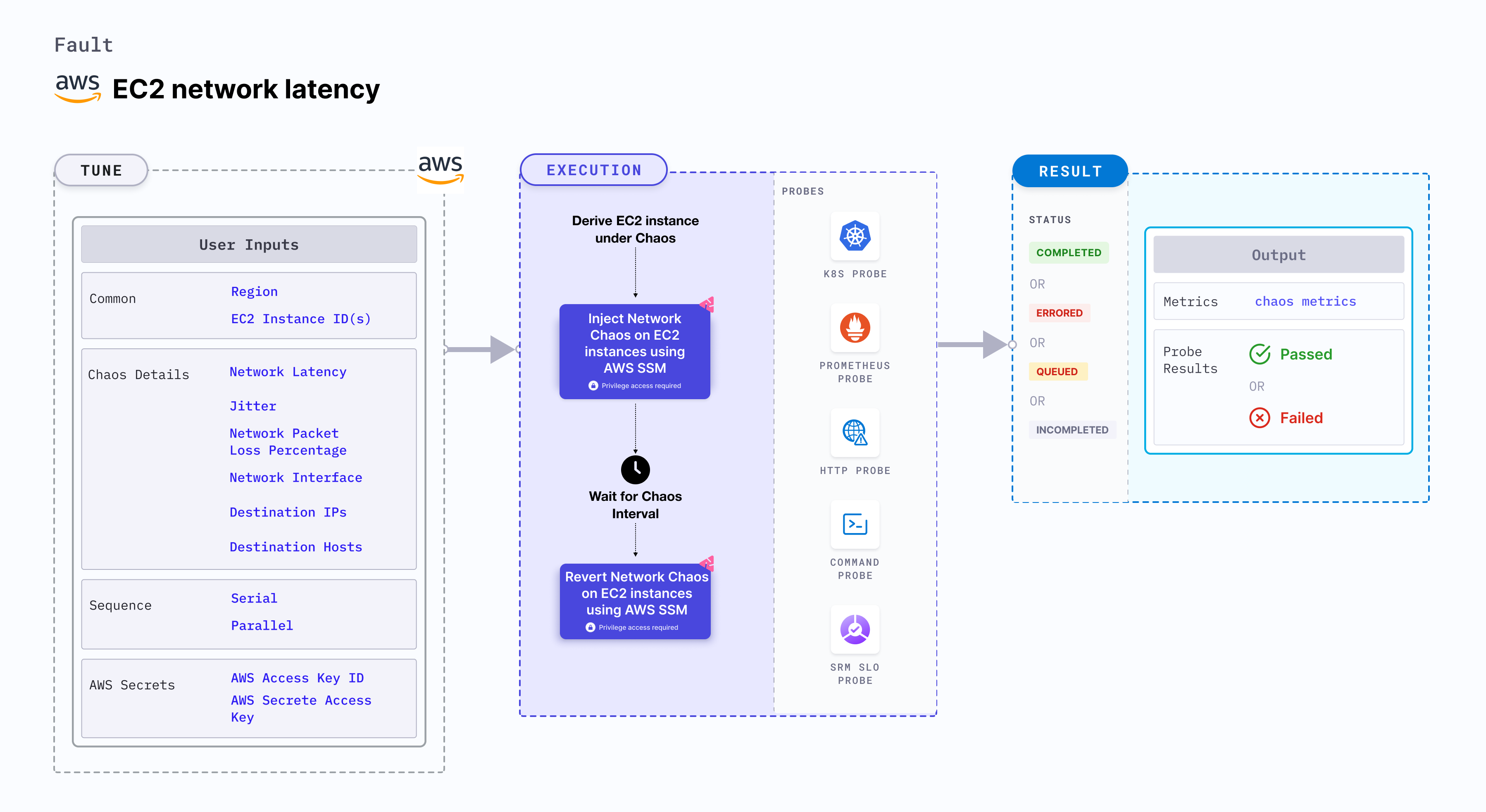
EC2 network latency
Introduction
EC2 network latency causes flaky access to the application (or services) by injecting network packet latency to EC2 instance(s). This fault:
- Degrades the network without marking the EC2 instance as unhealthy (or unworthy) of traffic, which is resolved using a middleware that switches traffic based on SLOs (performance parameters).
- May stall the EC2 instance or get corrupted waiting endlessly for a packet.
- Limits the impact (blast radius) to the traffic that you wish to test, by specifying the IP addresses.
Use cases
EC2 network latency:
- Determines the performance of the application (or process) running on the EC2 instances.
- Simulates a consistently slow network connection between microservices (for example, cross-region connectivity between active-active peers of a given service or across services or poor cni-performance in the inter-pod-communication network).
- Simulates jittery connection with transient latency spikes between microservices.
- Simulates a slow response on specific third party (or dependent) components (or services), and degraded data-plane of service-mesh infrastructure.
- Kubernetes version 1.17 or later is required to execute the fault.
- SSM agent is installed and running on the target EC2 instance.
- The EC2 instance should be in healthy state.
- The Kubernetes secret should have the AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key credentials in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. A sample secret file looks like:apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: cloud-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
cloud_config.yml: |-
# Add the cloud AWS credentials respectively
[default]
aws_access_key_id = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX - We recommend you use the same secret name, that is,
cloud-secret. Otherwise, you will need to update theAWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILEenvironment variable in the fault template, and you won't be able to use the default health check probes. - Go to the superset permission/policy to execute all AWS faults and AWS named profile for chaos to use a different profile for AWS faults.
- Go to the common tunables to tune the common tunables for all the faults.
Below is an example AWS policy to execute the fault.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ssm:GetDocument",
"ssm:DescribeDocument",
"ssm:GetParameter",
"ssm:GetParameters",
"ssm:SendCommand",
"ssm:CancelCommand",
"ssm:CreateDocument",
"ssm:DeleteDocument",
"ssm:GetCommandInvocation",
"ssm:UpdateInstanceInformation",
"ssm:DescribeInstanceInformation"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2messages:AcknowledgeMessage",
"ec2messages:DeleteMessage",
"ec2messages:FailMessage",
"ec2messages:GetEndpoint",
"ec2messages:GetMessages",
"ec2messages:SendReply"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus",
"ec2:DescribeInstances"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
Fault tunables
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| EC2_INSTANCE_ID | ID of the target EC2 instance. | For example, i-044d3cb4b03b8af1f. |
| REGION | The AWS region ID where the EC2 instance has been created. | For example, us-east-1. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Default: 30 s. |
| CHAOS_INTERVAL | Time interval between two successive instance terminations (in seconds). | Default: 30 s. |
| AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE | Provide the path for AWS secret credentials. | Default: /tmp/cloud_config.yml. |
| INSTALL_DEPENDENCY | Select to install dependencies used to run the network chaos. It can be either True or False. | If the dependency already exists, you can turn it off. Defaults to True. |
| NETWORK_LATENCY | The latency/delay in milliseconds. | Default: 2000, provide numeric value only. |
| JITTER | The network jitter value in ms. | Default: 0, provide numeric value only. |
| DESTINATION_IPS | IP addresses of the services or the CIDR blocks(range of IPs), the accessibility to which is impacted. | Comma-separated IP(S) or CIDR(S) can be provided. If not provided, it will induce network chaos for all ips/destinations. |
| DESTINATION_HOSTS | DNS names of the services, the accessibility to which, is impacted. | If not provided, it will induce network chaos for all ips/destinations or DESTINATION_IPS if already defined. |
| NETWORK_INTERFACE | Name of ethernet interface considered for shaping traffic. | Default: `eth0`. |
| SEQUENCE | It defines the sequence of chaos execution for multiple instances. | Default: parallel. Supports serial sequence. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s. |
Network packet latency
Network packet latency (delay) that is injected on the EC2 instances. Tune it by using the NETWORK_LATENCY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects the chaos into the egress traffic
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ec2-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# network packet latency
- name: NETWORK_LATENCY
value: '2000'
- name: EC2_INSTANCE_ID
value: 'instance-1'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-west-2'
Run with jitter
Introduces a network delay variation (in ms). Tune it by using the JITTER environment variable. Its default value is 0.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects the chaos into the egress traffic
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ec2-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# value of the network latency jitter (in ms)
- name: JITTER
value: '200'
- name: NETWORK_LATENCY
value: '2000'
- name: EC2_INSTANCE_ID
value: 'instance-1'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-west-2'
Run with destination IPs and destination hosts
Interruption of IPs/hosts. By default, all IPs/hosts are interrupted. Tune specific IPs/hosts by using the DESTINATION_IPS and DESTINATION_HOSTS environment variables, respectively.
DESTINATION_IPS: It contains the IP addresses of the services or the CIDR blocks (range of IPs) whose accessibility is impacted.
DESTINATION_HOSTS: It contains the DNS names of the services whose accessibility is impacted.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects the chaos into the egress traffic for specific IPs/hosts
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ec2-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# supports comma-separated destination ips
- name: DESTINATION_IPS
value: '8.8.8.8,192.168.5.6'
# supports comma-separated destination hosts
- name: DESTINATION_HOSTS
value: 'google.com'
- name: EC2_INSTANCE_ID
value: 'instance-1'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-west-2'
Network interface
Name of the ethernet interface considered for shaping traffic. Tune it by using the NETWORK_INTERFACE environment variable. Its default value is eth0.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects the chaos into the egress traffic for specific network interface
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ec2-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# name of the network interface
- name: NETWORK_INTERFACE
value: 'eth0'
- name: EC2_INSTANCE_ID
value: 'instance-1'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-west-2'