EC2 stop by ID
Introduction
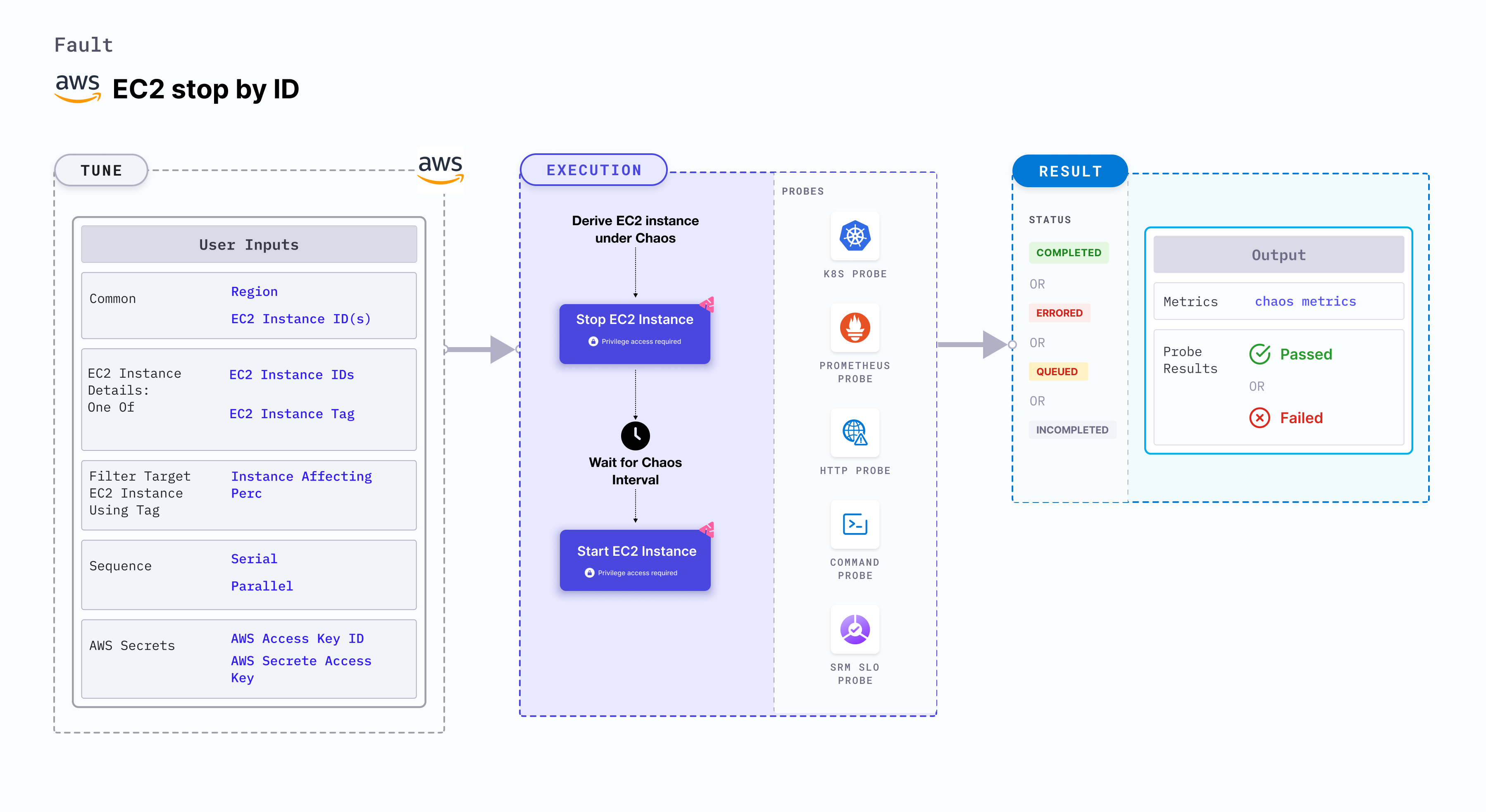
EC2 stop by ID stops an EC2 instance using the provided instance ID or list of instance IDs and brings back the instance after a specific duration. When the MANAGED_NODEGROUP environment variable is enabled, the fault will not try to start the instance after chaos. Instead, it checks for the addition of a new node instance to the cluster.
Use cases
EC2 stop by ID:
- Determines the performance of the application (or process) running on the EC2 instance.
- Determines the resilience of an application to unexpected halts in the EC2 instance by validating its failover capabilities.
- Kubernetes version 1.17 or later is required to execute the fault.
- Access to start and stop an EC2 instance in AWS.
- The EC2 instance should be in a healthy state.
- The Kubernetes secret should have the AWS access configuration(key) in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. Below is the sample secret file.apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: cloud-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
cloud_config.yml: |-
# Add the cloud AWS credentials respectively
[default]
aws_access_key_id = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX - We recommend you use the same secret name, that is,
cloud-secret. Otherwise, update theAWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILEenvironment variable in the fault template, and you won't be able to use the default health check probes. - Go to AWS named profile for chaos to use a different profile for AWS faults and the superset permission/policy to execute all AWS faults.
- Go to the common tunables and AWS-specific tunables to tune the common tunables for all faults and AWS-specific tunables.
If the target EC2 instance is a part of a managed node group, drain the target node of any application running on it. Isolate the target node before running the fault so that the faulty pods are not scheduled on it.
Below is an example AWS policy to execute the fault.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:StartInstances",
"ec2:StopInstances",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus",
"ec2:DescribeInstances"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingInstances"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Fault tunables
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| EC2_INSTANCE_ID | Instance ID of the target EC2 instance. Multiple IDs can also be provided as a comma(,) separated values. | Multiple IDs can be provided as `id1,id2`. |
| REGION | The region name of the target instance. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Defaults to 30s. |
| CHAOS_INTERVAL | The interval (in sec) between successive instance termination. | Defaults to 30s. |
| MANAGED_NODEGROUP | Set to enable if the target instance is the part of self-managed nodegroups. | Defaults to disable. |
| SEQUENCE | It defines sequence of chaos execution for multiple instance. | Defaults to parallel. Supports serial sequence as well. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30s. |
Stop Instances By ID
Comma-separated list of target instance IDs. Tune it by using the EC2_INSTANCE_ID environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# contains the instance id, to be terminated/stopped
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ec2-terminate-by-id
spec:
components:
env:
# ID of the EC2 instance
- name: EC2_INSTANCE_ID
value: 'instance-1'
# region for the EC2 instance
- name: REGION
value: 'us-east-1'