Lambda delete event source mapping
Introduction
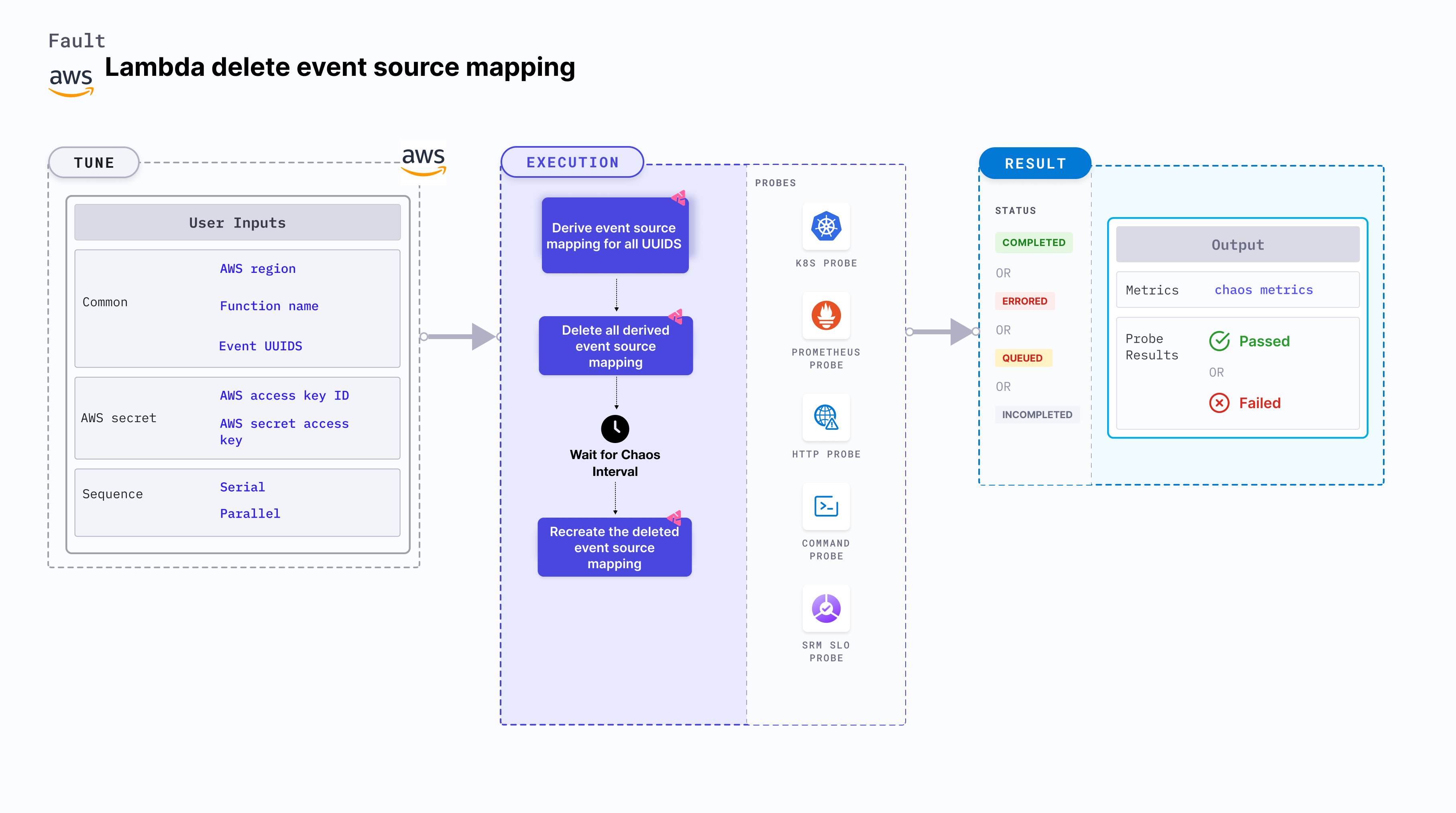
Lambda delete event source mapping removes the event source mapping from an AWS Lambda function for a specific duration. Deleting an event source mapping from a Lambda function is critical. It can lead to failure in updating the database on an event trigger, which can break the service.
Use cases
Lambda delete event source mapping:
- Determines the performance of the application (or service) without the event source mapping that may cause missing entries in a database.
- Determines whether proper error handling or auto-recovery options have been configured for the application.
note
- Kubernetes version 1.17 or later is required to execute this fault.
- AWS Lambda event source mapping must be healthy and attached to the Lambda function.
- Kubernetes secret should have the AWS access configuration(key) in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. A secret file looks like this:apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: cloud-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
cloud_config.yml: |-
# Add the cloud AWS credentials respectively
[default]
aws_access_key_id = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX - Harness recommends using the same secret name, that is,
cloud-secret. Otherwise, you must update theAWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILEenvironment variable in the fault template and you won't be able to use the default health check probes. - Refer to AWS named profile for chaos to use a different profile for AWS faults.
- Refer to the superset permission/policy to execute all AWS faults.
- Refer to the common tunables and AWS-specific tunables to tune the common tunables for all faults and AWS-specific tunables.
Below is an example AWS policy to execute the fault.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:ListEventSourceMappings",
"lambda:DeleteEventSourceMapping",
"lambda:UpdateEventSourceMapping",
"lambda:CreateEventSourceMapping",
"lambda:UpdateFunctionConfiguration",
"lambda:GetFunctionConcurrency",
"lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:DeleteFunctionConcurrency",
"lambda:PutFunctionConcurrency"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Fault tunables
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FUNCTION_NAME | Function name of the target Lambda function. Supports single function name. | For example, test-function |
| EVENT_UUIDS | Provide the UUID for the target event source mapping. | Can provide multiple values as comma-separated values. For example, id1,id2 |
| REGION | The region name of the target Lambda function. | For example, us-east-2 |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Default: 30 s |
| SEQUENCE | It defines sequence of chaos execution for multiple instance | Default: parallel. Supports serial and parallel. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injection of chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s |
Multiple event source mapping
Deletes multiple event source mappings for a specific duration using EVENT_UUIDS environment variable. This variable takes the UUID of the events as a comma-separated value.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# contains the removal of multiple event source mapping
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: lambda-delete-event-source-mapping
spec:
components:
env:
# provide UUIDS of event source mapping
- name: EVENT_UUIDS
value: 'id1,id2'
# provide the function name for the chaos
- name: FUNCTION_NAME
value: 'chaos-function'