Using OpenShift with Harness Kubernetes
Harness supports OpenShift for Kubernetes deployments. This topic reviews OpenShift support in the Harness Delegate and Workflows.
Before You Begin
Review: Kubernetes Delegate and OpenShift
Harness supports OpenShift using a Delegate running externally to the Kubernetes cluster.
For steps on connecting, see Kubernetes Cluster in Add Cloud Providers.Harness does support running Delegates internally for OpenShift 3.11 or greater, but the cluster must be configured to allow images to run as root inside the container in order to write to the filesystem.
Typically, OpenShift is supported through an external Delegate installation (shell script installation of the Delegate outside of the Kubernetes cluster) and a service account token, entered in the Kubernetes Service Account Token field. You only need to use the Master URL and Kubernetes Service Account Token fields in the Kubernetes Cloud Provider dialog.
The following shell script is a quick method for obtaining the service account token. Run this script wherever you run kubectl to access the cluster.
Set the SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME and NAMESPACE values to the values in your infrastructure.
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME=default
NAMESPACE=mynamepace
SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get sa "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o json | jq -r '.secrets[].name')
TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret "${SECRET_NAME}" --namespace "${NAMESPACE}" -o json | jq -r '.data["token"]' | base64 -D)
echo $TOKEN
Once configured, OpenShift is used by Harness as a typical Kubernetes cluster.
Review: Deployment Strategy Support
In order to successfully deploy the workloads in your Manifests section of the Harness Service, they must meet the minimum requirements of the type of deployment you are performing.
- Canary and Blue/Green Workflow Type - Deployment workloads only.
- Rolling Workflow Type - All workload types except Jobs. Jobs will be added soon.
- Apply Step - All workload types, including Jobs.
- OpenShift: Harness supports DeploymentConfig, Route, and ImageStream across Canary, Blue Green, and Rolling deployment strategies. Please use
apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1and notapiVersion: v1.
Review: Harness Supports List Objects
You can leverage Kubernetes list objects as needed without modifying your YAML for Harness.
When you deploy, Harness will render the lists and show all the templated and rendered values in the log.
Harness supports:
- List
- NamespaceList
- ServiceList
- For Kubernetes deployments, these objects are supported for all deployment strategies (Canary, Rolling, Blue/Green).
- For Native Helm, these objects are supported for Basic deployments.
If you run kubectl api-resources you should see a list of resources, and kubectl explain will work with any of these.
Step: Add Manifests and OpenShift Template
In your Harness Service, in Manifests, click Link Remote Manifests.
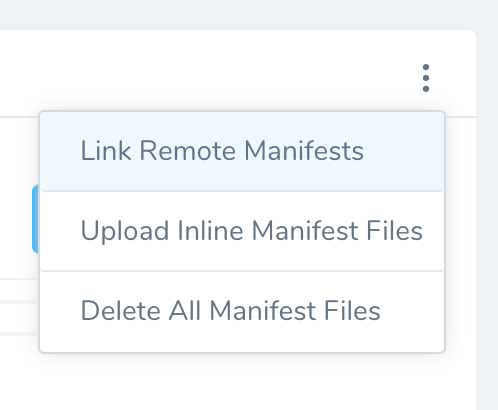
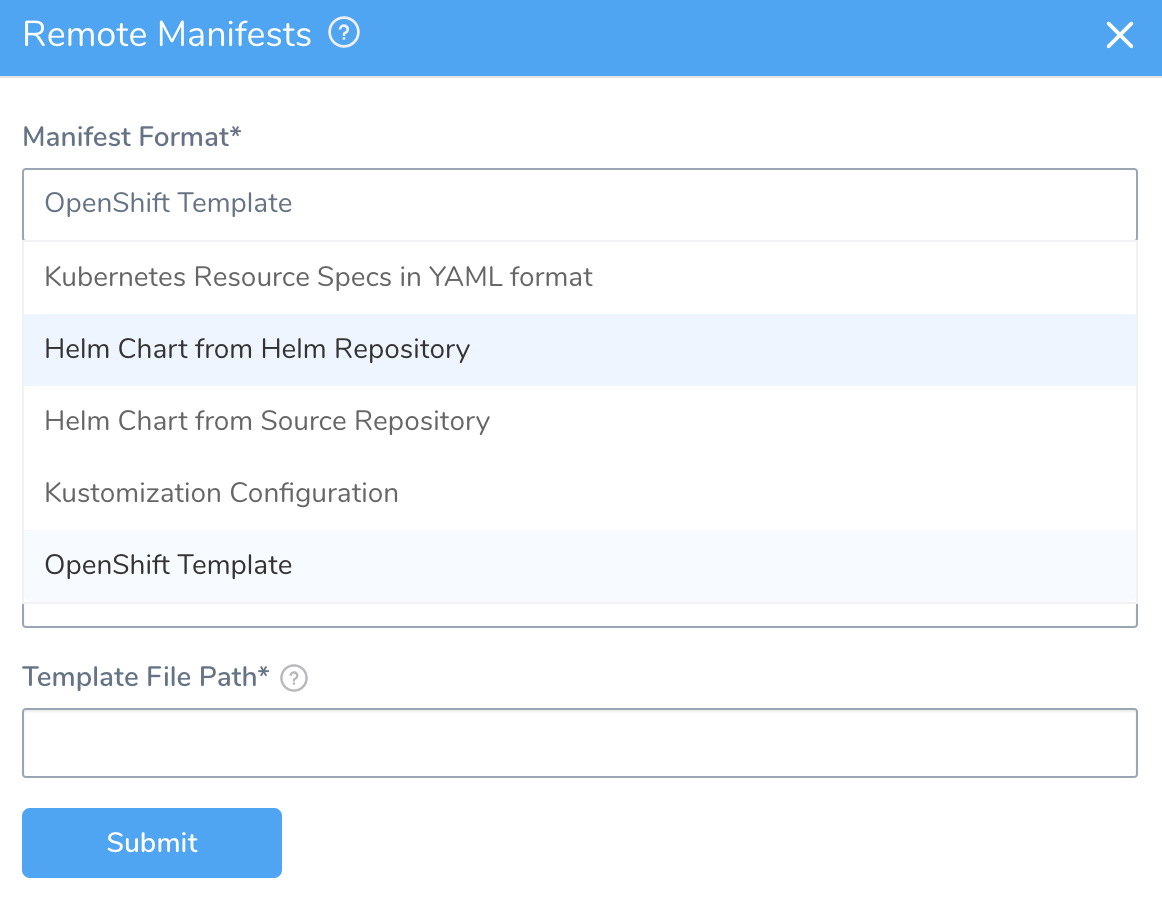
In Remote Manifests, in Manifest Format, click OpenShift Template.
Enter the following settings and click Submit.
Source Repository: Select the Source Repo Provider connection to your repo.
Commit ID: Select Latest from Branch or Specific Commit ID. Do one of the following:
- Branch: Enter the branch name, such as master.
- Commit ID: Enter the Git commit ID.
Template File Path: Enter the Openshift Template File Path.
Option: Define Service Variables
You can define Service variables in OpenShift Param File, after adding the OpenShift Template file. OpenShift Param File is visible only after you have selected an OpenShift Template in Remote Manifests.
- In the Harness Service, in the Configuration section, click Add Param.
- Select Inline or Remote Store Type.
a. If you select Inline, then enter the value inline. If you select Remote, perform the following steps.
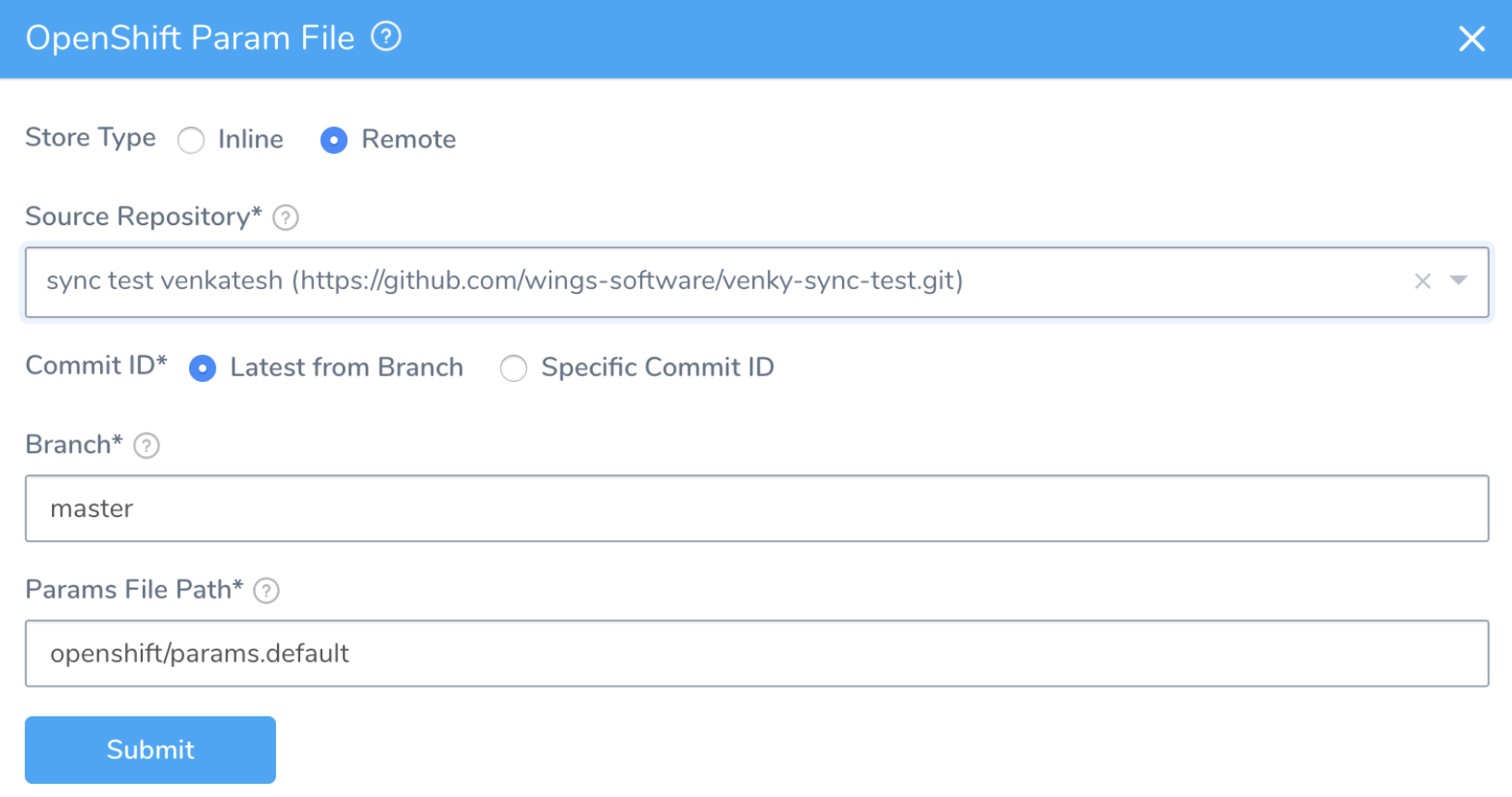
- Select Source Repository from the drop-down menu.
- Select Latest from Branch or Specific Commit ID. Do one of the following:
- Branch: Enter the branch name, such as master.
- Commit ID: Enter the Git commit ID.
- Enter the file path in Params File Path.
Service variables can be overwritten at the Harness Environment level. For details on overriding Service settings, see Override Harness Kubernetes Service Settings.
Option: Skip Versioning for Service
By default, Harness versions ConfigMaps and Secrets deployed into Kubernetes clusters. In some cases, you might want to skip versioning.
Typically, to skip versioning in your deployments, you add the annotation harness.io/skip-file-for-deploy to your manifests. See Deploy Manifests Separately using Apply Step.
In some cases, such as when using public manifests or Helm charts, you cannot add the annotation. Or you might have 100 manifests and you only want to skip versioning for 50 of them. Adding the annotation to 50 manifests is time-consuming.
Instead, enable the Skip Versioning for Service option in Remote Manifests.
When you enable Skip Versioning for Service, Harness will not perform versioning of ConfigMaps and Secrets for the Service.
If you have enabled Skip Versioning for Service for a few deployments and then disable it, Harness will start versioning ConfigMaps and Secrets.
Notes
- Make sure that you update your version to
apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1and notapiVersion: v1. - The token does not need to have global read permissions. The token can be scoped to the namespace.
- The Kubernetes containers must be OpenShift-compatible containers. If you are already using OpenShift, then this is already configured. But be aware that OpenShift cannot simply deploy any Kubernetes container. You can get OpenShift images from the following public repos: https://hub.docker.com/u/openshift and https://access.redhat.com/containers.
- Useful articles for setting up a local OpenShift cluster for testing: How To Setup Local OpenShift Origin (OKD) Cluster on CentOS 7, OpenShift Console redirects to 127.0.0.1.