Add an AWS Secrets Manager
This content is for Harness FirstGen. Switch to NextGen.You can use AWS Secrets Manager for your Harness secrets. AWS Secrets Manager differs from AWS KMS in that AWS Secrets Manager stores both secrets and encryption keys whereas with AWS KMS, Harness stores the secret in its Harness store and retrieves the encryption keys from KMS.
In this topic:
- Before You Begin
- Permissions: Test AWS Permissions
- Step 1: Configure Secrets Manager
- Step 2: Display Name
- Option: Credentials Type
- Option: Assume IAM Role on Delegate
- Option: AWS Access Keys Manually
- Option: Assume Role Using STS on Delegate
- Step 3: Secret Name Prefix
- Step 4: Region
- Step 5: Usage Scope
- Limitations
Before You Begin
Permissions: Test AWS Permissions
Harness uses the same minimum IAM policies for AWS secret manager access as the AWS CLI.
The AWS account you use for the AWS Secret Manager must have the following policies at a minimum:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": {
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"secretsmanager:Describe*",
"secretsmanager:Get*",
"secretsmanager:List*"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
}
These policies let you list secrets which will allow you to add the Secrets Manager and refer to secrets, but it will not let you read secrets values.
The following policy list lets Harness perform all the secrets operations you might need:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": {
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"secretsmanager:CreateSecret",
"secretsmanager:DescribeSecret",
"secretsmanager:DeleteSecret",
"secretsmanager:GetRandomPassword",
"secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"secretsmanager:ListSecretVersionIds",
"secretsmanager:ListSecrets",
"secretsmanager:PutSecretValue",
"secretsmanager:UpdateSecret"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
}
See Using Identity-based Policies (IAM Policies) for Secrets Manager from AWS.
To test use the AWS account when running aws secretsmanager list-secrets on either the Harness Delegate host or another host.
Step 1: Configure Secrets Manager
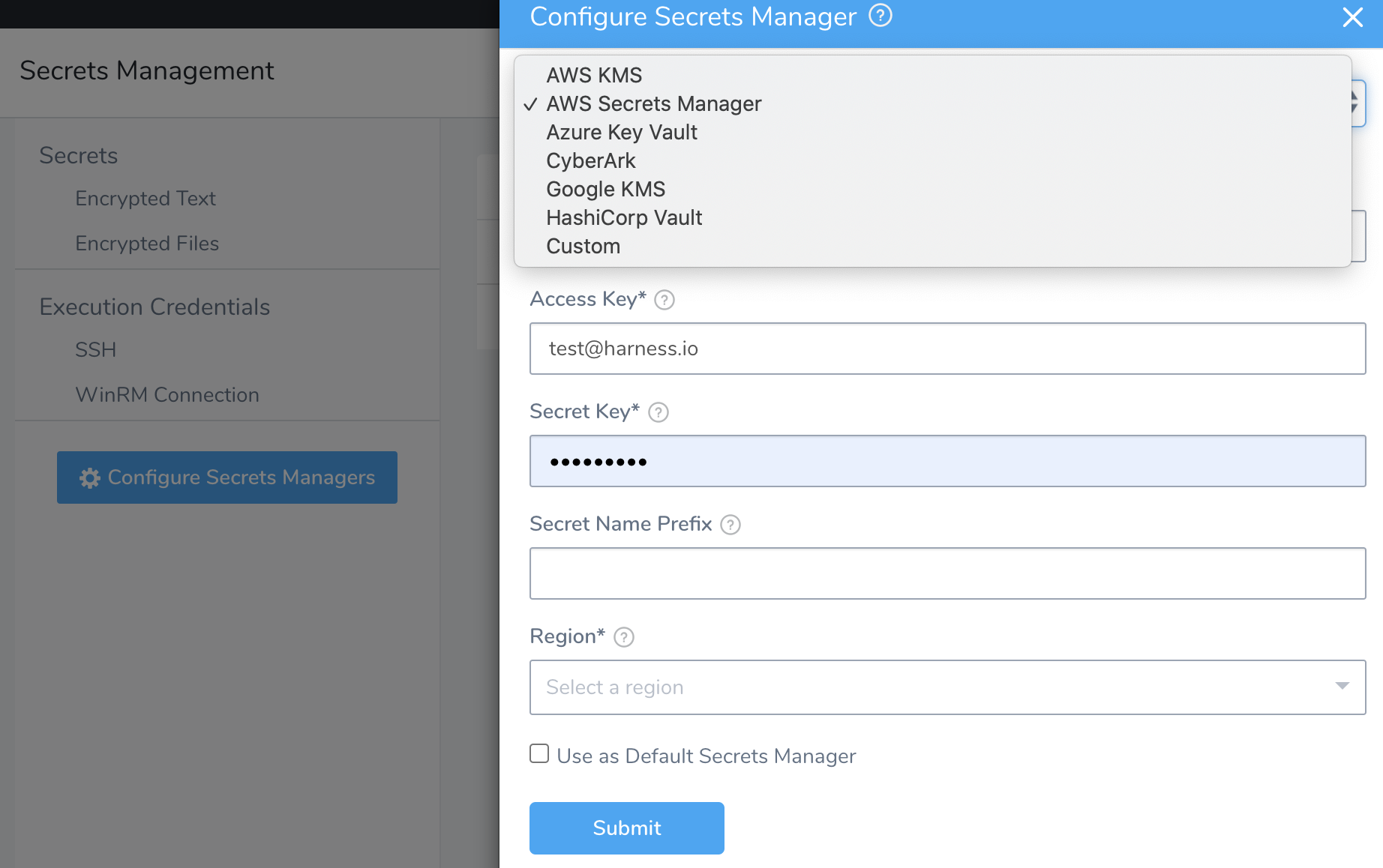
- In Security, select Secrets Management, and then click Configure Secrets Managers. In the resulting Secrets Managers page, the Status column indicates the Default provider.
- Click Add Secrets Manager. The Configure Secrets Manager settings appear.
- Select AWS Secrets Manager from the drop-down list.For information on restrictions on names and maximum quotas, see Quotas for AWS Secrets Manager.
Step 2: Display Name
Enter a name for this secrets manager.
Option: Credentials Type
You can select the following options for authenticating with AWS:
- Assume IAM Role on Delegate.
- Enter AWS Access Keys Manually.
- Assume Role Using STS on Delegate.
Option: Assume IAM Role on Delegate
If you select Assume the IAM Role on Delegate, Harness will authenticate using the IAM role assigned to the AWS host running the Delegate you select using a Delegate Selector.
Delegate Selector
In Delegate Selector, enter the Selector of the Delegate that this Secrets Manager will use for all connections. For information about Selectors, see Select Delegates for Specific Tasks with Selectors.
Option: AWS Access Keys Manually
Use your AWS IAM user login credentials.
Either from the JSON for the Key Policy, or in the AWS IAM console, under Encryption keys, gather the following required details — Display Name, AWS Access Key ID, AWS Secret Key, and AWS Resource Name (ARN).
For more information, see Finding the Key ID and ARN from Amazon.
Access Key
The AWS Access Key ID for the IAM user you want to use to connect to Secrets Manager.
Secret Key
Paste in the contents of the Secret Key corresponding to the Access Key ID.
Option: Assume Role Using STS on Delegate
This option uses the AWS Security Token Service (STS) feature. Typically, you use AssumeRole within your account or for AWS cross-account access.
Role ARN
Enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the role that you want to assume. This is an IAM role in the target deployment AWS account.
External ID
If the administrator of the account to which the role belongs provided you with an external ID, then enter that value.
For more information, see How to Use an External ID When Granting Access to Your AWS Resources to a Third Party from AWS.
Assume Role Duration
This is the AssumeRole Session Duration. See Session Duration in the AssumeRole AWS docs.
Step 3: Secret Name Prefix
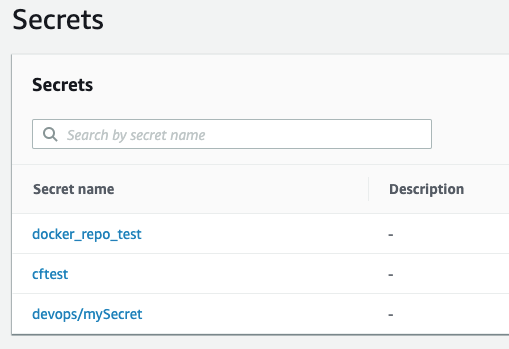
Enter a prefix to be added to all secrets. For example, devops will result in secrets like devops/mysecret. The prefix is not a folder name, but a prefix. Secrets Manager uses is a flat naming method.
Step 4: Region
Select the AWS Region for the Secrets Manager.
Step 5: Usage Scope
See Scope Secret Managers to Applications and Environments.
Limitations
- For limitations of AWS secrets, see Quotas for AWS Secrets Manager.
- Secret names must be alphanumeric (Vault and KMS do not have this limitation). When migrating secrets created using Vault or KMS into AWS Secrets Manager, failures might occur due to the secret name limitation. You will have to rename those secrets into an alphanumeric format before they can be transitioned into AWS Secrets Manager.