Harness API quickstart
Everything you can create in the Harness Manager you can create using our REST APIs.
This quickstart shows how to onboard Harness resources using the APIs. We'll add a new Project, Connector, and Pipeline using curl and the APIs.
Looking for the API reference docs? Go to Harness API Reference Docs.
Objectives
You'll learn how to:
- Authenticate with Harness via API using API keys.
- Onboard Harness Projects, Connectors, and Pipelines using the Harness API.
The API requests in this topic use curl, but Harness supports multiple languages, such as Go, Java, and Node.js. The Harness API Reference Docs provides examples for all supported languages.
Before you begin
- Harness Key Concepts
- Access Management(RBAC) Overview
- This quickstart walks you through adding the Harness API keys needed to authenticate with the API. To review Harness API keys, go to Add and Manage API Keys.
- Make sure your Harness account has the required permissions to Create, Edit, Delete, and View the Harness resources you are creating via API. Any of the following default roles are sufficient: Account Administrator, Organization Admin, Project Admin. For more, go to Permissions Reference.
Step 1: Create a Harness API Key and PAT
The Harness API uses API keys to authenticate requests. You create the API key in your Harness Manager User Profile, add a Personal Access Token (PAT) to the key, and then use the PAT in your API requests.
For an overview of Harness API keys, go to Add and Manage API Keys.
Let's create the API key and its Personal Access Token.
Here's a quick visual summary:
Create API Key
In Harness, navigate to your Profile.
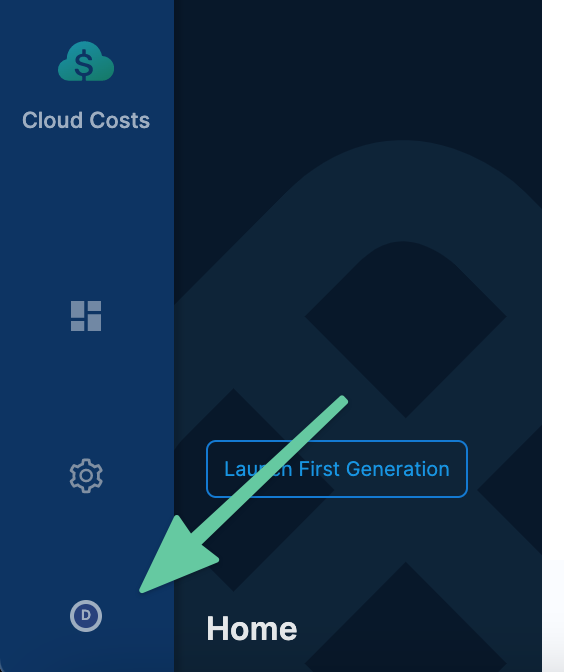
In My API Keys, Click API Key. The API Key settings appear.
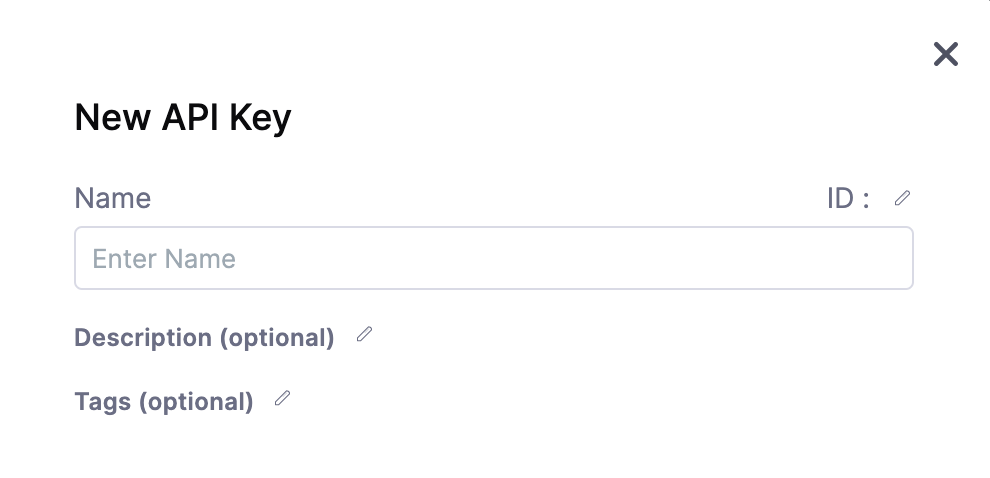
Enter Name, Description, and Tags for your API.
Click Save. The new API Key is created.
Create Personal Access Token
Next, we'll add the Personal Access Token (PAT) that you will use when you make API requests.
Click Token below the API Key you just created.
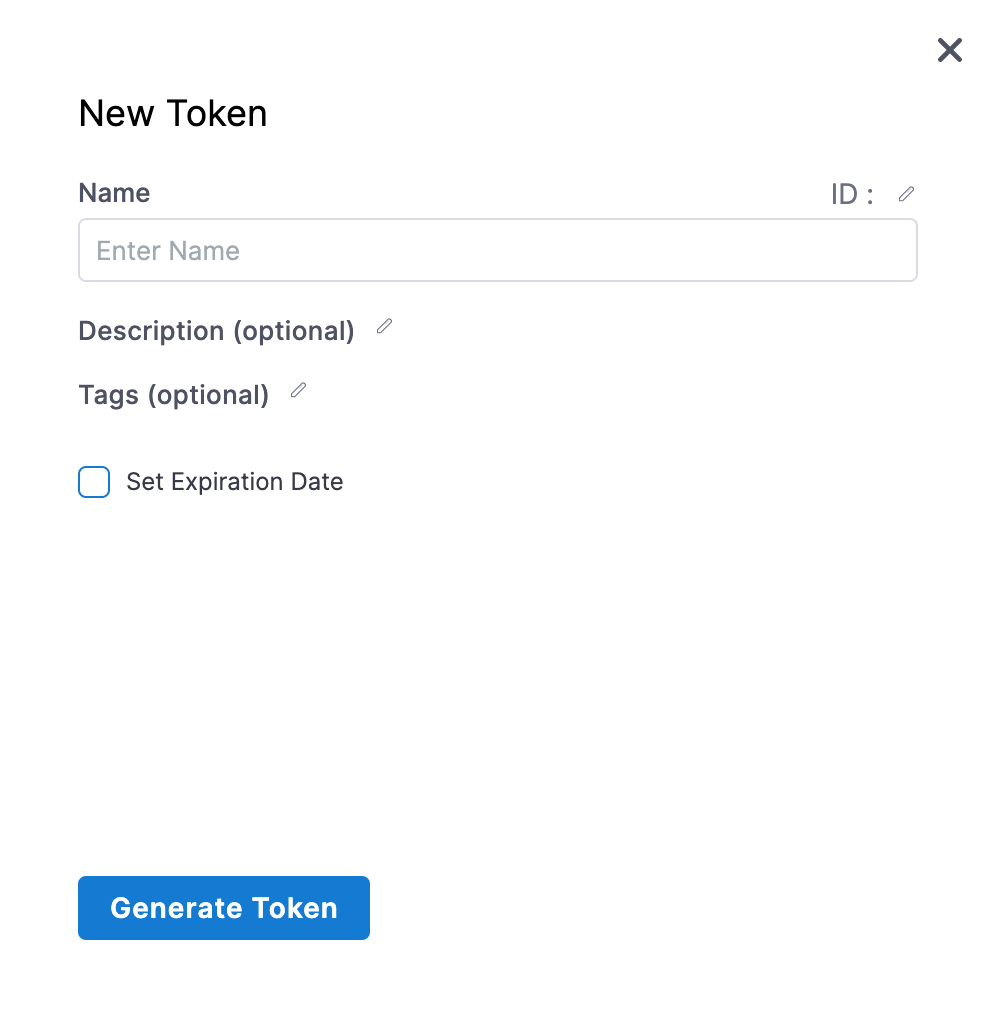
In the New Token settings, enter a Name, Description, and Tags.
To set an expiration date for this token, select Set Expiration Date and enter the date in Expiration Date (mm/dd/yyyy).
Click Generate Token.
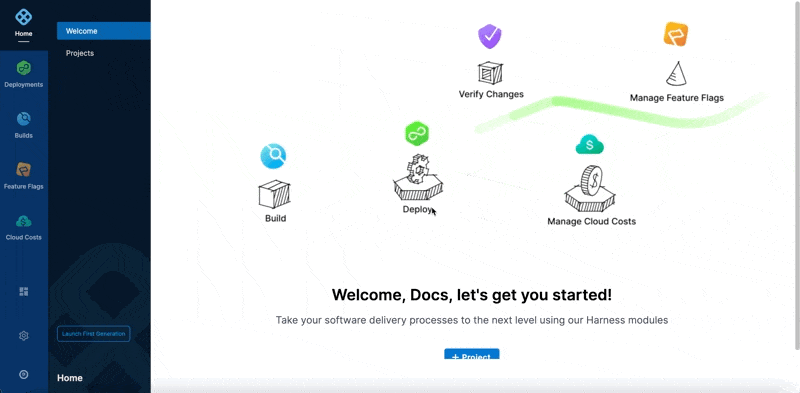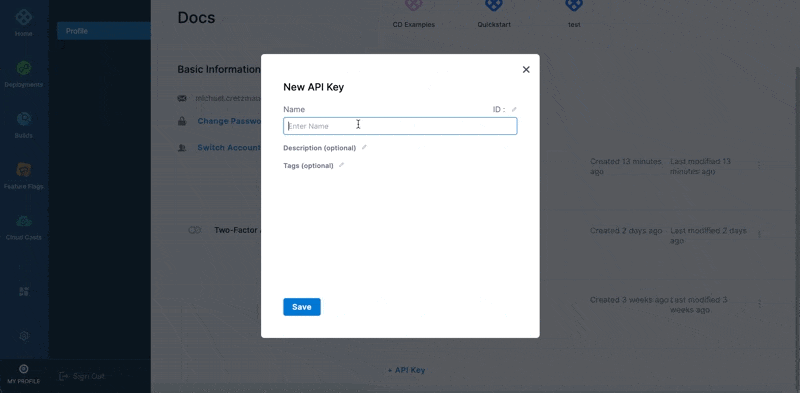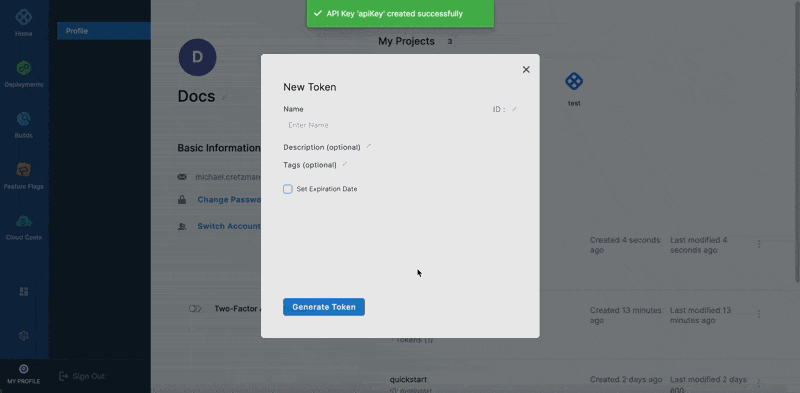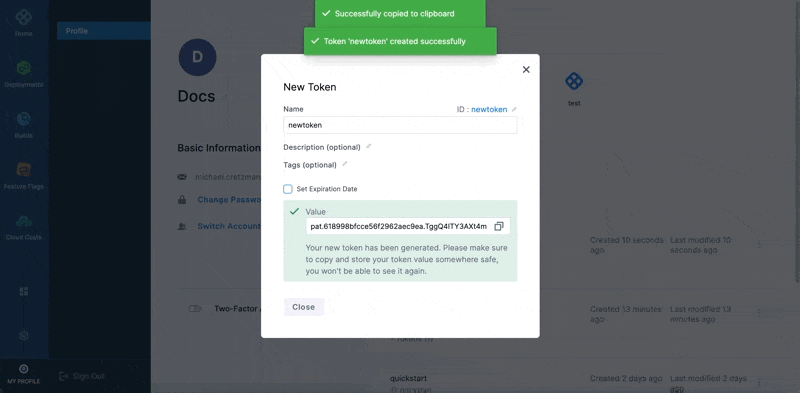
Your new token is generated.
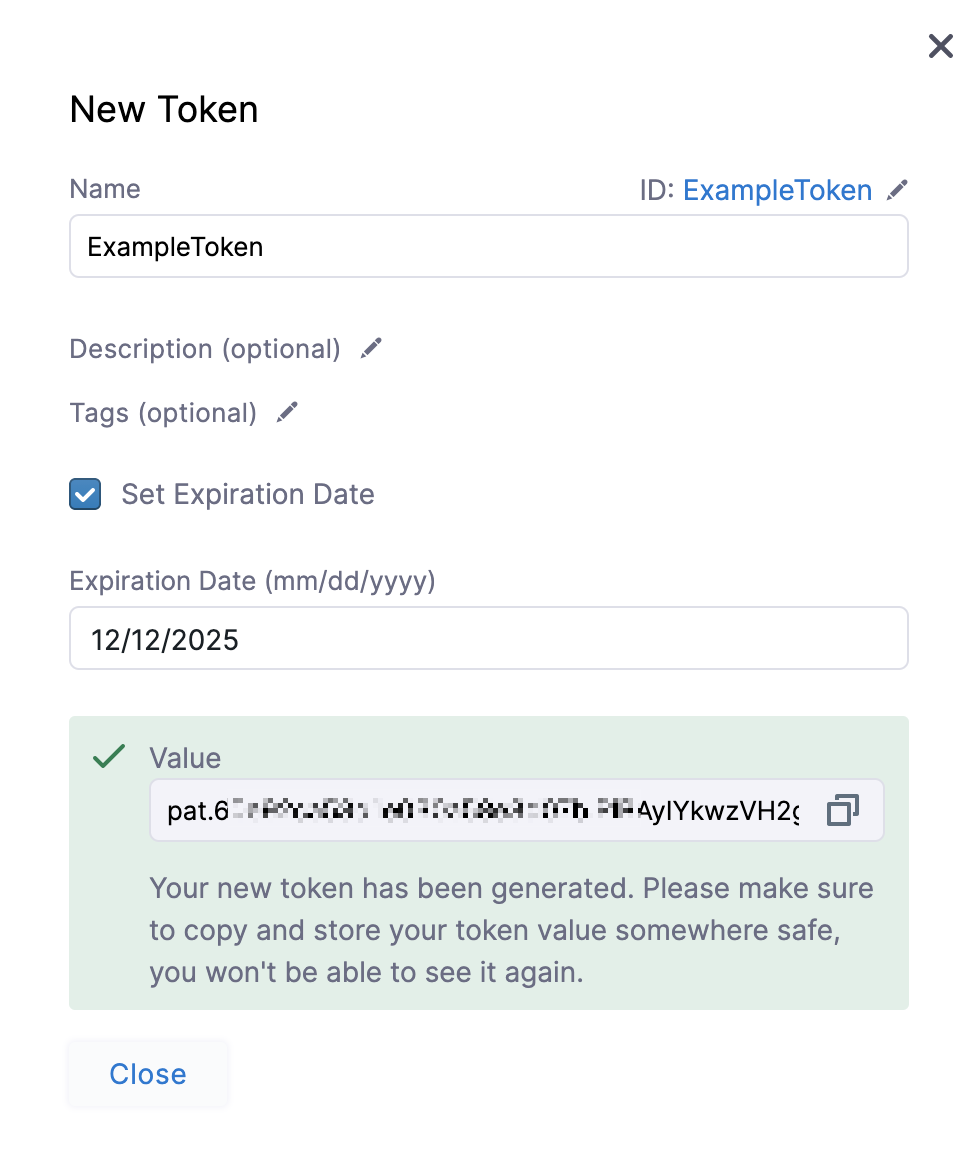
Please copy and store your token value somewhere safe. You won't be able to see it again.
Your API keys carry many privileges, so be sure not to share them in publicly accessible areas. Make sure you always use the updated API Key value after you rotate the token. For more details, go to Rotate Token.
Service Account Tokens
You can also use service account tokens instead of PAT. For more information, go to Add and Manage Service Accounts.
Step 2: Create a Project via API
Now that we have our token, we can create a Harness Project. A Harness Project is a group of Harness modules and their Pipelines.
To send the API request, you will need your Harness account Id and the token you created.
The account Id can be found in every URL when using Harness following account:
https://app.harness.io/ng/#/account/{accountid}/home/get-started
Open a terminal to run the API request.
We're going to create this Project in the built-in default Organization. If you want to use a different Org, just replace the instances of default in the command.
Copy the following curl command and paste it into a text editor:
curl --location --request POST 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/ng/api/projects?accountIdentifier={accountIdentifier}&orgIdentifier=default' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/yaml' \
--header 'x-api-key: {api-key}' \
--data-raw 'project:
name: APISample
orgIdentifier: default
color: "#0063F7"
description: ''
identifier: APISample
tags: {}
modules: []'
Replace {accountidentifier} with your Harness account Id and {api-key} with the PAT you created.
Paste the updated curl command into a terminal and run it.
The successful response will be something like this:
{"status":"SUCCESS","data":{"project":{"orgIdentifier":"default","identifier":"APISample","name":"APISample","color":"#0063F7","modules":["CD","CI","CV","CF","CE","CORE","PMS","TEMPLATESERVICE"],"description":"","tags":{}},"createdAt":1636410020671,"lastModifiedAt":1636410020671},"metaData":null,"correlationId":"3aa01bdd-e45c-4eb2-a65d-7673ec287fcc"}
Open Harness to see your new Project (you might need to refresh the Project page):
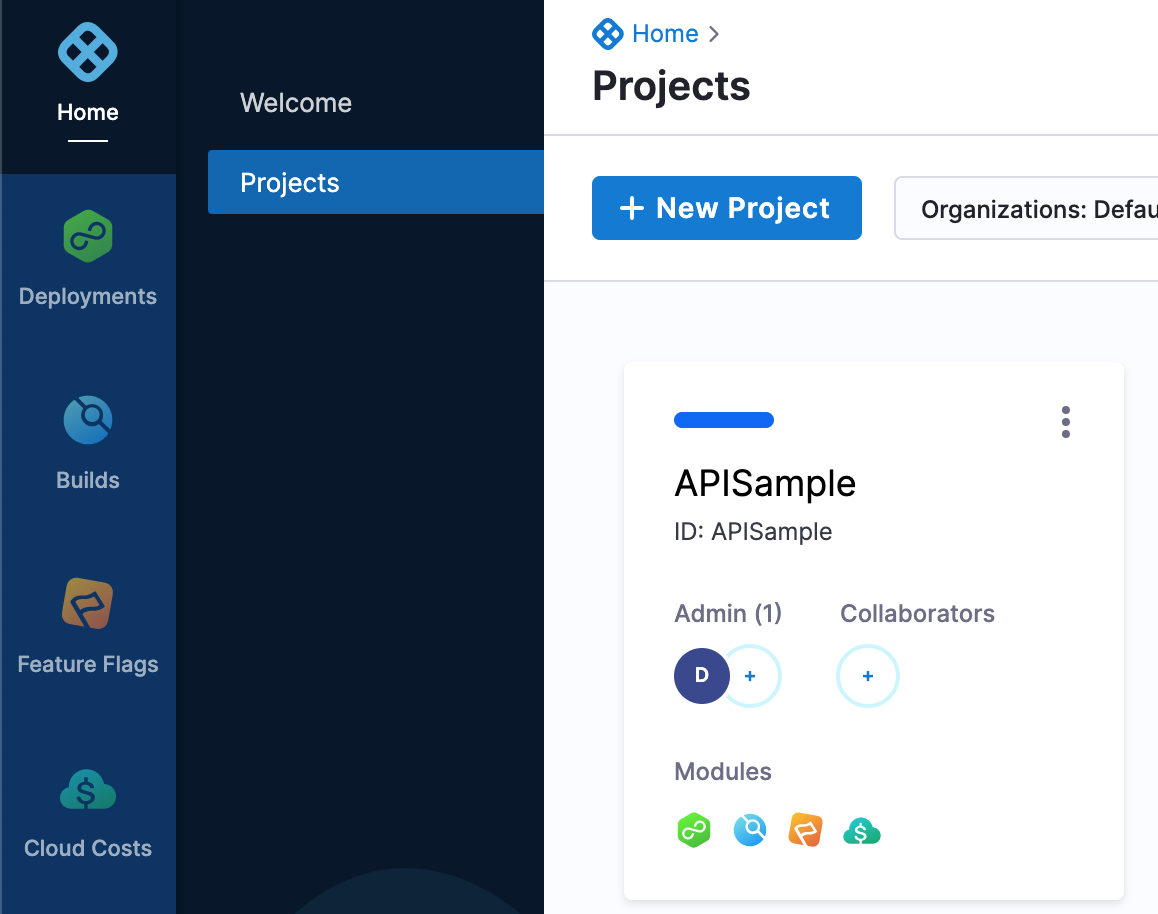
Step 3: Create a Connector via API
A Harness Connector contains the information necessary to integrate and work with 3rd party tools.
Harness uses Connectors at Pipeline runtime to authenticate and perform operations with a 3rd party tool.
Let's create a Docker Registry Connector that connects to Docker Hub anonymously.
Copy the following curl command:
curl --location --request POST 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/ng/api/connectors?accountIdentifier=H5W8iol5TNWc4G9h5A2MXg' \
--header 'Content-Type: text/yaml' \
--header 'x-api-key: pat.6186f434cce56f2962ae9bbf.HpGoIx7O4ZvFSE4rEuuF' \
--data-raw 'connector:
name: dockerhub
identifier: dockerhub
description: ""
tags: {}
orgIdentifier: default
projectIdentifier: APISample
type: DockerRegistry
spec:
dockerRegistryUrl: https://index.docker.io/v2/
providerType: DockerHub
auth:
type: Anonymous'
Replace {accountidentifier} with your Harness account Id and {api-key} with the PAT you created.
Paste the updated curl command into a terminal and run it.
The successful response will be something like this:
{"status":"SUCCESS","data":{"connector":{"name":"dockerhub","identifier":"dockerhub","description":"","orgIdentifier":"default","projectIdentifier":"APISample","tags":{},"type":"DockerRegistry","spec":{"dockerRegistryUrl":"https://index.docker.io/v2/","providerType":"DockerHub","auth":{"type":"Anonymous"},"delegateSelectors":[]}},"createdAt":1636476303660,"lastModifiedAt":1636476303657,"status":null,"activityDetails":{"lastActivityTime":1636476303657},"harnessManaged":false,"gitDetails":{"objectId":null,"branch":null,"repoIdentifier":null,"rootFolder":null,"filePath":null},"entityValidityDetails":{"valid":true,"invalidYaml":null}},"metaData":null,"correlationId":"fab579bc-bc6f-46d1-95be-d6ed02844cd4"}
Take a look at your new Connector in Harness:
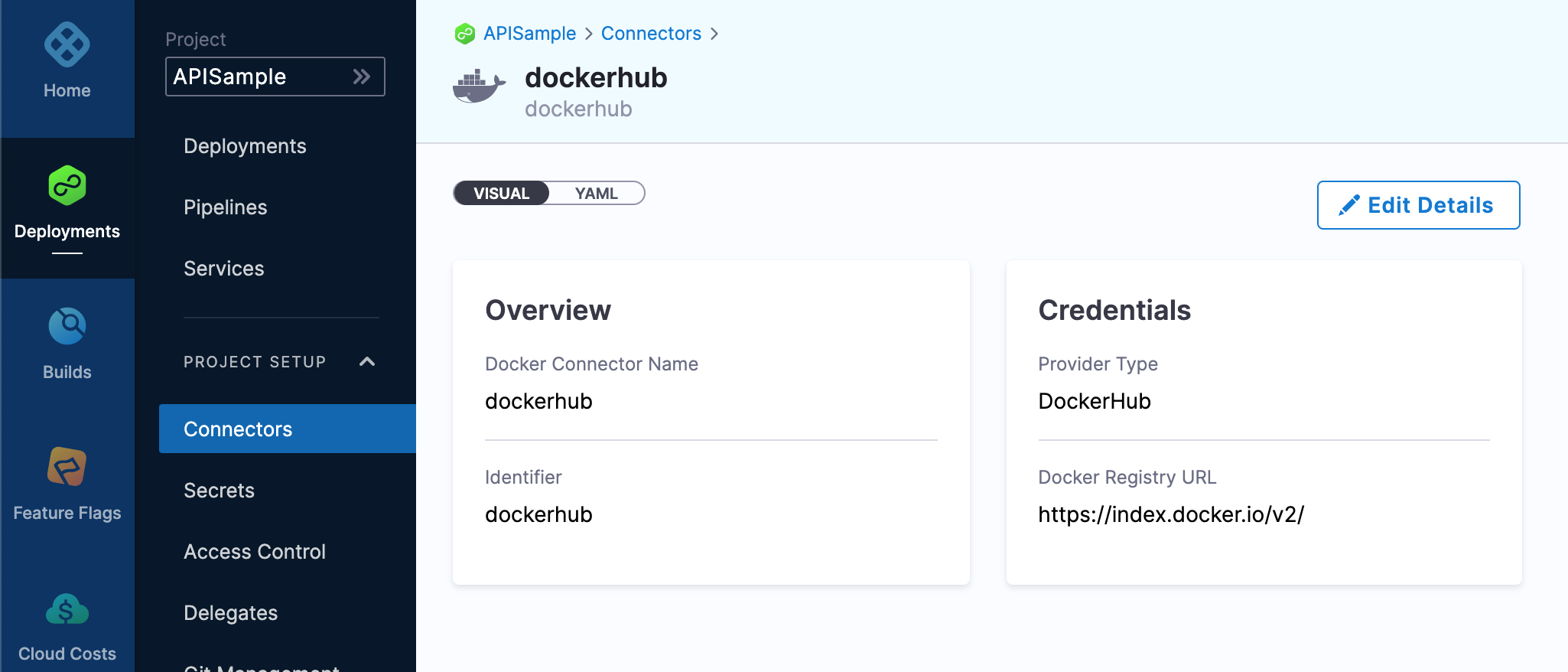
Step 4: Create a Pipeline
A CD Pipeline is an end-to-end process that delivers a new version of your software.
Let's create a simple CD Pipeline that contains a Shell Script step that echoes "hello world!".
The Pipeline uses Runtime Inputs (<+input>) for most settings.Copy the following curl command:
curl --location --request POST 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/pipeline/api/pipelines?accountIdentifier={accountidentifier}&orgIdentifier=default&projectIdentifier=APISample' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/yaml' \
--header 'x-api-key: {api-key}' \
--data-raw 'pipeline:
name: apiexample
identifier: apiexample
projectIdentifier: APISample
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: demo
identifier: demo
description: ""
type: Deployment
spec:
serviceConfig:
serviceRef: <+input>
serviceDefinition:
type: Kubernetes
spec:
variables: []
infrastructure:
environmentRef: <+input>
infrastructureDefinition:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: <+input>
namespace: <+input>
releaseName: release-<+INFRA_KEY>
allowSimultaneousDeployments: false
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: shell
identifier: shell
spec:
shell: Bash
onDelegate: true
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: echo "hello world!"
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
executionTarget: {}
timeout: 10m
rollbackSteps: []
tags: {}
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- AllErrors
action:
type: StageRollback'
This sample using Runtime Inputs for many settings.Replace {accountidentifier} with your Harness account Id and {api-key} with the PAT you created.
Paste the updated curl command into a terminal and run it.
The successful response will be something like this:
{"status":"SUCCESS","data":"apiexample","metaData":null,"correlationId":"6375a5cc-f1ce-4a82-9428-0cf6ead6140c"}
Take a look at your new Pipeline in Harness:
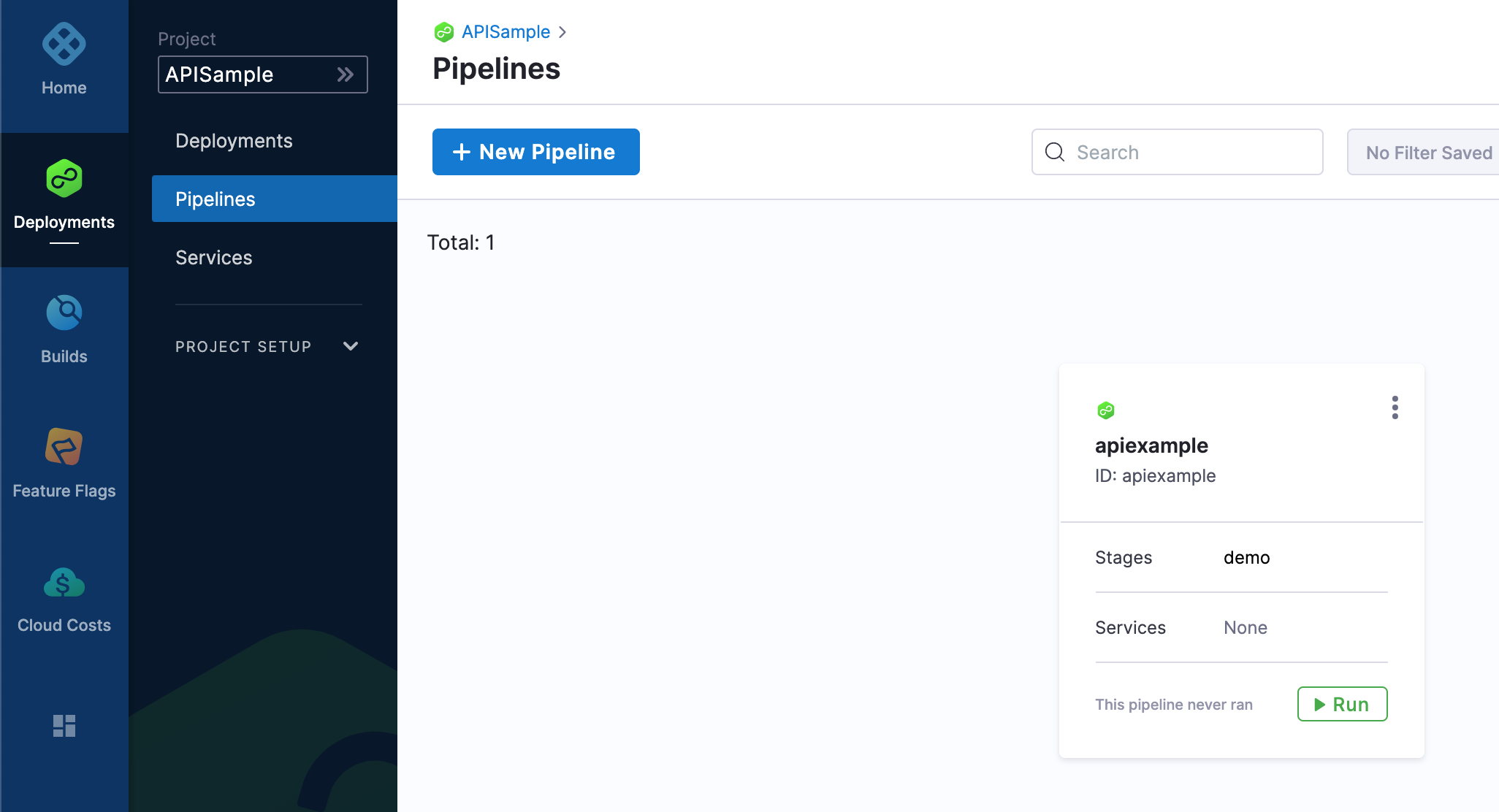 You're all done.
You're all done.
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Authenticate with Harness via API using API keys.
- Onboard Harness Projects, Connectors, and Pipelines using the Harness API.
To explore the Harness API, go to Harness API Reference Docs.
Notes
Rate Limiting: Harness uses rate limiting to control traffic and ensure the stability of the platform. For platform rate limit information, go to Rate limits.
Cross-origin Resource Sharing (CORS): Harness APIs support CORS. This allows interactions between resources from different origins, which is normally prohibited to prevent malicious behavior. Each request must provide credentials (personal access tokens and service access tokens are both supported options).
Errors: Harness uses conventional HTTP response codes to indicate the success or failure of an API request.
| HTTPS Status Code | Summary |
| 200 - OK | The request has been processed successfully on the server. |
| 400 - Bad Request | The request was not processed successfully due to incorrect syntax or missing parameters. |
| 401 - Unauthorized | The request was unauthorized due to an invalid API Key. |
| 402 - Request Failed | The request cannot be processed. |
| 403 - Forbidden | The API Key does not have permission to perform the request. |
| 404 - Not Found | The requested resource does not exist. |
| 429 - Server Errors | The rate limit is exceeded. |
| 500, 502, 503, 504 - Server Errors | The Harness server encountered an unexpected error. |