Add a custom artifact source for CD
Currently, this feature is behind the feature flag CUSTOM_ARTIFACT_NG. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.Harness includes artifact sources for the most common repositories, such as GCR, ECR, Nexus, Artifactory, and any Docker registry such as Docker Hub.
For cases where you are using a custom artifact repo, you can use the Custom Artifact repository type. The custom artifact uses a shell script to fetch a JSON payload of the artifacts from your repository, and then you can reference the artifact version to use in your deployment. You can also reference any metadata in the payload.
This topic described how to use the custom artifact repository type in your Harness service and how to reference its artifact information from the JSON payload.
Important notes
- Currently, custom artifact is supported in the Kubernetes, SSH, and WinRM deployment types only.
- The payload returned from your repo must be a JSON formatted array.
Create a service
Create a new service in Harness.
For Deployment Type, select Kubernetes. Custom Artifact is supported in the Kubernetes deployment type.
You can now see the Manifests and Artifacts sections.
We'll focus on Artifacts to demonstrate custom artifact, but you can find information on manifests in Kubernetes Services.
Add a custom artifact source
In Artifacts, select Add Primary Artifact.
Custom artifact is also supported in Sidecar. In Specify Artifact Repository Type, select Custom and select Continue.
In the Custom Artifact source, enter a script to fetch a JSON payload and add it to the Harness variable $HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATH. Here's an example:
curl -X GET "https://nexus3.dev.harness.io/service/rest/v1/components?repository=cdp-qa-automation-1" -H "accept: application/json" > $HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATH
Here's an example of the JSON payload returned from the cURL command:
{
"items" : [ {
"id" : "Y2RwLXFhLWF1dG9tYXRpb24tMTo5M2I5YjllYjlhN2VjYjA2NWJlYjdkNWUxNDgyMDFjOQ",
"repository" : "cdp-qa-automation-1",
"format" : "docker",
"group" : null,
"name" : "nginx",
"version" : "latest",
"assets" : [ {
"downloadUrl" : "https://nexus3.dev.harness.io/repository/cdp-qa-automation-1/v2/nginx/manifests/latest",
"path" : "v2/nginx/manifests/latest",
"id" : "Y2RwLXFhLWF1dG9tYXRpb24tMTo5MTJkMGZlN2I4MTkyMzkyODc0NTUyYTgyZWVmYzhkZQ",
"repository" : "cdp-qa-automation-1",
"format" : "docker",
"checksum" : {
"sha1" : "33acb567b9635e73ae566691eb22a89c84138c0b",
"sha256" : "bb129a712c2431ecce4af8dde831e980373b26368233ef0f3b2bae9e9ec515ee"
}
} ]
...
Next, in Artifacts Array Path, define where to find each artifact in the array ($.items).
Next, in Versions Path, define where to find the artifact versions in your payload (version).
Once done, the artifact details will look something like this:
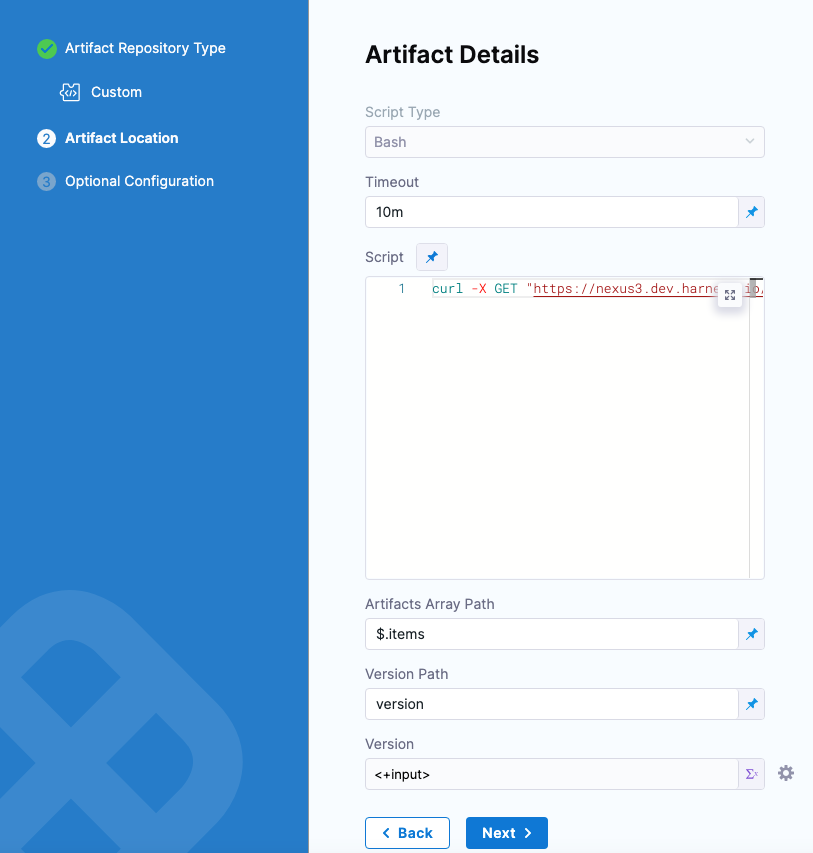
Enter the following settings.
Timeout: Enter a time limit for the script to execute before failing the artifact JSON retrieval.
Script: Enter a script to fetch a JSON payload and add it to the Harness variable
$HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATH.Here's an example:
curl -X GET "https://nexus3.dev.harness.io/service/rest/v1/components?repository=cdp-qa-automation-1" -H "accept: application/json" > $HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATHThe shell script you enter will query the Custom Artifact repository and output the JSON payload to a file on the Harness Delegate host using the environment variable
HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATH, initialized by Harness.HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATHis a random, unique file path created on the Delegate by Harness.You can use Harness text secrets in the script. For example:
curl -u 'harness' <+secrets.getValue("repo_password")> https://myrepo.example.io/todolist/json/ > $HARNESS_ARTIFACT_RESULT_PATHYou must delete the Artifact Source and re-add it to re-collect the artifacts if the Artifact Source or its script information has been changed.
Artifacts Array Path: Enter the path in the payload array to the artifacts listing. For example, in the following payload the artifacts are listed using
items, so in Artifacts Array Path you reference the path with$.items.{
"items" : [ {
"id" : "Y2RwLXFhLWF1dG9tYXRpb24tMTo5M2I5YjllYjlhN2VjYjA2NWJlYjdkNWUxNDgyMDFjOQ",
"repository" : "cdp-qa-automation-1",
"format" : "docker",
"group" : null,
"name" : "nginx",
"version" : "latest",
"assets" : [ {
"downloadUrl" : "https://nexus3.dev.harness.io/repository/cdp-qa-automation-1/v2/nginx/manifests/latest",
"path" : "v2/nginx/manifests/latest",
"id" : "Y2RwLXFhLWF1dG9tYXRpb24tMTo5MTJkMGZlN2I4MTkyMzkyODc0NTUyYTgyZWVmYzhkZQ",
"repository" : "cdp-qa-automation-1",
"format" : "docker",
"checksum" : {
"sha1" : "33acb567b96xxx9c84138c0b",
"sha256" : "bb129a712cxxx33ef0f3b2bae9e9ec515ee"
}
} ]
...Version Path: Enter the path in the payload array to the version. Using the above payload example, the path is
version.Version: Enter the version number for this deployment, or select Runtime Input or Expression to select the version dynamically.
For more information on Fixed Value, Runtime Input, and Expression got to Fixed Values, Runtime Inputs, and Expressions.
When you done Artifact Details will look something like this:
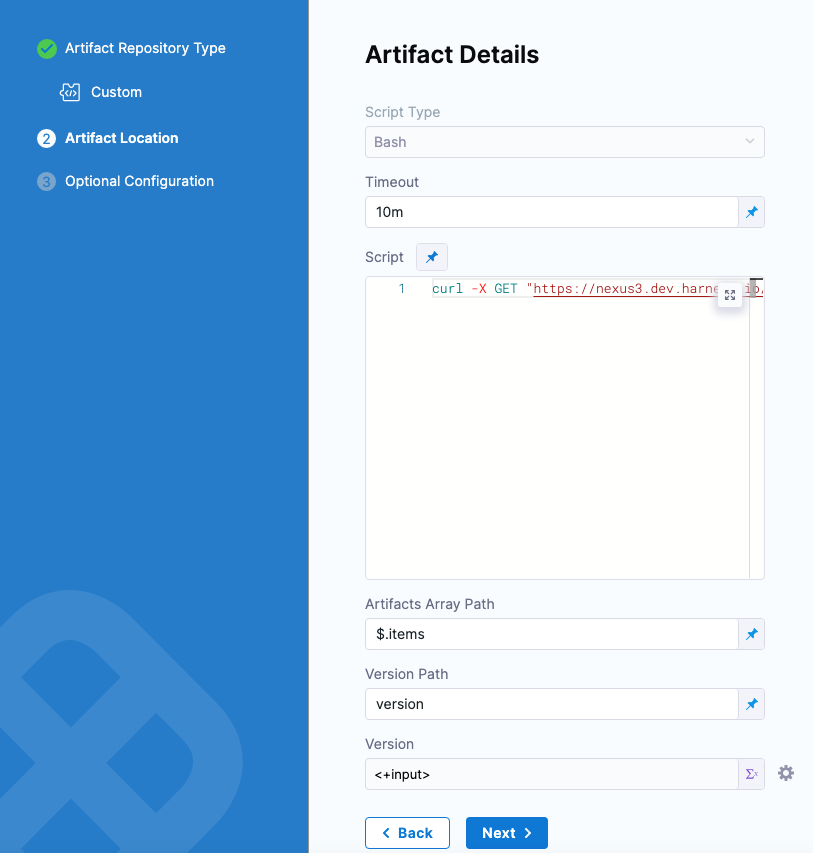
Later, you can reference the Version using this expression format, which will resolve to the version pulled from the array at runtime:
<+pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.version>
Script input variables
While you can simply declare a variable in your script using a Harness expression or string for its value, using Script Input Variables provides some additional benefits:
- You can more easily identify and manage the Harness expressions used in your script.
- You can template your script.
You can declare the variable using Name and Value in Script Input Variables and then reference the variable in the script just as you would any other variable: $var_name.
Additional attributes (metadata)
In Additional Attributes, you can map any additional values from your JSON array.
For example, the following payload has downloadUrl and path in its assets:
{
"items" : [ {
"id" : "Y2RwLXFhLWF1dG9tYXRpb24tMTo5M2I5YjllYjlhN2VjYjA2NWJlYjdkNWUxNDgyMDFjOQ",
"repository" : "cdp-qa-automation-1",
"format" : "docker",
"group" : null,
"name" : "nginx",
"version" : "latest",
"assets" : [ {
"downloadUrl" : "https://nexus3.dev.harness.io/repository/cdp-qa-automation-1/v2/nginx/manifests/latest",
"path" : "v2/nginx/manifests/latest",
"id" : "Y2RwLXFhLWF1dG9tYXRpb24tMTo5MTJkMGZlN2I4MTkyMzkyODc0NTUyYTgyZWVmYzhkZQ",
"repository" : "cdp-qa-automation-1",
"format" : "docker",
"checksum" : {
"sha1" : "33acb567b96xxx9c84138c0b",
"sha256" : "bb129a712cxxx33ef0f3b2bae9e9ec515ee"
}
} ]
...
You can assign these items to variables. In Name, enter the variable name and in Value enter the path to the item.
For example, to reference downloadUrl and path in the first item in the array:
assets[0].downloadUrlassets[0].path
Here's an example:
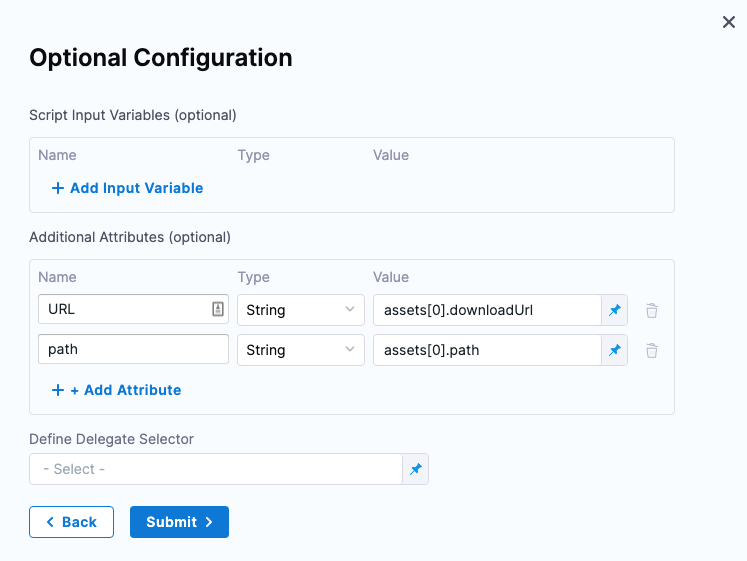
Later, in a Shell Script step, you can reference these attributes using the expression format:
<+pipeline.stages.[stage_Id].spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.metadata.[attribute_name]>
For example:
echo "URL: <+pipeline.stages.Kube.spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.metadata.URL>"
echo "Path: <+pipeline.stages.Kube.spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.metadata.path>"
At runtime, these expressions will resolve to the data from the array.
Reference custom artifact
You can reference the custom artifact in your values.yaml file and in a Shell Script step.
Values YAML in manifests
You add a values.yaml file along with your manifests in the Manifests section of the Service.
The values.yaml file can use Harness expressions to reference artifacts in the Artifacts section of the service.
To reference the artifact, use the expression <+artifact.image> in your values.yaml file.
For example:
name: example
replicas: 2
image: <+artifact.image>
# dockercfg: <+artifact.imagePullSecret>
createNamespace: true
namespace: <+infra.namespace>
...
For details on using values.yaml in Harness, go to Kubernetes Services.
Harness Variables and Expressions can be added to Values files (for example values.yaml), not the manifests themselves. This provides more flexibility.
Shell script step
In the stage Execution section, add a Shell Script step.
In Script, reference the artifact and any additional attributes you configured. Here's an example where the stage is named Kube:
echo "Version: <+pipeline.stages.Kube.spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.version>"
echo "URL: <+pipeline.stages.Kube.spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.metadata.URL>"
echo "Path: <+pipeline.stages.Kube.spec.serviceConfig.output.artifactResults.primary.metadata.path>"