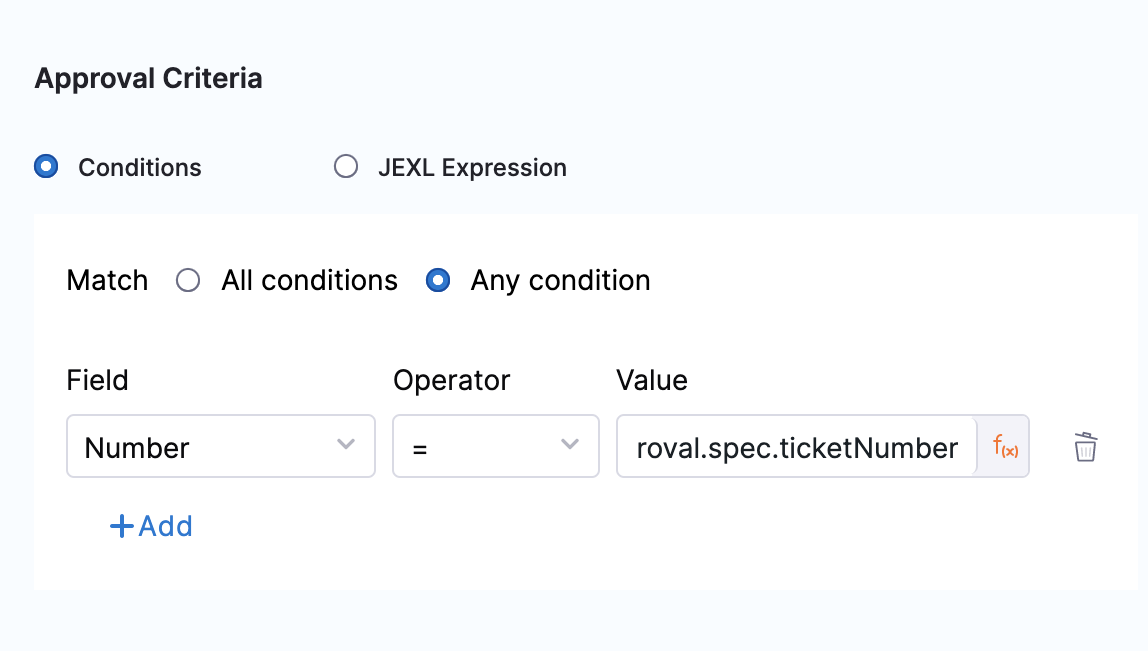
Whether the Pipeline/stage stops executing depends on the stage or step Failure Strategy. You can specify criteria using Conditions and/or JEXL Expression. If you use them in combination, they both must evaluate to a Boolean True for the step to be approved.
In Conditions, you can define approval criteria using outputs from the step script, Harness expressions, or your custom ticketing system.
If you use Harness expressions, ensure that the expression can be resolved at runtime.
If you use custom variable expressions that reference information from subsequent steps, ensure that those custom variable expressions will be resolved.
In JEXL Expression, you can use JEXL expressions. You can use a JEXL expression if the field is set to Fixed value or Expression.
Option: Script Input Variables
While you can simply declare a variable in your script using a Harness expression or string for its value, using Input Variables provides some additional benefits:
- You can easily identify and manage the Harness expressions used in your script.
- You can template your script.
You can declare the variable using Name and Value in Script Input Variables and then reference the variable in the script just as you would any other variable: $var_name.
You can also use expressions in Value. For example, if you have an Output Variable from a previous Custom Approval or Shell Script step, you can copy it from the executed step Outputs.
In Script Input Variables, you simply select Expression and paste the expression in Value.
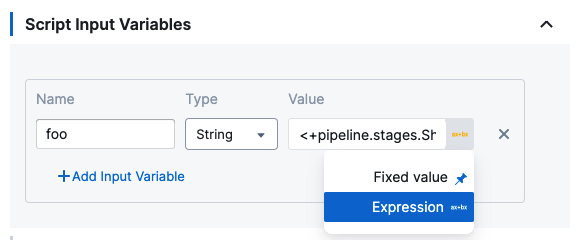
In Script, you declare the variable using the Name value:
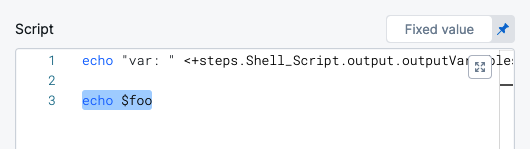
At deployment runtime, Harness will evaluate the expression and the variable will contain its output.
Option: Set Rejection Criteria
In Optional Configuration, in Rejection Criteria, you can define criteria for rejecting the approval.
If you add rejection criteria it is used in addition to the settings in Approval Criteria. Both Rejection Criteria and Approval Criteria must evaluate to a Boolean true for the step to be successful.
Option: Harness Expressions in Variables
You can use Harness variable expressions in your scripts and in the Script Input Variables and Script Output Variables.
For Script Input Variables and Script Output Variables, you simply select Expression, and then paste in the Harness variable expression.
Option: Advanced Settings
In Advanced, you can use the following options:
Apply and Test
Click Apply Changes. The Custom Approval step is added to the stage.
Run the Pipeline.
When the Custom Approval step is reached, you can see its approval and rejection criteria.
YAML example
Here's the YAML for a Pipeline that demonstrates how to set up a Custom Approval stage and step.
You can paste this YAML into a new Pipeline and simply update the pipeline settings (name, identifier, projectIdentifier, orgIdentifier) if needed.
pipeline:
name: Example
identifier: Example
projectIdentifier: myproject
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: test1
identifier: test1
description: ""
type: Approval
spec:
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: CustomApproval
name: custom approval
identifier: custapprove
timeout: 1d
spec:
shell: Bash
retryInterval: 10s
scriptTimeout: 10m
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: test="Approved"
environmentVariables: []
delegateSelectors: []
approvalCriteria:
type: KeyValues
spec:
matchAnyCondition: false
conditions:
- key: var1
operator: equals
value: Approved
rejectionCriteria:
type: KeyValues
spec:
matchAnyCondition: false
conditions: []
onDelegate: true
outputVariables:
- name: var1
type: String
value: test
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: vars
identifier: vars
spec:
shell: Bash
onDelegate: true
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |-
echo "output var: "<+steps.custapprove.output.outputVariables.var1>
test=<+steps.custapprove.output.outputVariables.var1>
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables:
- name: foo
type: String
value: test
executionTarget: {}
timeout: 10m
tags: {}
Notes
Stopping Scripts After Failures
The Custom Approval command will continue to process through the script even if a script step fails. To prevent this, you can simply include instructions to stop on failure in your script. For example:
set -e- Exit immediately when a command fails.set -o pipefail- Sets the exit code of a pipeline to that of the rightmost command to exit with a non-zero status, or to a zero status if all commands of the pipeline exit successfully.set -u- Treat unset variables as an error and exit immediately.
For more information, see this article: Writing Robust Bash Shell Scripts.
Published Variables Not Available
This error happens when you are publishing output via the Script Output Variables setting and your Custom Approval step exits early from its script.
There are many errors that can result from this situation. For example, you might see an error such as:
FileNotFoundException inside shell script execution task
If you exit from the script (exit 0), values for the context cannot be read.
Instead, if you publish output variables in your Custom Approval command, structure your script with if...else blocks to ensure it always runs to the end of the script.
Using Secrets in Scripts
You can use Harness secrets in your Custom Approval steps.
See Add Text Secrets.
Basically, you use <+secrets.getValue("secret_Id")> to refer to the secret Id.
Shell Scripts and Security
Harness assumes that you trust your Harness users to add safe scripts to your Custom Approval steps.
Please ensure that users adding scripts, as well as executing deployments that run the scripts, are trusted.