Use SSH Key via Kerberos for Server Authentication
Harness supports SSH server authentication using Kerberos, enabling you to SSH into a target host via the Kerberos protocol. For a quick Kerberos summary, see Explain like I’m 5: Kerberos by Lynn Root.
In this topic:
- Before You Begin
- Step 1: Access SSH Configuration
- Step 2: Auth Scheme
- Step 3: Principal
- Step 4: Realm
- Step 5: TGT Generation
- Step 6: Keytab File Path
Before You Begin
- See Harness Key Concepts.
- See Secrets Management Overview.
- Make sure you can generate TGT using
kinitcommand on the machine where the Delegate is running. For more information aboutkinitcommand, see kinit documentation.
Step 1: Access SSH Configuration
- In Secrets Management, click SSH.
- Click Add SSH Key. The SSH Configuration dialog appears.
- Enter a Display Name for the SSH credentials.
Step 2: Auth Scheme
Select Kerberos.
Step 3: Principal
Principal is a string that names a specific entity to which a set of credentials may be assigned. Enter the account name associated with the Kerberos account, such as johndoe.
Step 4: Realm
Realm is the logical network served by a single Kerberos database and a set of Key Distribution Centers (KDCs). Typically, this is the domain where the service (that the user is trying to authenticate with) is located. For example: US-EAST-2.COMPUTE.INTERNAL.Typically, the target host(s) that your SSH connection is intending to authenticate with via Kerberos are located in a domain name with the same name you enter in Realm. For example, ip-172-31-44-168.us-east-2.compute.internal. The realm naming convention is all uppercase letters to differentiate the realm from the internet domain, but the Realm field does not enforce the convention.
Step 5: TGT Generation
Select one of the following options:
- Key Tab File Path (on Delegate) - You can choose this option to generate a new TGT from the KDC every time you authenticate with the service. This ensures that the TGT is always valid and not expired when you try to authenticate.
- Password - Select a password for TGT generation. Make sure you use a Harness Encrypted Text secret to save the password and refer to it using this option. Either select an existing secret from the drop down list or create a new one by clicking + Create Encrypted Text. For more information on creating Encrypted Text, see Harness Encrypted Text secret.
- None - Select this option to skip TGT Generation. If you select this option, you must ensure that the TGT that is on the server running the Harness delegate is always available.
Step 6: Keytab File Path
This field is displayed if you select Key Tab File Path for TGT Generation. Enter the file path to the keytab file on the server running the Harness delegate. For example, /home/johndoe/a.keytab. The file is not uploaded to Harness.
To use the Kerberos SSH connection to connect to a target host, you select it in SSH Connection Attributes while specifying the target host in the Service Infrastructure/ Infrastructure Definition settings of an environment.
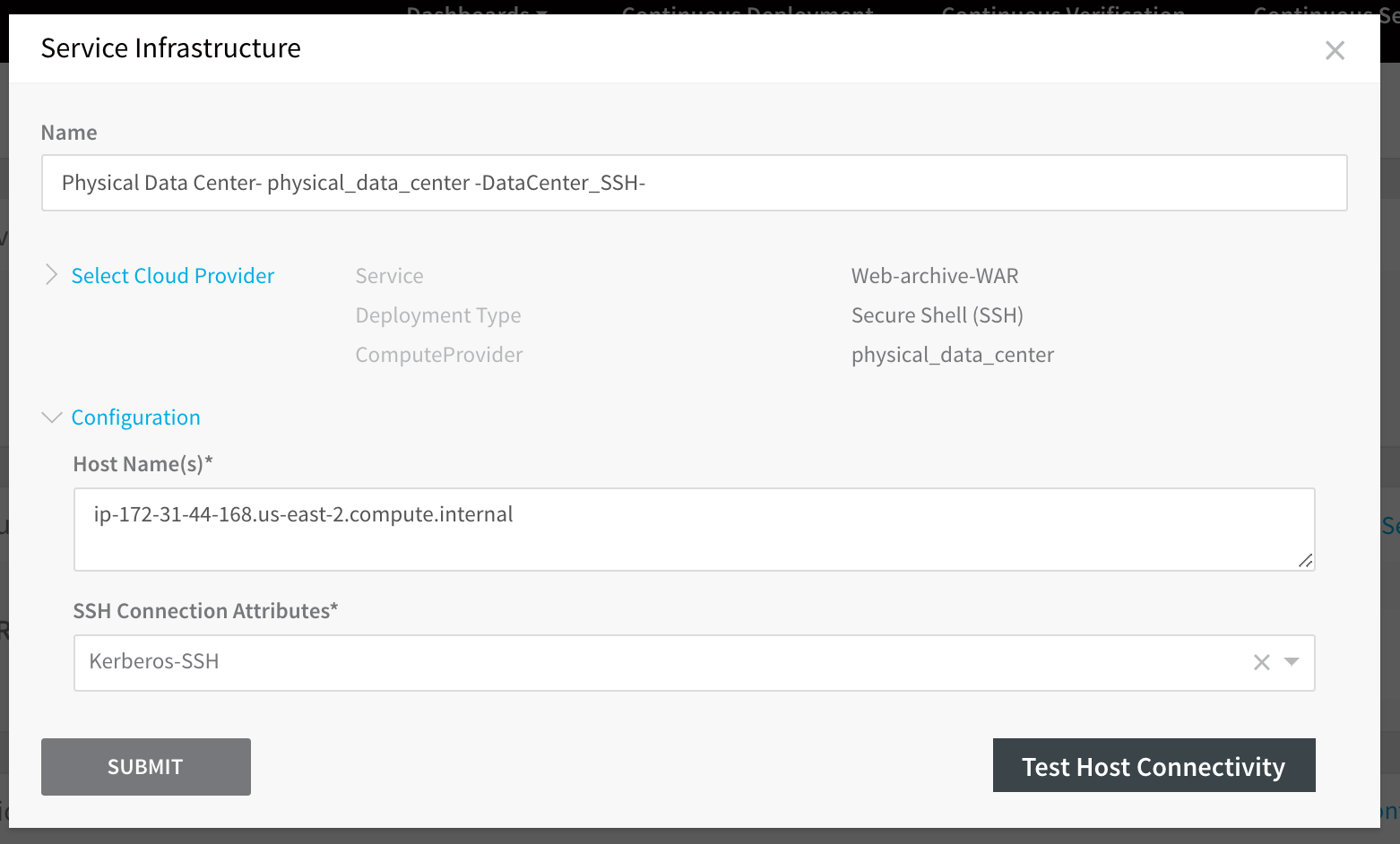 In this example, the target host that you want to use Kerberos authentication with is entered in Host Name(s).
In this example, the target host that you want to use Kerberos authentication with is entered in Host Name(s).
Note that the domain name used to identify the hosts in the Host Name(s) field is likely to be the same as the domain name you entered in Realm when configuring the SSH connection.