Connect to Your Target Kubernetes Platform
This content is for Harness FirstGen. Switch to NextGen.
To connect Harness to your target Kubernetes cluster, you must first install a Harness Delegate in your target platform or target Kubernetes cluster.
Next, use the vendor-agnostic Harness Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider to connect Harness to your cluster (recommend). You can also use a platform-specific Cloud Provider, such as the AWS, GCP, or Azure Cloud Providers.
The simplest method is to install the Harness Delegate in your Kubernetes cluster and then set up the Harness Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider to use the same credentials as the Delegate.
Before You Begin
- Kubernetes Deployments Overview
- The target Kubernetes Cluster must meet the following minimum requirements:
- Number of nodes: minimum of 3.
- Machine type: 4vCPU
- Memory: 12GB RAM and 6GB Disk Space. 8GB RAM is for the Delegate. The remaining memory is for Kubernetes and containers.
- Networking: Outbound HTTPS for the Harness connection, and to connect to any container image repo. Allow TCP port 22 for SSH.
Review: Cluster Connection Options
This is a brief summary of the ways to connect to your target Kubernetes platform and clusters.
Using Delegates Inside or Outside of the Target Cluster
Typically, you install the Harness Kubernetes Delegate in your target cluster and then add a Kubernetes Cluster or GCP Cloud Provider that inherits its credentials from the Delegate.
You can also install the Kubernetes Delegate outside of the target cluster (anywhere in your environment), and use a non-Kubernetes Delegate type (Helm, Docker, Shell Script).
In this case, the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider will not inherit credentials from the Delegate, but use the cluster master URL and some authentication method (Service Account Token, etc).
The GCP and Azure Cloud Providers will not inherit credentials from the Delegate (the Azure Cloud Provider never does), but use platform-specific credentials, such as encrypted keys.
Running Scripts with a Delegate Outside of the Target Cluster
If you use a Delegate installed outside of the target cluster, any scripts in your Pipeline need to use the ${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH} expression to reference the path to a Harness-generated kubeconfig file containing the credentials you provided.
For example:
export KUBECONFIG=${HARNESS_KUBE_CONFIG_PATH} kubectl get pods -n pod-test
Now the script will run using the correct credentials.
Target Namespace
By default the Delegate can deploy to any namespace. To target specific namespaces only, see Target Delegates to Specific Namespaces.
Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider
You can use the vendor-agnostic Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider for connections to your target cluster on any platform, including AWS EKS.
If you use the Kubernetes Delegate, you can have the Harness Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider inherit its credentials (Service Account).
The Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider can also use other types of credentials like username/password, CA certs, or Service Account Tokens. This is helpful if you use other types of Delegates that run outside Kubernetes (Shell Script, Docker, ECS).
GCP and Azure Cloud Providers
You can also use the GCP and Azure Cloud Providers to connect Harness with the platform hosting your target cluster. The account you use to connect them must provide the necessary credentials to change the target cluster.
For GCP, the service account used with the GCP Cloud Provider requires the Kubernetes Engine Admin (GKE Admin) role to get the Kubernetes master username and password. Harness also requires Storage Object Viewer permissions.
For Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS), the Client ID (Application ID) must be assigned to a role that has the Owner permission on the AKS cluster. If you are using the Kubernetes Cloud Provider and the Kubernetes Delegate in the AKS cluster, then AKS permissions are not required at all. This is recommended.
Step 1: Install the Harness Kubernetes Delegate in Your Target Cluster
- In Harness, click Setup, and then click Harness Delegates.
- Click Download Delegate and then click Kubernetes YAML.
- In the Delegate Setup dialog, enter a name for the Delegate, such as doc-example, select a Profile (the default is named Primary), and click Download. The YAML file is downloaded to your machine.
- Install the Delegate in your cluster. You can copy the YAML file to your cluster any way you choose, but the following steps describe a common method.
- In a Terminal, connect to the Kubernetes cluster, and then use the same terminal to navigate to the folder where you downloaded the Harness Delegate YAML file. For example, cd ~/Downloads.
- Extract the YAML file:
tar -zxvf harness-delegate-kubernetes.tar.gz. - Navigate to the harness-delegate folder that was created:
cd harness-delegate-kubernetes- Paste the following installation command into the Terminal and press enter:
You will see the following output (this Delegate is named doc-example):kubectl apply -f harness-delegate.yamlnamespace/harness-delegate created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.doc-example/harness-delegate-cluster-admin created
statefulset.apps/doc-example-lnfzrf created- Run this command to verify that the Delegate pod was created:
kubectl get pods -n harness-delegate
You will see output with the status Pending. The Pending status simply means that the cluster is still loading the pod.
Wait a few moments for the cluster to finish loading the pod and for the Delegate to connect to Harness Manager.
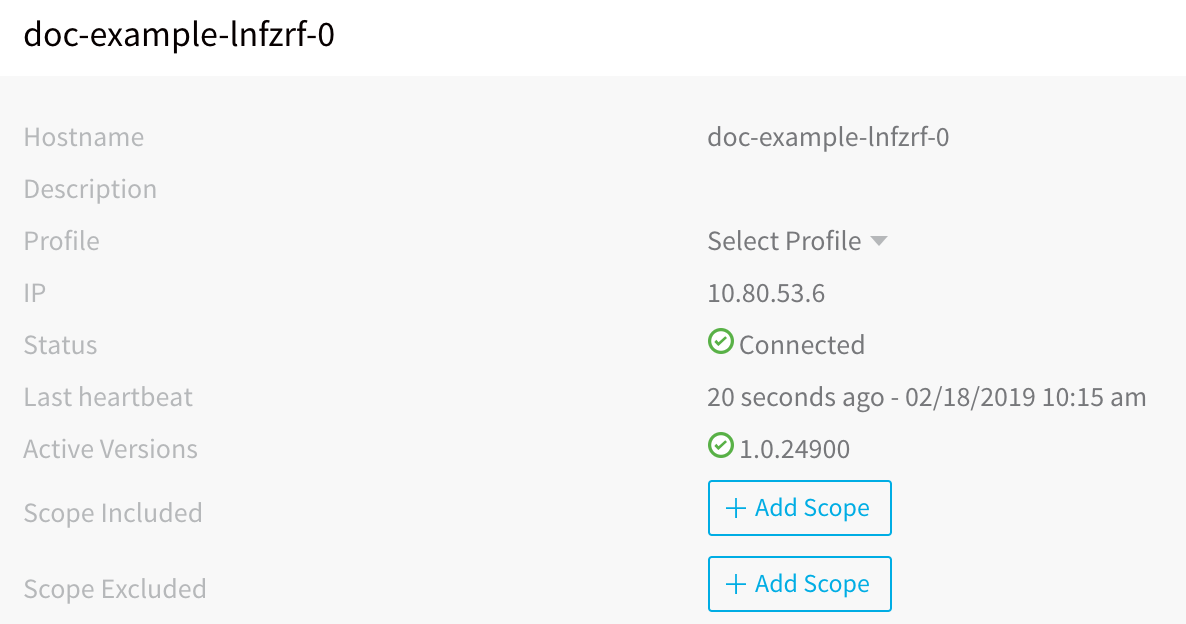
In Harness Manager, in the Harness Delegates page, the new Delegate will appear. You can refresh the page if you like.
Note the Delegate name. You will use this name when you set up the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider.
When you onboard your own applications, you might need to install multiple Delegates, depending on their workloads, network segmentation, and firewall zones. Typically, you will need one Delegate for every 300-500 service instances across your applications, and will need one Delegate in each subnet or zone.
Step 2: Choose a Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider or Platform Cloud Provider
The Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider is platform-agnostic. Consequently, you can use it to access a cluster on any platform, but it cannot also access platform-specific services and resources.
For example, if you have a Kubernetes cluster hosted in Google Cloud Platform (GCP), you can use the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider to connect Harness to the cluster, but the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider cannot also access Google Container Registry (GCR).
In this case, you can use a single Google Cloud Platform Cloud Provider to access the GKE cluster and all other GCP resources you need, such as GCR, or you could set up a Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider for the GKE cluster, and a Google Cloud Platform Cloud Provider for all other GCP services and resources.
No matter which option you choose, the Harness Kubernetes Delegate should be installed in your target cluster first.
Option 1: Add a Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider
The following steps describe how to use the credentials of the Harness Kubernetes Delegate installed in your target cluster. If you use this option, the service account you use must have the Kubernetes cluster-admin role.
- In Harness Manager, click Setup.
- Click Cloud Providers. On the Cloud Providers page, click Add Cloud Provider. The Cloud Provider appears.
- Enter the following settings:
- Type: Select Kubernetes Cluster.
- Display Name: Enter a name. You will use this name later to select this Cloud Provider when you create a Harness Infrastructure Definition.
- Inherit from selected Delegate: Enable this option. Since the Delegate is already installed in the target cluster, you can use the Delegate's credentials for this Cloud Provider. This is the recommended configuration.
- Delegate Name: Select the name of the Delegate you installed in your cluster.
- Select Skip Validation: Enable this option for the setup of this Cloud Provider. Later, when you create an Infrastructure Definition, Harness will need to validate, so you can disable this setting then.
- Usage Scope: Use this setting to limit the use of the Cloud Provider to specific Harness Applications and Environments.
- Click Test. Verify that the
The test was successful messageappears, and then click Submit.
Your Kubernetes Cloud Provider is set up. Now Harness can use the Cloud Provider to perform operations in your cluster.
Option 2: Add a Platform-Specific Cloud Provider
For steps on setting up a Platform-Specific Cloud Provider, see Add Cloud Providers.
Notes
- Helm Client Only Mode — When you use a remote Helm chart in your Harness Service, you do not need to have Tiller installed on the Harness Delegate because Harness interacts directly with the Kubernetes API server to install, upgrade, query, and remove Kubernetes resources. The Helm client is used to fetch charts from the repository and render a template. Consequently, when you install Helm on the Harness Delegate pod you can use the client-only option, as described in Common Delegate Profile Scripts.