Harness Chaos Engineering (HCE) FAQs
General
For an overview of Harness support for platforms, methodologies, and related technologies, go to Supported platforms and technologies.
How to add and manage a custom chaos hub?
You can navigate to chaos hubs in the chaos module and select + New ChaosHub, and fill in the details regarding your public or private hub. Ensure that you have chaos hub read or write permission enabled and a GitHub connector configured for the repository you are about to connect.
How do I connect to a private chaos hub?
To connect to a private chaos hub repository, connect to a Harness GitHub connector through a Harness delegate, or GitHub directly by providing your GitHub SSH key or Personal Access Token (PAT). Once this is done, you can select the connector when adding a chaos hub.
How are faults different from experiments?
Faults refer to the failures that are injected into the target resource as part of an experiment. Whereas a chaos experiment is a set of different faults coupled together to achieve a desired chaos impact.
What are the possible reasons I can’t see tunables in Tune Fault UI?
Since the tuning of a chaos experiment is highly declarative, sometimes it may cause parsing issues, these may be the possible reasons:
- The step name of the fault and the template name might have been changed due to custom editing.
- The step name has been removed completely.
- The template definition has been erased.
How are probes useful in an experiment?
A probe can help understand the underlying patterns and laws that govern the behavior of your systems, and you can use that understanding to predict or control their behavior. Probes can be used to test scenarios such as network partitioning, pod failures, and node failures, by adding additional checks, it can also be used to test the behavior of applications during such scenarios.
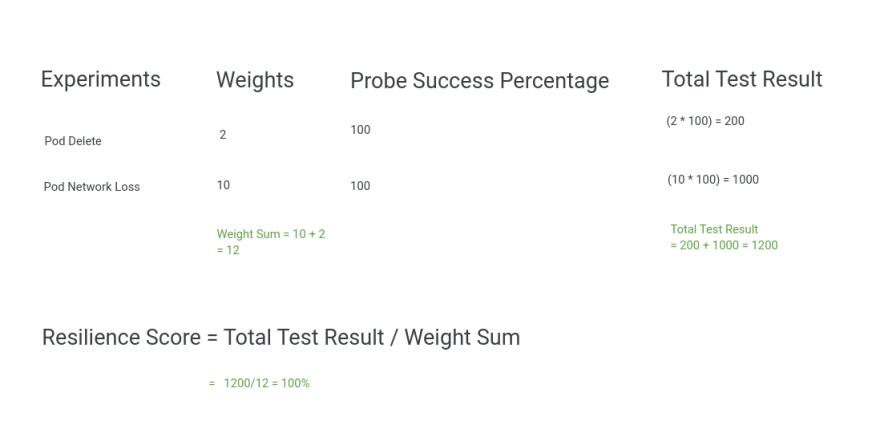
How is resilience score affected if a few of my probes fail?
The weighted average of probe success percentage of each of the probe determines the value of the overall resilience score of the experiment. The value depends on the successful outcome of the probe criteria based on the type and mode selected. There are two possible values of probe success percentage for each of the probe criterias, either 0(if the criteria assertion fails) or 100(if the criteria assertion passes).
Total Resilience for one single experiment = (Weight Given to that experiment * Probe Success Percentage)
I’m having trouble creating an experiment YAML from scratch, can I generate one?
Yes, you can generate a YAML file by choosing the normal flow of creating an experiment (blank canvas or through a template), in the YAML/Visual toggle you can see a generated YAML based on the inputs provided by you. A generated YAML can also be downloaded after navigating to Chaos Experiments and clicking on Download Experiments.
Additionally you can also leverage Harness Go SDK repository and generate a template.
My issue is not mentioned here, how can I report it?
To report an issue which is not mentioned here, head over to Help in Harness SaaS and click Submit a ticket and provide your feedback.
Security
What are the identity providers supported by Harness Chaos for user authentication?
The Harness platform is fully integrated with several public OAuth providers, with support for two-factor authentication and domain whitelisting. To learn more, go to authentication overview.
How does the chaos infrastructure connect to the Harness SaaS control plane? Which ports should be opened in the users’ environments?
The chaos infrastructure connects to the Harness control plane through outbound connectivity over HTTP(s) using port 443. To learn more, go to chaos infrastructures.
What are the permissions and privileges required to deploy and run the chaos infrastructure?
The chaos infrastructure setup involves the creation of CRDs and RBAC resources. This setup typically needs cluster-admin intervention. To learn more, go to Kubernetes roles for the chaos infrastructure.
How do I control user actions in a given environment in Harness Chaos?
The scope of a user's access to chaos resources added to a given Harness account or project can be controlled by assigning them a predefined or custom role. To learn more, go to chaos access control.
How do I control the security blast radius in terms of access to application microservices and infrastructure resources in a user environment?
The chaos infrastructure can be installed in a cluster-wide scope (with the ability to discover and inject chaos on microservices across namespaces and infrastructure components such as nodes and volumes) as well as in a namespace-specific scope (where discovery and chaos injection are limited to resources within a specific namespace).
In addition, users can provide a custom service account to carry out experiments, thereby limiting the fault types in the user environment. To learn more, go to blast radius control using permissions.
How does Harness Chaos access cloud resources in the users’ environment?
Harness Chaos experiment pods consume Kubernetes secrets that contain access credentials, which are leveraged to make provider-specific API calls to the cloud platform to inject chaos. To learn more, go to Secrets management.
Can cloud service accounts be used instead of user credentials to access cloud resources?
When the chaos infrastructure is deployed on EKS clusters, the experiments can leverage the IAM service account (IRSA) instead of consuming secrets with user account access details. To learn more, go to IAM integration for AWS authentication.
How does Harness Chaos access APM platforms to perform hypothesis validation?
Harness Chaos experiments can consume K8s secrets containing authentication information for the desired APM and use it within the command-probe pods that leverage this information to make the right provider-specific API calls to retrieve metrics and other pertinent data. To learn more, go to command probes.
What are the details about the user and the user’s environment accessed and stored by Harness?
The following user information is stored in the Harness database and object store:
- FQDNs or URLs or IPs of microservices in user clusters
- Chaos experiment execution logs, with process information and results
The information is purged on a policy basis, with defaults set at "x" days.
How can I track the actions of a user on the Harness platform?
Harness provides an audit log to the account admin where user actions on the chaos resources are logged with timestamps. To learn more, go to audit trail.
Can Harness perform security chaos tests in the users’ environments?
Harness Chaos supports experiments that simulate DoS attacks on services. You can achieve this by simulating very high loads that render the system slow (if the correct rate limits are in place) or non-functional (if rate limiting is not implemented). To learn more, go to generic locust fault.