Target Delegates to Specific Namespaces
By default, Harness Delegates deploy to all namespaces in a Kubernetes cluster. This topic describes how to configure Delegates to deploy into specific namespaces.
In this topic:
- Before You Begin
- Visual Summary
- Review: Harness Connections to Kubernetes
- Step 1: Create Service Account
- Step 2: Create Role and RoleBinding
- Option 1: Use the Service Account Token
- Option 2: Add Service Account to Delegate Spec
- Review: Enable Skip Validation in Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider
- Notes
- Next Steps
Before You Begin
Visual Summary
Let's take a quick look at the two ways the Delegate can deploy to namespaces in a cluster.
Central Model
By default, the Delegate resides in a namespace in the target cluster with a service account attached to it. The service account uses a ClusterRole for permission to deploy to all namespaces in the cluster.
The is called this the central model. Here is a simple illustration of the central model:
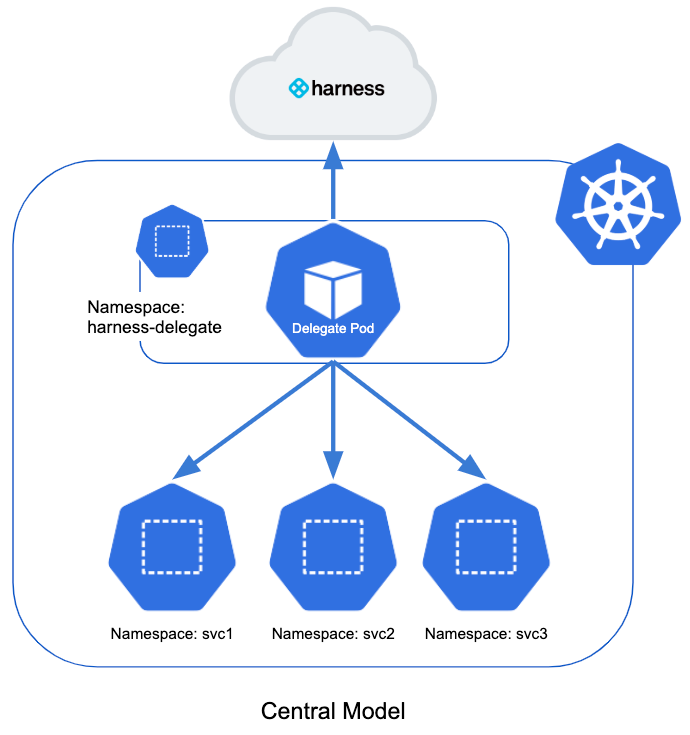
The central model is simple and efficient, but it does not let you restrict teams to deploying into specific namespaces. Any team member can deploy to any namespace.
As an alternative, you can use a distributed model.
Distributed Model
This model places a Delegate in each namespace in the cluster. It limits each Delegate to deploying into its own namespace.
Here is the illustration of the distributed model:
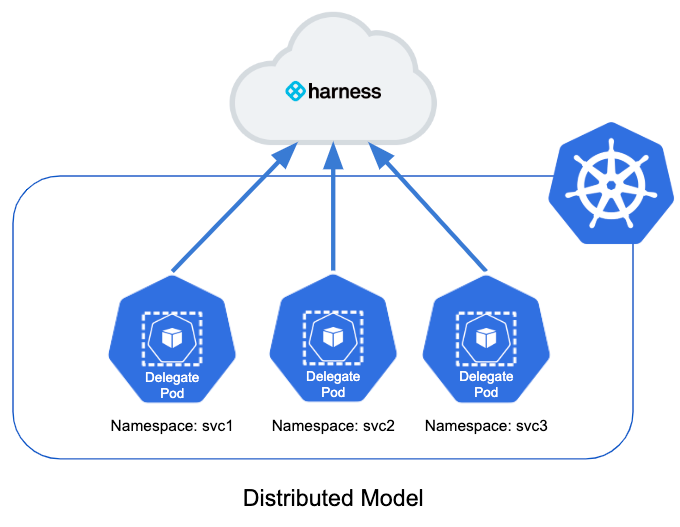
In this model, each team uses their own Delegate for their deployments into their own namespace.
The distributed model is more complex, but it prevents a team member from deploying into the wrong namespace.
Review: Harness Connections to Kubernetes
First, we'll review how Harness connects to the target Kubernetes cluster using the Delegate.
For the Delegate to perform operations on a target Kubernetes cluster, it requires one of the following:
- A service account. The default service account created by the Kubernetes and Helm Delegates uses the Kubernetes cluster-admin role.
- Service account token.
- Username and password.
- CA certificate, client certificate, and client key.
For this topic, we will focus on the service account.
The Harness Kubernetes and Helm Delegates are designed to create the Kubernetes resources they need when you install them. This includes the namespace, service account, and a ClusterRole that enables the Delegate to deploy to any namespaces in the cluster.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: harness-delegate-cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: harness-delegate
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
This ClusterRoleBinding binds the service account with the cluster-admin ClusterRole. The cluster-admin ClusterRole exists by default in your Kubernetes cluster, and allows superuser operations in all of the cluster resources.
For other type of Delegates (Shell Script, Docker, ECS), you need to create the Kubernetes resources yourself and then use the service account when setting up the Harness Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider.Once a Delegate is installed and running, you can add a Harness Kubernetes Cluster Could Provider to connect to the target cluster.
There are two ways for the Kubernetes Cluster Could Provider to get credentials:
- Inherit from selected Delegate
- Enter manually
Both methods can use the service account to provide either the central or distributed models.
Inherit from selected Delegate
Supported Delegate types: Kubernetes and Helm Delegate.
In this option, the Cloud Provider inherits the service account created when you installed the Delegate.
Enter Manually
Supported Delegate types: Shell Script, Docker, ECS, Kubernetes, Helm.
In this option, the Cloud Provider uses the credentials that you enter manually. The Delegate uses these credentials to send deployment tasks to the cluster.
The Delegate can be outside or within the target cluster.
Some examples:
- Shell Script Delegate on a VM.
- Docker Image Delegate outside of the target cluster.
- Kubernetes Delegate in a pod outside of the target cluster.
Providing the Master URL is mandatory. This is the Kubernetes master node URL.
The remaining steps in this topic explain how to create the Kubernetes resources needed for the service account used by the Delegates in the distributed model.
Step 1: Create Service Account
To restrict the Delegate to deploy to a specific namespace, first you create the namespace, if it isn't already created.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: mynamespace
Next you create the service account in that namespace for the Delegate.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: mynamespace-delegate-sa
namespace: mynamespace
Step 2: Create Role and RoleBinding
By default, the Delegate can deploy to all namespaces. Its service account uses the cluster-admin ClusterRole. This method enables the central model.
In the distributed model, you restrict the Delegate to a specific namespace by using the following:
- A Role in the namespace that grants access to items in that namespace only.
- A RoleBinding in the namespace. It binds the Role in that namespace to the service account you created.
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: default-full-access
namespace: mynamespace
rules:
- apiGroups: ["", "extensions", "apps", "autoscaling", "rbac.authorization.k8s.io", "roles.rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs: ["*"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: default-view
namespace: mynamespace
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: mynamespace-delegate-sa
namespace: mynamespace
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: default-full-access
The service account is bound to a Role that limits it to the namespace.
Now you have two options:
- Option 1: Install a Delegate outside of the namespace and simply enter the service account token in the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider.
- Option 2: Install a Kubernetes or Helm Delegate in the namespace using the service account. You simply reference the service account in the Delegate spec. You can then have the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider inherit credentials from the Delegate.
Resources and Verbs
If you don't want to use resources: ["*"] for the role you can list out the resources you want to grant. Harness needs configMap, secret, event, deployment, and pod at a minimum. Beyond that, it depends on the resources you are deploying via Harness.
If you don't want to use verbs: ["*"] for the role you can list out the verbs you want to grant (create, delete, get, list, patch, update, watch).
Option 1: Use the Service Account Token
If you are using the Enter Cluster Details manually option in the Kubernetes Cloud Provider, use the service account in the Service Account Token setting.
The following shell script is a quick method for obtaining the service account token. Run this script wherever you run kubectl to access the cluster.
Set the SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME and NAMESPACE values to the values in your infrastructure:
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME=default
NAMESPACE=mynamespace
SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get sa "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o json | jq -r '.secrets[].name')
TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret "${SECRET_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o json | jq -r '.data["token"]' | base64 -d)
echo $TOKEN
Next, enter the service account token in the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider:
Option 2: Add Service Account to Delegate Spec
In you are using the Inherit from selected Delegate option in the Kubernetes Cloud Provider, add the service account to the Delegate YAML. See serviceAccountName: mynamespace-delegate-sa below:
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/app: harness-delegate
harness.io/account: wsxvws
harness.io/name: demo-delegate
# Name must contain the six letter account identifier: wsxvws
name: demo-delegate-wsxvws
namespace: harness-delegate
spec:
**serviceAccountName: mynamespace-delegate-sa**
replicas: 1
...
When you download the Kubernetes Delegate YAML from Harness, you get the harness-delegate-kubernetes.tar.gz file. Once you extract the file, you get the harness-delegate.yaml file.
By default, the harness-delegate.yaml uses a role with the default service account and harness-delegate namespace.
As discussed above, to restrict the Delegate to a single namespace, you will create a namespace, service account, Role, and RoleBinding, and then reference the service account in the Delegate spec.
Edit the harness-delegate.yaml file to create these new resources.
Here is an example of the Kubernetes Delegate YAML that creates all the necessary resources:
Kubernetes Delegate YAML Sample
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: mynamespace
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: mynamespace-delegate-sa
namespace: mynamespace
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: default-full-access
namespace: mynamespace
rules:
- apiGroups: ["", "extensions", "apps", "autoscaling", "rbac.authorization.k8s.io", "roles.rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs: ["*"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: default-view
namespace: mynamespace
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: mynamespace-delegate-sa
namespace: mynamespace
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: default-full-access
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: demo-delegate-proxy
namespace: mynamespace
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: mynamespace-delegate-sa
type: Opaque
data:
# Enter base64 encoded username and password, if needed
PROXY_USER: ""
PROXY_PASSWORD: ""
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/app: harness-delegate
harness.io/account: wsxvws
harness.io/name: demo-delegate
# Name must contain the six letter account identifier: wsxvws
name: demo-delegate-wsxvws
namespace: harness-delegate
spec:
serviceAccountName: mynamespace-delegate-sa
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
harness.io/app: harness-delegate
harness.io/account: wsxvws
harness.io/name: demo-delegate
serviceName: ""
template:
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/app: harness-delegate
harness.io/account: wsxvws
harness.io/name: demo-delegate
spec:
containers:
- image: harness/delegate:latest
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: harness-delegate-instance
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "8Gi"
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- test
- -s
- delegate.log
initialDelaySeconds: 20
periodSeconds: 10
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- bash
- -c
- '[[ -e /opt/harness-delegate/msg/data/watcher-data && $(($(date +%s000) - $(grep heartbeat /opt/harness-delegate/msg/data/watcher-data | cut -d ":" -f 2 | cut -d "," -f 1))) -lt 300000 ]]'
initialDelaySeconds: 240
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 2
env:
- name: ACCOUNT_ID
value: wsxvws
- name: DELEGATE_TOKEN
value: 123abc
- name: MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT
value: https://qa.harness.io
- name: WATCHER_STORAGE_URL
value: https://qa.harness.io/storage/wingswatchers
- name: WATCHER_CHECK_LOCATION
value: watcherqa.txt
- name: DELEGATE_STORAGE_URL
value: https://qa.harness.io/storage/wingsdelegates
- name: DELEGATE_CHECK_LOCATION
value: delegateqa.txt
- name: DEPLOY_MODE
value: KUBERNETES
- name: DELEGATE_NAME
value: demo-delegate
- name: DELEGATE_PROFILE
value: ""
- name: MANAGER_TARGET
value: "qa.harness.io"
- name: MANAGER_AUTHORITY
value: "manager-grpc-qa.harness.io"
- name: PROXY_HOST
value: ""
- name: PROXY_PORT
value: ""
- name: PROXY_SCHEME
value: ""
- name: NO_PROXY
value: ""
- name: PROXY_MANAGER
value: "true"
- name: PROXY_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: demo-delegate-proxy
key: PROXY_USER
- name: PROXY_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: demo-delegate-proxy
key: PROXY_PASSWORD
- name: POLL_FOR_TASKS
value: "false"
- name: HELM_DESIRED_VERSION
value: ""
- name: CF_PLUGIN_HOME
value: ""
restartPolicy: Always
Next, connect to your cluster and run the kubectl command to install the Delegate:
kubectl apply -f harness-delegate.yaml
For Helm Delegate, you download the Delegate file harness-delegate-values.yaml. It includes instructions for adding the Harness Helm repo and
helm repo add harness https://app.harness.io/storage/harness-download/harness-helm-charts/
Next, you fetch the Delegate file:
helm fetch harness/harness-delegate
This results in the file harness-delegate-1.0.0.tgz. Extract it to see the YAML files.
In the harness-delegate folder you will see the values.yaml file where you specify the namespace for the Delegate to use.
namespace: harness-delegate
Simply replace the namespace with the new namespace:
namespace: mynamespace
In the harness-delegate/templates folder you will see the default YAML files that use values.yaml.
Modify these files in the same way that you modified the Kubernetes Delegate YAML. Use placeholder {{ .Values.namespace }} for to reference the new namespace in values.yaml.
You will delete cluster-rolebinding.yaml. and replace it a new file(s) for the service account, Role, and RoleBinding.
For details on installing the Helm Delegate, see Install the Harness Helm Delegate.
Review: Enable Skip Validation in Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider
By default, Harness uses the default namespace to validate credentials the first time you set up a Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider.
If you add a Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider in Harness with a Service Account that does not have list all namespaces permissions in the cluster, ensure that you enable the Skip Validation option.
Notes
You can also enable a Delegate to deploy to namespaces outside its own. In this model, the Delegate does not have to be in the same namespace as the deployment target.
For this method, do the following:
- Create a service account for the Delegate in the namespace where you will install the Delegate. Let's call this the
delegate-ns. We'll call the deployment target namespacetarget. - Create the service account in namespace
delegate-ns. - Create a Role in namespace
target. - Create a RoleBinding in namespace
target, with the following properties:- RoleRef pointing to the Role in the same namespace
target - Subject pointing to the Delegate service account and namespace:
delegate-ns.
- RoleRef pointing to the Role in the same namespace