Add Lambda Functions
This content is for Harness FirstGen. Switch to NextGen.This topic describes how to create a Harness Application and adds a Service that uses a function file, runtime, and handler information to define the Lambda function to deploy.
Before You Begin
Review: Artifact Source Support
Harness supports the following artifact sources with Lambda:
Supported runtimes
Harness supports the following runtimes:
- nodejs4.3
- nodejs4.3-edge
- nodejs6.10
- nodejs8.10
- nodejs10.x
- nodejs12.x
- nodejs14.x
- nodejs16.x
- nodejs18.x
- java8.al2
- java11
- python2.7
- python3.6
- python3.7
- python3.8
- python3.9
- dotnetcore1.0
- dotnetcore2.0
- dotnetcore2.1
- dotnetcore3.1
- dotnet6
- go1.x
- ruby2.5
- ruby2.7
- provided
- provided.al2
Step 1: Create a Harness Lambda Service
To add the Lambda Service, do the following:
- In your new Application, click Services. The Services page appears.
- In the Services page, click Add Service. The Service dialog appears.
- In Name, enter a name for your Service, such as aws-lambda. You will use this name to select this Service when you set up a Harness Environment and Workflow.
- In Description, enter a description for your Service.
- In Deployment Type, select AWS Lambda.
- Click SUBMIT. The new Service is displayed.
Step 2: Add Lambda Functions
An Artifact Source in a Lambda Service is the Lambda function file you want to deploy. The Artifact Source uses the AWS Cloud Provider you set up for your Harness account, as described in Delegate and Connectors for Lambda.
To add an Artifact Source to this Service, do the following:
In your Lambda Service, click Add Artifact Source, and then click Amazon S3. For information on using a Custom Artifact Source, see Custom Artifact Source.
The Amazon S3 Artifact Source dialog appears.
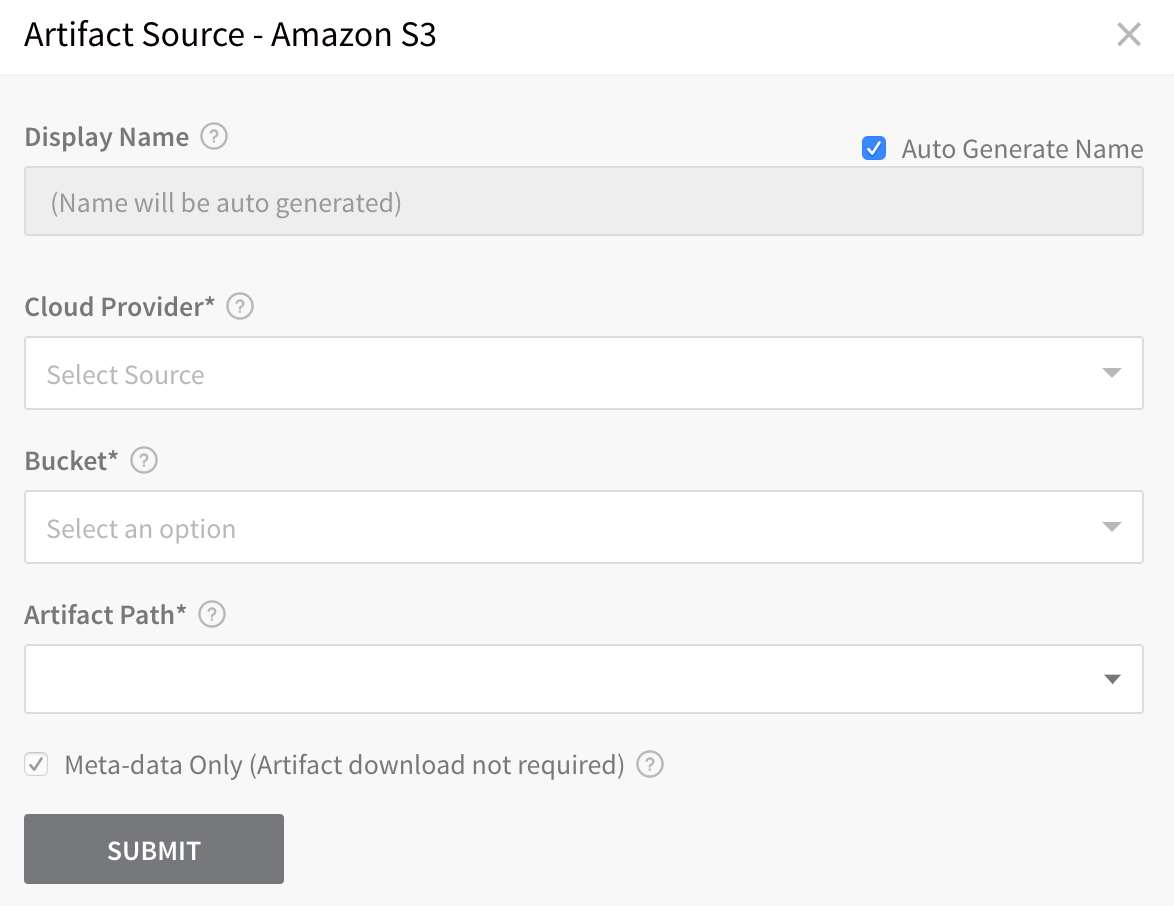
In Cloud Provider, select the AWS Cloud Provider you set up in Delegate and Connectors for Lambda.
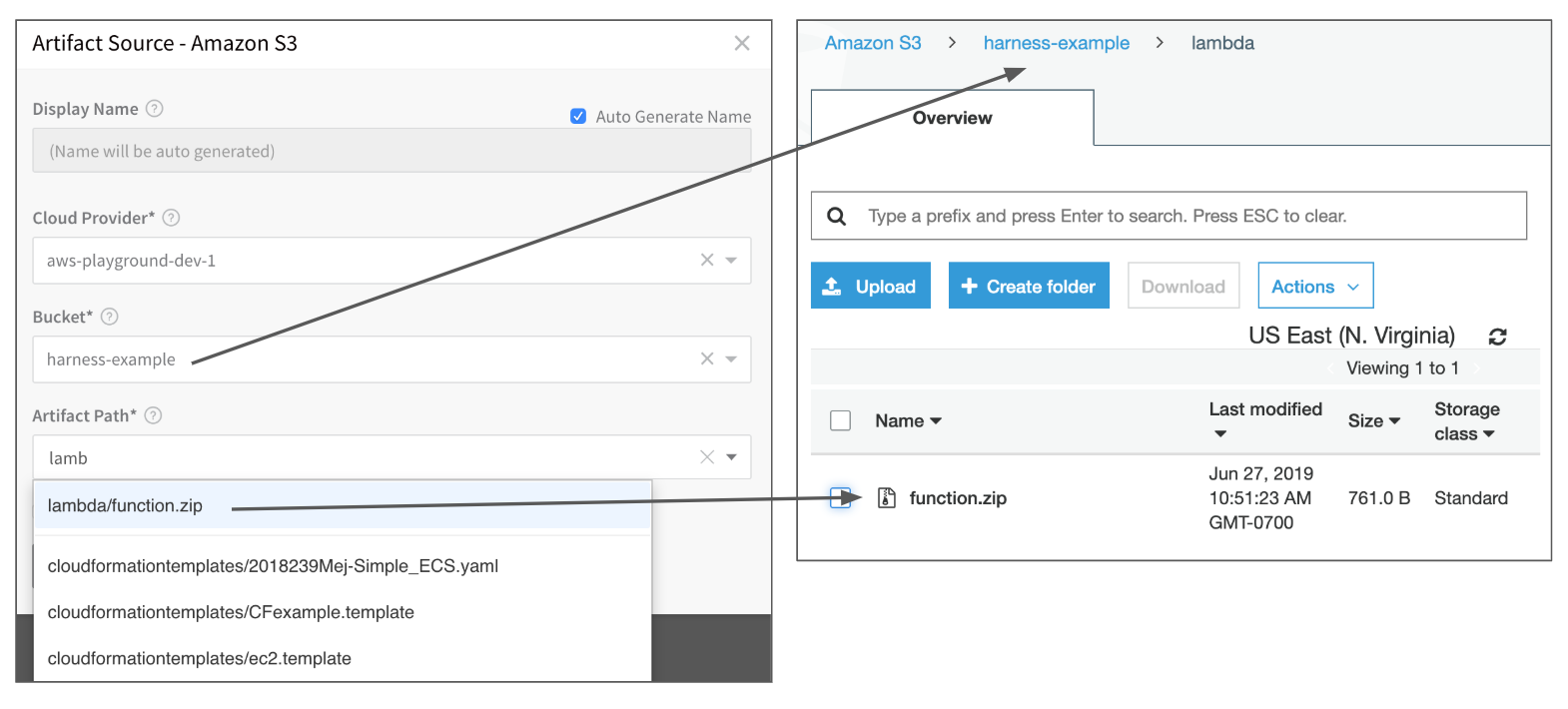
In Bucket, select the S3 bucket containing the Lambda function zip file you want.
In Artifact Path, select the Lambda function zip file containing your functions. Here is how your S3 bucket and file relate to the Artifact Source dialog:
The Meta-data Only option is selected by default. Harness will not copy the actual zip file. During runtime, Harness passes the metadata to Lambda where it is used to obtain the file.
Click SUBMIT. The Lambda function file is added as an Artifact Source.
Step 3: Lambda Function Specification
In Lambda Function Specification, you provide details about the Lambda functions in the zip file in Artifact Source.
Click Lambda Function Specification. The AWS Lambda Function Specifications dialog appears.
The details you provide are very similar to the options in the AWS CLI aws lambda create-function command. For more information, see create-function from AWS.
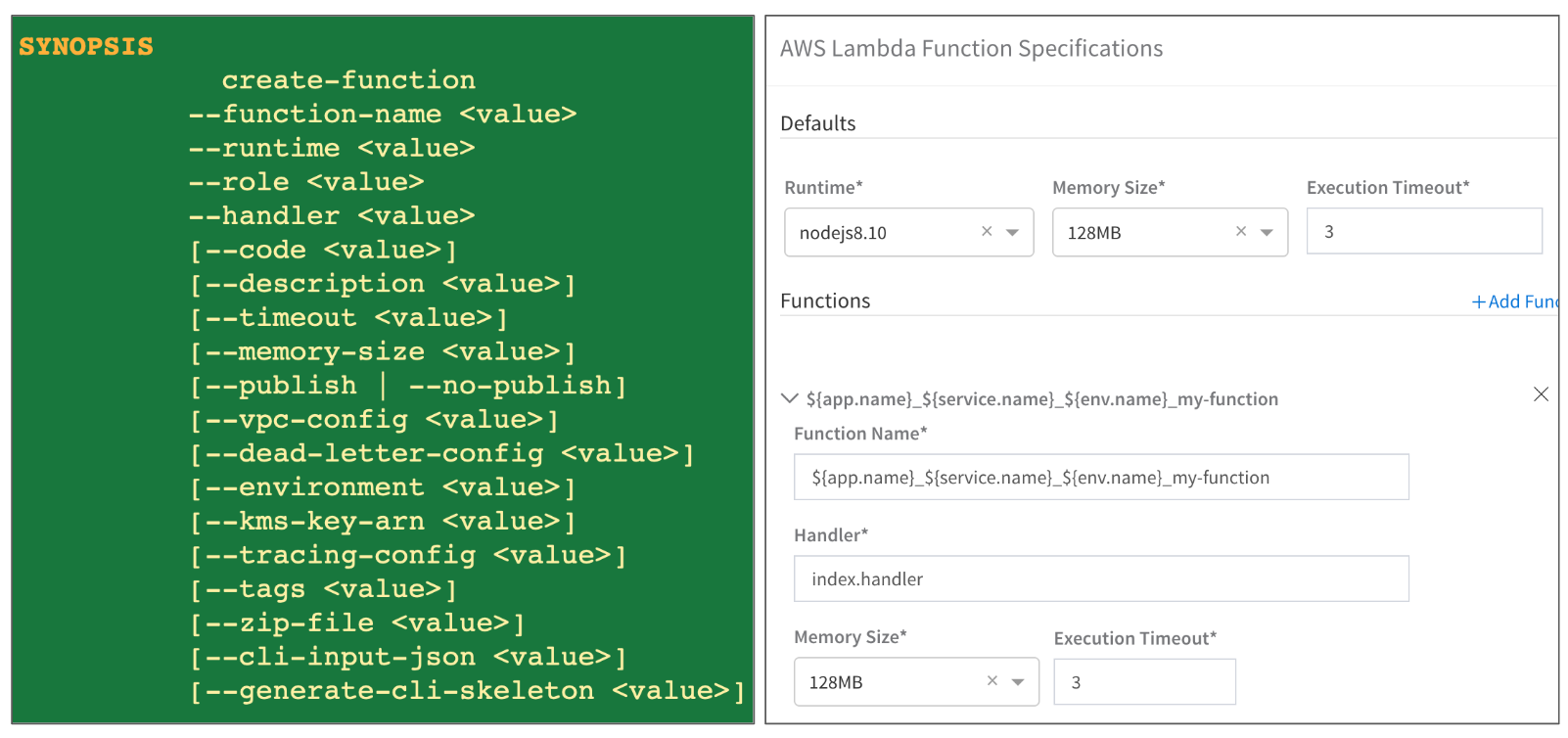
Some of the options are specified in Harness Environments and Workflows to help you reuse the Service with multiple Environments and Workflows.
By default, the AWS Lambda Function Specifications dialog displays a function. If you have multiple Lambda functions in the zip file in Artifact Source, click Add Function and provide details for each function.
For each function in the Functions section, enter the following function information:
- Runtime - The Lambda runtime that executes your function. This is the runtime for all functions in this spec. AWS can change its runtime version support. For example, AWS no longer supports nodejs6.10.
- Function Name - The name of your function. This name will become part of the function ARN in Lambda.
Harness uses default variables for the name that include your Harness Application, Service, and Environment names (${app.name}_${service.name}_${env.name}). If you use these, you need to append a unique suffix to each function name, for example${app.name}_${service.name}_${env.name}_my-function. Or you can replace the entire name. - Handler - The method that the runtime executes when your function is invoked. The format for this value varies per language. See Programming Model for more information.
For example, let's look at a Node.js function in a file named index.js:
exports.handler = async function(event, context) {
console.log("EVENT: \n" + JSON.stringify(event, null, 2))
return context.logStreamName
}
The value of the Handler setting is the file name (index) and the name of the exported handler module, separated by a dot. In our example, the handler is index.handler. This indicates the handler module that's exported by index.js.
- Memory Size - The amount of memory available to the function during execution. Choose an amount between 128 MB and 3,008 MB in 64 MB increments. There are two Execution Timeout settings. A default setting and a function-specific setting.
- Execution Timeout - The amount of time that Lambda allows a function to run before stopping it. The default is 3 seconds. The maximum allowed value is 900 seconds. There are two Execution Timeout settings. A default setting and a function-specific setting.
When you are done, the AWS Lambda Function Specifications dialog will look something like this:
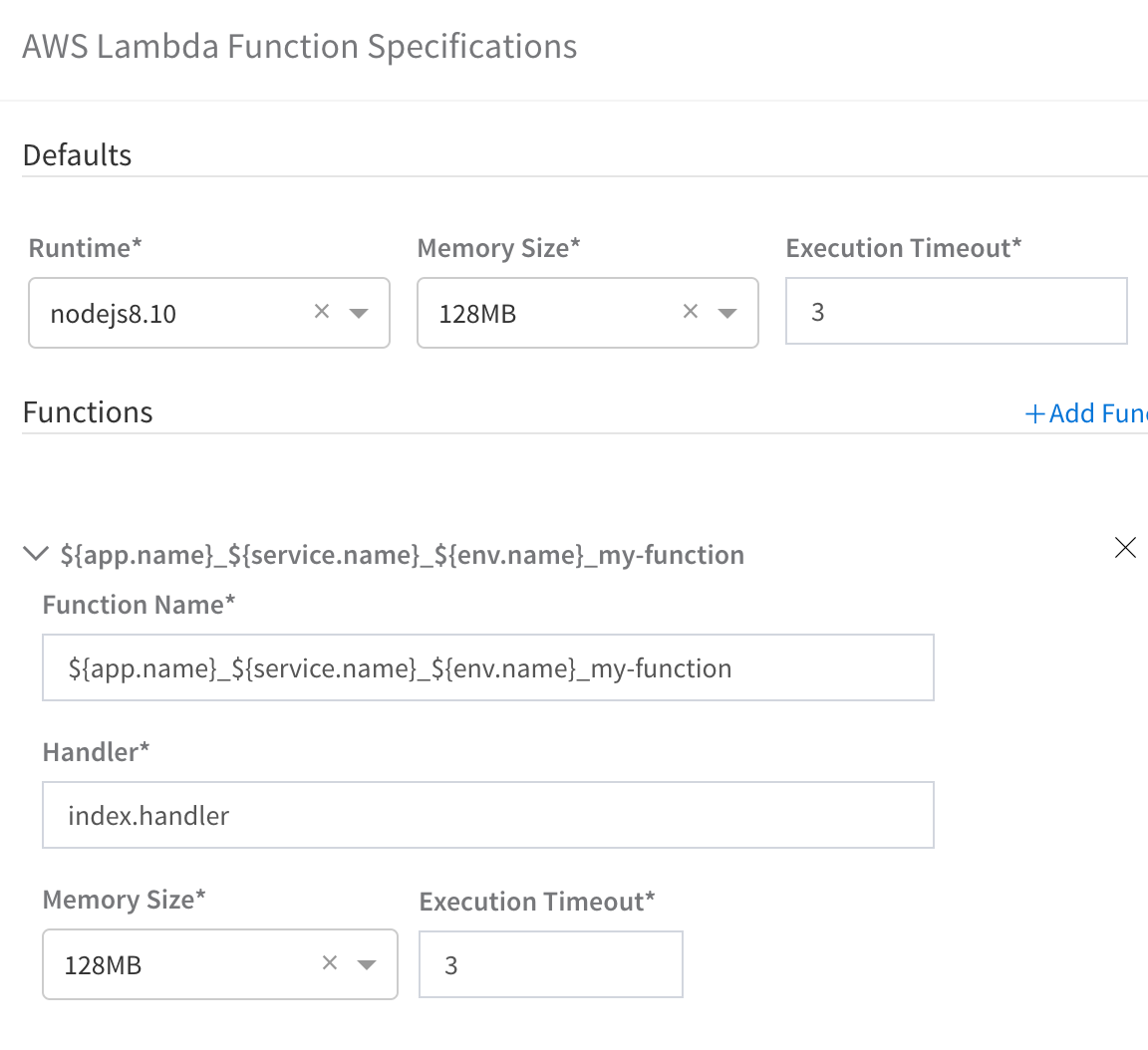
When you are done, click Submit. Your function is added to the Service.
Option: Lambda Environment Variables using Service Config Variables
You can use Config Variables in your Service to create Lambda Environment Variables.
Encrypted Config Variables will appear as plaintext Environment Variables in Lambda.
When you deploy your function, Harness replaces any existing Environment variables with the variables you added as Service Config Variables.